Skeletal System Objectives 2.2 Illustrate the skeletal system (the bones and their parts) and relate...
-
Upload
natalie-kennedy -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of Skeletal System Objectives 2.2 Illustrate the skeletal system (the bones and their parts) and relate...
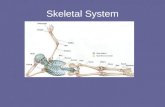
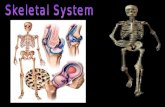
Skeletal System
Objectives
22 Illustrate the skeletal system (the bones and their parts) and relate the physiological mechanisms that help the skeletal system fulfill its function
38 Analyze diseases as related to each system
FUNCTIONS
206 bones in the body
1Supports body and provides shape
2Protects internal organs
3Movement and anchorage of muscles
4Mineral storage (Calcium and phosphorus)
5Hemopoiesis
OSTEOCYTE ndash mature bone cell
BONE FORMATION
Embryo skeletal starts as osteoblasts
(primitive embryonic cells) ndash then change to cartilage
At 8 weeks OSSIFICATION begins (Mineral
matter begins to replace cartilage) Infant
bones soft because ossification not complete
at birth
FONTANEL - Soft spot on babyrsquos head
STRUCTURE OF LONG BONEDIAPHYSIS ndash shaft
EPIPHYSES ndash ends
MEDULLARY CAVITY ndash center of shaft filled with yellow bone marrow which is mostly fat cells also cells that form white blood cells
ENDOSTEUM ndash lines marrow cavity
Shaft is made of COMPACT BONE ndash ends are SPONGYBONE Ends contain red marrow where red blood cells aremade
PERIOSTEUM ndash tough outside covering of bone ndashcontains blood vessels lymph vessels and nerves
AlertLong Bone Anatomy Quiz on Day 2
Label as structures of the long bone
AlertSkeletal Chapter Test on Day 5
Structure of a Long Bone Gross Anatomy
1 _________________ 7 ____________________ 13 _______________________
2 _________________ 8 _____________ 14 _______________________ 3_________________ 9 ____________________ 15 _______________________ 4 _________________ 10 ____________________ 16 _______________________
5 _________________ 11 _____________ 17 _______________________ 6 _________________ 12 ____________________ 18 _______________________ 4 10 1 11 5 12 6 7 13 8 9 2 14 15 16 17 18 3 Word Bank Articular cartilage Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Periosteum Medullary cavity Yellow bone marrow Endosteum Nutrient arteries Distal epiphysis Proximal epiphysis Diaphysis Perforating fibers
AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
AXIAL ndash skull spinal column ribs sternum hyoid
APPENDICULAR ndash shoulder girdle arms pelvis legs
Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
Eight Cranial Bones1 frontal2 parietal2 temporal1 occipital 1 ethmoid1 sphenoid
Fourteen Facial Bones2 nasal1 vomer2 inferior concha2 maxilla2 lacrimal2 zygomatic2 palatine1 mandible
Facial
Cranium
Spine ndash Vertebral Column26 Bones
Encloses the spinal cord
Vertebrae ndash separated by pads of cartilage = intervertebral discs
Cervical vertebrae (7)
Thoracic vertebrae (12)
Lumbar vertebrae (5)
Sacrum Coccyx
26 Bones
Ribs and Sternum Sternum divided into 3 parts ndash bottom tip isXIPHOID PROCESS
12 pairs of ribs ndash first 7pairs are true ribs ndash connected to sternum by cartilage
-next 5 pairs are false ribs ndash first 3 attach to cartilage connects them to 7th rib
(not sternum) next 2 are floating (not attached on front of body)
Appendicular Skeleton
bull clavicle ndash collar bonebull scapula ndash shoulder bladebull humerus ndash upper armbull radius and ulna ndash lower armbull carpals ndash wrist bones ndash held together by ligamentsbull metalcarpals ndash hand bonesbull phalanges ndash fingersbull pelvis ndash 3 bones (ilium ischium and pubis)bull femur ndash upper leg longest and strongest bone in bodybull tibia and fibula ndash lower legbull patella ndash kneecapbull tarsal bones ndash anklebull calcaneus ndash heel bonebull metatarsals ndash foot bones
Teamwork
Working in pairs assemble and label a
model skeleton Be creative and choose
from materials provided Also you may
provide any materials for the activity
Learning Activity
JOINTS
Joints are points of contact between 2 or more bonesand classified according to movement
BALL AND SOCKET JOINT ndash bone with ball-shaped head fits into concave socket of 2nd bone Shoulders and hips
HINGE JOINTS ndash move in one direction or plane Knees elbows outer joints of fingers
PIVOT JOINT ndash those with an extension rotate on a 2nd arch shaped bone Radius and ulna atlas and axis
