SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins structures, and interactions of complex societies in the...
-
Upload
oscar-whitehair -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
2
Transcript of SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins structures, and interactions of complex societies in the...

SSWH1: The student will analyze the origins structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BCE to 500 BCE.

Located in the Fertile Crescent between the
Persian Gulf and Mediterranean Sea, the Mesopotamians
developed Hammurabi’s Code,
one of the first detailed sets of laws.

In Ancient Egypt, Pharaohs were worshipped as Gods.

Zoroastrians were one of the first Monotheistic religions and influenced
Judaism, Christianity, and Islam

The Phoenicians were known for their extensive trade networks and their
alphabet

Hieroglyphics and Cuneiform were some of the earliest forms of writing.
Cuneiform Hieroglyphics

SSWH2 The student will identify the major achievements of Chinese and Indian societies from 1100 BCE to 500 CE.

The Maurya Empire and Gupta Empire in India developed Indian civilization.

Both Hinduism and Buddhism emerged in India. Buddhism spread North into China.
Hinduism Buddhism

• Zhou and Qin Dynasties began the Chinese series of dynasties.
• Qin She Huangdi built an elaborate tomb with soldiers to protect him.

Confucianism became an important philosophy in China.
• Emphasized the importance of family and the father.
• Promoted the idea of a civil service examination for government officials.

Geography played a very important role in Indian History. Pay attention to the major physical features.

SSWH3 The student will examine the political, philosophical, and cultural interaction of Classical Mediterranean societies from 700 BCE to 400 CE.

Athens focused more on democracy, education, and art while Sparta focused on
the military.

Greek philosophy influenced both Alexander the Great and Julius Caesar.

Alexander the Great spread Hellenism in all the areas he conquered.

Both the Greeks and Romans were polytheistic until Christianity spread to those areas in the 3rd century

Rome fell in the 5th century as a result of invasions from Germanic tribes.

SSWH4 The student will analyze the importance of the Byzantine and Mongol empires between 450 CE and 1500 CE.

The Byzantine Empire under Justinian briefly recaptured much of the Roman Empire and lasted another 1000 years.

The Byzantine Empire influenced the early Russian Empire. Constantinople became an important cultural center.
Tsar Ivan III (the Great)
Constantinople

• The Western Church (Roman Catholic) and Eastern Church (Eastern Orthodox) split in 1054 because of disagreements over the use of Icons and who was head of the Church.

Genghis (Chinggis) Khan conquered much of Eurasia and set up the Mongol Empire.

The Byzantine Empire ended in 1453 when Constantinople fell to the Ottoman Turks

SSWH5 The student will trace the origins and expansion of the Islamic World between 600 CE and 1300 CE.

Islam began in 632 with the teachings of Muhammed.

Islam spread along the major trade routes of the Arabs.

Sunni and Shi’a split Islam because of a dispute between who is the leader of
Islam.

Ibn Battuta was a major explorer who spread Islam to Africa and Eastern Asia.

The Crusades began in 1096 and lasted over 200 years. Christians fought Muslims for control of the “Holy Land”.

Judaism, Christianity and Islam are all monotheistic religions with common prophets and basic ideas.

SSWH6 The student will describe the diverse characteristics of early African societies before
1800 CE.

The Bantu Migrations spread culture and economic activities to central and southern
Africa.

Sundiata and Mansa Musa were African Muslim leaders.
Sundiata Mansa Musa

Elaborate trading networks developed across the Sahara to trade mainly salt and
gold.

Religious syncretism blended traditional African beliefs with new ideas from Islam and Christianity.

• Africa’s geographical features play an important role regarding trade routes, distribution of resources, and spread of culture.

SSWH7 The student will analyze European medieval society with regard to culture,
politics, society, and economics.

Charlemagne helped develop the feudal system in Europe.

The Middle Ages was a constant battle between Kings and Popes over power.
• Pope Gregory VII declares Interdict on King Henry IV (Holy Roman Emperor).

The Church dominated the lives of common people during the Middle Ages and had
supreme power.

Medieval Trade routes led to the development of towns in Europe

SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies
in Central and South America.

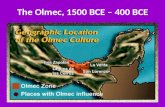
The Olmecs and Mayans were early civilizations in Central and South America
Olmecs Mayans

The Aztecs and other pre-Columbian civilizations practiced human sacrifice.
Aztec Incan

SSWH9 The student will analyze change and continuity in the Renaissance and Reformation.

The European Renaissance began in Florence Italy.

Leonardo da Vinci is an example of a “Renaissance Man”.

Erasmus believed in the idea of Humanism or the potential of man.

