Solid solution strengthening
-
Upload
jayesh-parekh -
Category
Engineering
-
view
966 -
download
2
Transcript of Solid solution strengthening

TOPIC NO.- 8 SOLID SOLUTION STRENGHENING
NAME- PAREKH JAYESH M. ROLL NO. - 388

Why strengthening of metal is required?As pure metal are inherently weak due to presence of dislocation. So, We can enhance the mechanical properties by eliminating
dislocation. So, by introducing some mechanism that prohibits the mobility of
dislocations, that are called Strengthing mechanism.
Methods For Strengthening Of Metal
(1)Strain hardening(2)Grain boundary strengthening (3)Solid solution strengthening(4)Precipitation hardening

Solid Solution
• When the atoms of base metal (solvent) and the alloying elements (solute) completely dissolve in each other and become an integral part of the solid phase of alloy, the resulting phase is called a Solid Solution.
Types of Solid Solution:
(1)Interstitial solid solution(2)Substitutional solid solution

Interstitial Solid Solution
Solute atoms are much smaller than solvent atoms, so they occupy interstitial position in solvent lattice.
Carbon ,nitrogen ,hydrogen ,oxygen and boron are the element which commonly form interstitial solid solution.

Substitutional Solid Solution
Solute atoms sizes are roughly similar to solvent atoms. Due to similar size solute atoms occupy vacant site in solvent atoms. Copper and zinc, copper and nickel, are the example of substitutional
solid solution.

Hume Rothery’s RuleHume rothery studied a number of alloy systems and formulated
condition that favour extensive substitutional solid solubility.Three conditions of Hume Rothery’s rule
(1)The size difference between solute and solvent atoms must be less than 15%
(2)The crystal structure of metal must be same.(3)The electronegativity difference between the metal must be small.
Strengthening Mechanisms Depends On,
Difference in size between solute and solvent atoms Amount of solute added, Nature of distortion produced by solute atoms.

How This Parameter Affect Strengthening Mechanisms.
(1)As the size difference between solute and solvent atoms increases , the intensity of stress field around solute atom increases and resistance to dislocation is increases, so strength of metal is also increases.
(2)A large concentration of solute atoms are added it means more frequent obstacles to dislocation. The strength increases in proportion of C ½, where c is a concentration of solute atoms.
(3)The nature of distortion produced by solute atoms are also important.
Spherical distortion produced by Substituional solute atoms. Non spherical distortion produced by interstitial solute atoms. Non spherical distortion produced maximum effect i.e. it increases
yield strength.
.

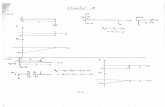
Results of Solid Solution Strengthening

Effect of solute alloy additions on stress-strain curve

THANK YOU….











![[Ashcroft & Mermin]Solid State Physics Solution](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/55344d125503469d708b4a7d/ashcroft-merminsolid-state-physics-solution.jpg)