GLIDING JOINTS ndash flat surfaces glide across each other Vertebrae of spine
SUTURE ndash immovable joint
SYNOVIAL FLUID ndash lubricating substance in joints
Types of Motion
1048707 FLEXION- decreasing angle
1048707 EXTENSION- increasing angle
1048707 ABDUCTION- moving away
1048707 ADDUCTION- moving towards
1048707 CIRCUMDUCTION-
1048707 ROTATION- turning on an axis
1048707 PRONATION- turning palm down
1048707 SUPINATION- turning palm up
Disorders of the Bones and Joints FRACTURE ndash a crack or break in bone
Types of fractures ( see table pp )
Treated by CLOSED REDUCTION ndash cast or splint applied OPEN REDUCTION ndash surgical intervention with devices such as wires
metal plates or screws to hold the bones in alignment (internal fixation) TRACTION ndash pulling force used to hold the bones in place ndash used for
fractures of long bones
DISLOCATION ndash bone displaced from proper position in joint
SPRAIN ndash sudden or unusual motion ligaments torn but joint not dislocated
STRAIN ndash overstretching or tearing muscle
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
FUNCTIONS
206 bones in the body
1Supports body and provides shape
2Protects internal organs
3Movement and anchorage of muscles
4Mineral storage (Calcium and phosphorus)
5Hemopoiesis
OSTEOCYTE ndash mature bone cell
BONE FORMATION
Embryo skeletal starts as osteoblasts
(primitive embryonic cells) ndash then change to cartilage
At 8 weeks OSSIFICATION begins (Mineral
matter begins to replace cartilage) Infant
bones soft because ossification not complete
at birth
FONTANEL - Soft spot on babyrsquos head
STRUCTURE OF LONG BONEDIAPHYSIS ndash shaft
EPIPHYSES ndash ends
MEDULLARY CAVITY ndash center of shaft filled with yellow bone marrow which is mostly fat cells also cells that form white blood cells
ENDOSTEUM ndash lines marrow cavity
Shaft is made of COMPACT BONE ndash ends are SPONGYBONE Ends contain red marrow where red blood cells aremade
PERIOSTEUM ndash tough outside covering of bone ndashcontains blood vessels lymph vessels and nerves
AlertLong Bone Anatomy Quiz on Day 2
Label as structures of the long bone
AlertSkeletal Chapter Test on Day 5
Structure of a Long Bone Gross Anatomy
1 _________________ 7 ____________________ 13 _______________________
2 _________________ 8 _____________ 14 _______________________ 3_________________ 9 ____________________ 15 _______________________ 4 _________________ 10 ____________________ 16 _______________________
5 _________________ 11 _____________ 17 _______________________ 6 _________________ 12 ____________________ 18 _______________________ 4 10 1 11 5 12 6 7 13 8 9 2 14 15 16 17 18 3 Word Bank Articular cartilage Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Periosteum Medullary cavity Yellow bone marrow Endosteum Nutrient arteries Distal epiphysis Proximal epiphysis Diaphysis Perforating fibers
AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
AXIAL ndash skull spinal column ribs sternum hyoid
APPENDICULAR ndash shoulder girdle arms pelvis legs
Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
Eight Cranial Bones1 frontal2 parietal2 temporal1 occipital 1 ethmoid1 sphenoid
Fourteen Facial Bones2 nasal1 vomer2 inferior concha2 maxilla2 lacrimal2 zygomatic2 palatine1 mandible
Facial
Cranium
Spine ndash Vertebral Column26 Bones
Encloses the spinal cord
Vertebrae ndash separated by pads of cartilage = intervertebral discs
Cervical vertebrae (7)
Thoracic vertebrae (12)
Lumbar vertebrae (5)
Sacrum Coccyx
26 Bones
Ribs and Sternum Sternum divided into 3 parts ndash bottom tip isXIPHOID PROCESS
12 pairs of ribs ndash first 7pairs are true ribs ndash connected to sternum by cartilage
-next 5 pairs are false ribs ndash first 3 attach to cartilage connects them to 7th rib
(not sternum) next 2 are floating (not attached on front of body)
Appendicular Skeleton
bull clavicle ndash collar bonebull scapula ndash shoulder bladebull humerus ndash upper armbull radius and ulna ndash lower armbull carpals ndash wrist bones ndash held together by ligamentsbull metalcarpals ndash hand bonesbull phalanges ndash fingersbull pelvis ndash 3 bones (ilium ischium and pubis)bull femur ndash upper leg longest and strongest bone in bodybull tibia and fibula ndash lower legbull patella ndash kneecapbull tarsal bones ndash anklebull calcaneus ndash heel bonebull metatarsals ndash foot bones
Teamwork
