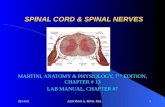
Spinal Cord Physiology
-
Upload
lim-shih-liang -
Category
Documents
-
view
228 -
download
2
Transcript of Spinal Cord Physiology
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
1/38
Physiology
Spinal Cord Physiology
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
2/38
Introductiony A thin column of nerve tissue that extends downward from
the brain through the vertebral column to the level of thesecond lumbar vertebra.
y
Transmits pain signals and other nerve impulses to and fromthe brain and controls reflexes actions.
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
3/38
Three Main Components1 . Spinal nerves2. Nerve Tissue3. Meninges
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
4/38
N erve TissueThe spinal cord consists of two types of nerve tissue.1 . Gray matter2. White matter
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
5/38
G ray Mattery Makes up the centre of the spinal cord.y Consists primarily of dendrites.
Dendrites- short fiber that conducts toward the cell body of theneuron
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
6/38
W hite Mattery Surrounds the gray matter.y Consists of bundles of nerve fibers that form conduction
paths called spinal tracts.
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
7/38
G ray Matter and W hite Matter
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
8/38
G ray Matter and W hite Matter
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
9/38
Sensory (Ascending) Pathways1 . Lateral spinothalamic tract
-pain and temperature (warm & coolness)2. Ventral spinothalamic tract
-crude touch, pressure
3. Posterior column-conscious proprioception, discriminative touch, pressure,vibration
-consists 2 tracts: gracile fasciculus and cuneate fasciculus.4. A nterior & posterior spinocerebellar tracts
-muscle toneProprioception: the ability to sense the position and location and orientation and
movement of the body and its partsDiscriminative: capable of making fine distinctions
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
10/38
Sensory (Ascending) Pathways
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
11/38
Motor (Descending) Pathways1 . Direct pathways
(a) Lateral corticospinal tract(b) A nterior corticospinal tract
(c) Corticobulbar tract-Caused voluntary movements at skeletal muscles
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
12/38
Motor (Descending) Pathways2. Indirect pathways
(a) Tectospinal tract(b) Vestibulospinal tract
(c) Rubrospinal tract(d) Lateral reticulospinal tract(e) Media reticulospinal tract-regulate muscle tone, posture, balance, orientation of thehead and body.
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
13/38
Motor (Descending) Pathways
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
14/38
R eflexes are y inborny unlearnedy unconscious
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
15/38
R eflexesy A reflex is a predictable involuntary response to a stimulus.y A reflex involving the skeletal muscles is called asomatic
reflex .y
A reflex involving responses of smooth muscle, cardiacmuscle, or a gland is av isc er a l reflex.
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
16/38
R eflex ArcsDefinition: highly specific neural pathway through which a
reflex occurs.
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
17/38
5 Essential Componentsof the R eflex Arc1 . Receptor2. Sensory Neuron3. integrating center
4. motor neuron5. Effector
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
18/38
2. 5 Essential Componentsof the R eflex Arc
Figure 7.11a
Stimulus at distal
end of neuron
Skin Spinal cord(in cross section)
Interneuron
Receptor
Effector
Sensory neuron
Motor neuron
Integrationcenter
(a)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
19/38
The R eflex Arc
Figure 7.11a, step 1
Stimulus at distal
end of neuron
Skin
Receptor
(a)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
20/38
The R eflex Arc
Figure 7.11a, step 2
Stimulus at distal
end of neuron
Skin
Receptor Sensory neuron
(a)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
21/38
The R eflex Arc
Figure 7.11a, step 3
Stimulus at distal
end of neuron
Skin Spinal cord(in cross section)
Interneuron
Receptor Sensory neuron
Integrationcenter
(a)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
22/38
The R eflex Arc
Figure 7.11a, step 4
Stimulus at distal
end of neuron
Skin Spinal cord(in cross section)
Interneuron
Receptor Sensory neuron
Motor neuron
Integrationcenter
(a)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
23/38
The R eflex Arc
Figure 7.11a, step 5
Stimulus at distal
end of neuron
Skin Spinal cord(in cross section)
Interneuron
Receptor
Effector
Sensory neuron
Motor neuron
Integrationcenter
(a)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
24/38
y Somatic reflex A ny reflex (relatively rapid and predictablemotor response to a stimulus) in which the effectors areskeletal muscles
y A
utonomic reflex -A
ny of a large number of normal reflexesgoverning and regulating the functions of the viscera.
