Structure of Amino Acids. Amino Acids Amino acids are the structural building blocks (monomers) of...
Transcript of Structure of Amino Acids. Amino Acids Amino acids are the structural building blocks (monomers) of...

Structure of Amino Acids
Structure of Amino Acids

Amino Acids
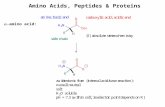
• Amino acids are the structural building blocks (monomers) of proteins.
• There are twenty different kinds of amino acids used in proteins.
• Proteins are referred to as heteropolymers due the variety of amino acids involved in their structure.

-carbon

Amino Acids (cont’d.)• Amino acids, like carbohydrates, show
isomerism. Proteins are only made up of amino acids which are L-isomers.
L-isomerD-isomer

Amino Acids (cont’d.)
• At neutral pH’s amino acids exist in an ionised form and have both acidic and basic properties. This is because the carboxylic group donates hydrogen ions to the solution (acidic) whereas the amino group (NH2) attracts hydrogen
ions from the solution.

Amino Acids (cont’d.)
• The repeating sequence of atoms along a proteins is referred to as the polypeptide backbone. Attached to this repetitive chain are the different amino acid side chains (R-groups) which are not involved in the peptide bond but which give each amino acid its unique property.

Amino Acids (cont’d.)
• Amino acids are grouped according to whether their side chains are:-
•acidic•basic•uncharged polar•non polar

Aspartic
Acid
asp
D
AcidicPolar
AsparticAcid asp Acidic
Polar
GlutamicAcid glu Acidic
Polar

Lysine lys Basic
Polar
Arginine arg Basic
Polar

Glutamine gln NeutralPolar
Tyrosine tyr Neutral Polar

Isoleucine ileNeutralNon-polar
Methionine met Neutral
Non-polar

Amino Acids (cont’d.)• The type of side chain is very important
as it affects the solubility of the amino acid.
• Hydrophobic features include long non-polar (uncharged) chains or complex aromatic rings.
• Hydrophilic features include additional carboxyl groups or amino groups not involved in peptide bonding which are ionised in solution.

Amino Acids (cont’d.)• Amino acids link together by covalent
peptide bonds. This involves a condensation /dehydration reaction. These bonds are very strong. When this takes place the charged amino and carboxylic groups disappear.