Surgical jaundice
-
Upload
scu-hospital -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
47 -
download
2
Transcript of Surgical jaundice
DEFINITION OF JAUNDICE:
Jaundice ( icterus ) is a yellow discoloration of the sclerae and skin as a result of a raised serum bilirubin .
YELLOW SKIN AND SCLERAE APPEAR WHENEVER BILIRUBIN REACHES 3.0 mg/mL .
Two form of bilirubin:
1.Unconjugated, insoluble and not excreted in the urine.
2. Conjugated, soluble and excreted in the urine.
1. Pre hepatic
Increase breakdown of red cells leads to increased production of bilirubin.
It is due to hemolytic anemia as:-SCD.-G6PD def.-H. spherocytosis.
3. Post hepatic
It is due to:1. Extrahepatic obstruction (obstructive jaundice):- Gallstone obstruction of biliary tree.- Carcinoma of head of pancreas, extrahepatic bile
duct, ampulla of vater and duodenum .- Extrahepatic biliary atresia.- Biliary strictures and choledochal cysts.- Biliary sclerosing cholangitis (extrahepatic).- Liver fluk infestation.
Impairment of bile flow subsequent to secretion by the hepatocyte
LAB DIFFERENTIATION
Pre hepatic J. Hepatic J. Post hepatic J.
color Achaluric (colorless)
As usual Dark
Conjugated bilirubin
NL0 mg
NL or
Urobilinogen NL or 0-4 mg/D
Absent or
Color Dark As usual Pale
stercobilingen NL40-280mg
URINE
STOOL
To differentiate between obstructive jaundice from hepatic and pre hepatic jaundice :
History of dyspepsia , pain or biliary colic .
No pre monitary period of malaise and loss of appetite .
A sudden onset
Simultaneous appearance of pale feces and dark urine
Itching of the skin
If the pain is sudden and regressive it is due to stone
If the pain is progressive it is due to tumor
In young age mostly due to stone
In old age mostly due to tumor
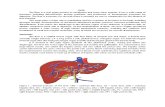
Surgical anatomy :
The cystic duct joined common hepatic duct to form common bile duct .
The bile duct (common bile duct) is about 3 inches (8 cm) long . In the third part of its caurse it lies in the in a groove on the posterior surface of the head of the pancreas . Here , the bile duct comes into contact with the main pancreatic duct and they open into ampulla of vater in the second part of the duodenum.
The goal of treatment is to relieve the obstruction in the common bile duct. Surgical removal of the gallbladder and the stones (via either an open procedure or a laparoscopic procedure) is one option.
Another possibility is removal of the stones by ERCP and sphinterotomy (an incision into the sphinter muscle of the duct).
TUMORS OF THE PANCREAS
If the tumer has no metastesis and no inviding the surround vessels it is operable
If the tumor has metastisis and inviding the surround vessels it is inoperable and treated by radiochemotherapy
Pancreatoduodenectomy(Whipple Procedure)
By remove of
Head of pancreas
Entire duodenum
Portion of jejunun
Distal third of the stomach
Lower half of the commom bile duct
Reestablishment of continuity of the biliary, pancreatic, and GI tract system
Investigation
Routine :CBCRFTcreatine & electrolyte & BUNFBS RBSURINE ANALYSISCHEST X-RAY AND ECG if he is above 40
yearsPT & PTT
SPECIFIC INVESTIGATION :
ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiography)
MRCP (magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography)
Abdominal CT scan
Abdominal ultrasound
Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram (PTCA)
Liver function test:
serum enzymes: normally
alkaline phosphatase 13-39U/ml
aspartate aminotransferase 5-40U/ml
alanine aminotransferase 5-35U/ml
lactate dehydrogenase 200-500U/ml
5-nucleotidase 2-11U/ml
Gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase men:80-200U/L women 45yr:5-27U/L
BILIRUBIN METABOLISM:Serum bilirubin: Indirect(uncojugated) 0.8mg/dl Direct(conjugated) 0.2-0.4mg/dlTotal 1mg/dlUrine bilirubin 0(bilirubin in the urine may be seen with hepatic disease or
biliary obstruction; only conjugated bilirubin spills into the urine because the unconjugated bilirubin is bound to albumin in the serum and thus cannot pass the glomerular membrane)
Urine urobilinogen 0-4mg/24hFecal urobilinogen 40-280mg/24h
AMMONIA adult 15-110/dl
SERUM PROTEINSAlbumin 3.5-5.5g/dlGlobulin 2.5-3.5g/dlTotal 6-7g/dlAlbumin/globulin(A/G) ratio1.5/1 to 2.5/1Transferring 250-300 mg/dl
BLOOD-CLOTTING FUNCTIONS
Prothrombin time(PT) 11.5-14 sec or 90% of control
Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) 25-40 sec