Viscera - internal organs collectively (especially those in theabdominal cavity)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
25/38
Somatic Spinal R eflexes1 . The stretch reflexes2. The tendon reflexes3. The flexor reflexes
4. The crossed extensor reflexes
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
26/38
Stretch R eflexy A lso called myotatic reflexy Causes contraction of a skeletal muscle in response to
stretching of the muscle.y
Three components:(a) Muscle spindles(b) Sensory neuron(c) Motor neuron
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
27/38
Stretch R eflex
Figure 7.11bc
Spinal cord
Sensory (afferent)neuron
Inter-neuron
Motor (efferent)neuron
Motor (efferent)neuron
Sensory receptors
(stretch receptorsin the quadricepsmuscle)
Sensory (afferent)neuron
Sensory receptors(pain receptors inthe skin)
Effector (quadricepsmuscle of thigh)
Effector (bicepsbrachiimuscle)
Synapse inventral horngray matter
(c)
(b)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
28/38
3 . W hy test your reflexes?
Reflexes determine the general health of themotor portion of the nervous system.
Whenever reflexes are exaggerated, distorted, or
absent, nervous system disorders are indicated.
Reflex changes often occur before the pathologicalcondition has become obvious
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
29/38
Stretch R eflex
Figure 7.11b, step 1
Spinal cord
Sensory receptors
(stretch receptorsin the quadricepsmuscle)
(b)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
30/38
Stretch R eflex
Figure 7.11b, step 2
Spinal cord
Sensory (afferent)neuron
Sensory receptors
(stretch receptorsin the quadricepsmuscle)
(b)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
31/38
Stretch R eflex
Figure 7.11b, step 3
Spinal cord
Sensory (afferent)neuron
Sensory receptors
(stretch receptorsin the quadricepsmuscle)
Synapse inventral horngray matter
(b)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
32/38
Stretch R eflex
Figure 7.11b, step 4
Spinal cord
Sensory (afferent)neuron
Motor (efferent)neuron
Sensory receptors
(stretch receptorsin the quadricepsmuscle)
Synapse inventral horngray matter
(b)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
33/38
Stretch R eflex
Figure 7.11c, step 1
Spinal cord
Sensory receptors(pain receptors inthe skin)
(c)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
34/38
Stretch R eflex
Figure 7.11c, step 2
Spinal cord
Sensory (afferent)neuron
Sensory receptors(pain receptors inthe skin)
(c)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
35/38
Stretch R eflex
Figure 7.11c, step 3
Spinal cord
Inter-neuron
Sensory (afferent)neuron
Sensory receptors(pain receptors inthe skin)
(c)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
36/38
Stretch R eflex
Figure 7.11c, step 4a
Spinal cord
Inter-neuron
Motor (efferent)neuron
Sensory (afferent)neuron
Sensory receptors(pain receptors inthe skin)
(c)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
37/38
Stretch R eflex
Figure 7.11c, step 4b
Spinal cord
Inter-neuron
Motor (efferent)neuron
Sensory (afferent)neuron
Sensory receptors(pain receptors inthe skin)
Effector (bicepsbrachiimuscle)
(c)
-
8/3/2019 Spinal Cord Physiology
38/38
Stretch R eflex
Figure 7.11bc
Spinal cord
Sensory (afferent)neuron
Inter-neuron
Motor (efferent)neuron
Motor (efferent)neuron
Sensory receptors
(stretch receptorsin the quadricepsmuscle)
Sensory (afferent)neuron
Sensory receptors(pain receptors inthe skin)
Effector (quadricepsmuscle of thigh)
Effector (bicepsbrachiimuscle)
Synapse inventral horngray matter
(c)
(b)