Martin Luther started the Protestant Reformation in 1517 when he challenged the Church over the issue of Indulgences.

The Catholic Church responded to the Reformation with the Council of Trent.

Henry VIII and Elizabeth I set up the English Reformation.
Henry VIII Elizabeth I

Johannes Gutenberg invented the printing press in 1453.

SSWH10 The student will analyze the impact of the age of discovery and expansion into the
Americas, Africa, and Asia.

Fifteenth century explorers traveled to Africa, America, and Pacific Islands
Magellan Zheng He

The Columbian Exchange traded plants, animals, ideas and disease.

Navigational technology (such as the Astrolabe) made it possible for the explorers to travel.

SSWH11 Students will investigate political and social changes in Japan and in China from the seventeenth
century CE to mid-nineteenth century CE.

Oda Nobanuga and Kangxi set up the Tokugawas in Japan and Qing in China to rule for a long period.
Oda Nobanuga (Tokugawa) Kangxi (Qing)

Rapid population growth in China and Japan led to unique social structures in those areas.

SSWH12 The student will examine the origins and contributions of the Ottoman, Safavid, and
Mughal empires.

The Ottoman Empire threatened southeastern Europe.
Suleyman the Magnificent Safavid Empire

The Mughal Empire dominated India in the 16th and 17th centuries

SSWH13 The student will examine the intellectual, political, social, and economic factors
that changed the world view of Europeans.

Copernicus, Galileo, Keplar and Newton developed new ways to view the world.

John Locke—Natural Rights
• The Enlightenment took a more scientific approach to politics and society.

SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions.

Absolute monarchs in Europe and Asia had total power over their kingdoms.
Louis XIV of France Tokugawa Ieyasu of Japan

Revolutions in England, America, France, Haiti and Latin America sought more political rights
for their people.

Napoleon represented the new power of the common man

Asian countries often resisted contact with Western countries.

SSWH15 The student will be able to describe the impact of industrialization, the rise of nationalism, and the
major characteristics of worldwide imperialism.

Industrialization led to new views on economics and society.
Adam Smith Karl Marx

Nationalism led to the emergence of strong nation states.
Bismarck-Germany Emperor Meiji-Japan

The Russo-Japanese War demonstrated the reaction to foreign domination.

European countries competed for colonies throughout Africa and Asia

SSWH16 The student will demonstrate an understanding of long-term causes of World
War I and its global impact.

Alliances led to the start of WWI.

World War I was mainly Trench Warfare on the Western Front.

The Treaty of Versailles blamed Germany for WWI.

WWI ended the great dynasties in Russia, Austria, and Ottoman Empires

SSWH17 The student will be able to identify the major political and economic factors that shaped world societies
between World War I and World War II.

Pablo Picasso’s Guernica is an example of Cubism and modern art.

Lenin led the Russian Revolution and Stalin set up the 5 Year Plans.

Fascist governments were set up in Italy, Germany, and Japan in the 1920s and 1930s.

Nationalism became a strong idea in Asia.

Totalitarian governments restricted people’s rights.

Appeasement (peace at all costs) of Hitler led to the start of WWII.

SSWH18 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the global political, economic,
and social impact of World War II.

WWII destroyed much of Europe and Japan

Nazi policies of anti-Semitism led to the Holocaust.

Churchill, Stalin, and Roosevelt met at Yalta to decide on a common strategy for ending WWII.

The Marshall Plan helped rebuild Europe after the war.

SSWH19 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the global social, economic, and political impact of the Cold War and decolonization from 1945 to 1989.

Nationalist revolutionary movements led to radical changes in China, India, and Ghana
Chiang Kai-shek-China Kwame Nkrumah-Ghana

The state of Israel formed in 1947 and immediately started wars in the region.

The Cold War included the arms race, space race, and many crises.

Khrushchev and Gorbachev made significant reforms to the USSR.
Khrushchev Gorbachev

Freedom movements spread around the world.

SSWH20 The student will examine change and continuity in the world since the 1960s.

Ethnic conflicts continued after WWII in Bosnia, Rwanda, and the Middle East.

In 1991, the USSR fell due to corruption and an inability to provide basic necessities to its people.

Terrorism has become the new form of warfare after WWII.

Women have emerged as powerful leaders around the world.
Golda Meir-Israel Indira Gandhi-India Margaret Thatcher-UK

SSWH21 The student will analyze globalization in the contemporary world.

Globalization of communication, ideas, and technology grows each year.

Organizations such as the UN, OPEC, and the WTO (World Trade Organization) try to
set rules for trade and conflicts.

The Environment is one of the major issues governments have to address in the future.