Working in pairs assemble and label a
model skeleton Be creative and choose
from materials provided Also you may
provide any materials for the activity
Learning Activity
JOINTS
Joints are points of contact between 2 or more bonesand classified according to movement
BALL AND SOCKET JOINT ndash bone with ball-shaped head fits into concave socket of 2nd bone Shoulders and hips
HINGE JOINTS ndash move in one direction or plane Knees elbows outer joints of fingers
PIVOT JOINT ndash those with an extension rotate on a 2nd arch shaped bone Radius and ulna atlas and axis
GLIDING JOINTS ndash flat surfaces glide across each other Vertebrae of spine
SUTURE ndash immovable joint
SYNOVIAL FLUID ndash lubricating substance in joints
Types of Motion
1048707 FLEXION- decreasing angle
1048707 EXTENSION- increasing angle
1048707 ABDUCTION- moving away
1048707 ADDUCTION- moving towards
1048707 CIRCUMDUCTION-
1048707 ROTATION- turning on an axis
1048707 PRONATION- turning palm down
1048707 SUPINATION- turning palm up
Disorders of the Bones and Joints FRACTURE ndash a crack or break in bone
Types of fractures ( see table pp )
Treated by CLOSED REDUCTION ndash cast or splint applied OPEN REDUCTION ndash surgical intervention with devices such as wires
metal plates or screws to hold the bones in alignment (internal fixation) TRACTION ndash pulling force used to hold the bones in place ndash used for
fractures of long bones
DISLOCATION ndash bone displaced from proper position in joint
SPRAIN ndash sudden or unusual motion ligaments torn but joint not dislocated
STRAIN ndash overstretching or tearing muscle
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
BONE FORMATION
Embryo skeletal starts as osteoblasts
(primitive embryonic cells) ndash then change to cartilage
At 8 weeks OSSIFICATION begins (Mineral
matter begins to replace cartilage) Infant
bones soft because ossification not complete
at birth
FONTANEL - Soft spot on babyrsquos head
STRUCTURE OF LONG BONEDIAPHYSIS ndash shaft
EPIPHYSES ndash ends
MEDULLARY CAVITY ndash center of shaft filled with yellow bone marrow which is mostly fat cells also cells that form white blood cells
ENDOSTEUM ndash lines marrow cavity
Shaft is made of COMPACT BONE ndash ends are SPONGYBONE Ends contain red marrow where red blood cells aremade
PERIOSTEUM ndash tough outside covering of bone ndashcontains blood vessels lymph vessels and nerves
AlertLong Bone Anatomy Quiz on Day 2
Label as structures of the long bone
AlertSkeletal Chapter Test on Day 5
Structure of a Long Bone Gross Anatomy
1 _________________ 7 ____________________ 13 _______________________
2 _________________ 8 _____________ 14 _______________________ 3_________________ 9 ____________________ 15 _______________________ 4 _________________ 10 ____________________ 16 _______________________
5 _________________ 11 _____________ 17 _______________________ 6 _________________ 12 ____________________ 18 _______________________ 4 10 1 11 5 12 6 7 13 8 9 2 14 15 16 17 18 3 Word Bank Articular cartilage Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Periosteum Medullary cavity Yellow bone marrow Endosteum Nutrient arteries Distal epiphysis Proximal epiphysis Diaphysis Perforating fibers
AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
AXIAL ndash skull spinal column ribs sternum hyoid
APPENDICULAR ndash shoulder girdle arms pelvis legs
Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
Eight Cranial Bones1 frontal2 parietal2 temporal1 occipital 1 ethmoid1 sphenoid
Fourteen Facial Bones2 nasal1 vomer2 inferior concha2 maxilla2 lacrimal2 zygomatic2 palatine1 mandible
Facial
Cranium
Spine ndash Vertebral Column26 Bones
Encloses the spinal cord
Vertebrae ndash separated by pads of cartilage = intervertebral discs
Cervical vertebrae (7)
Thoracic vertebrae (12)
Lumbar vertebrae (5)
Sacrum Coccyx
26 Bones
Ribs and Sternum Sternum divided into 3 parts ndash bottom tip isXIPHOID PROCESS
12 pairs of ribs ndash first 7pairs are true ribs ndash connected to sternum by cartilage
-next 5 pairs are false ribs ndash first 3 attach to cartilage connects them to 7th rib
(not sternum) next 2 are floating (not attached on front of body)
Appendicular Skeleton
bull clavicle ndash collar bonebull scapula ndash shoulder bladebull humerus ndash upper armbull radius and ulna ndash lower armbull carpals ndash wrist bones ndash held together by ligamentsbull metalcarpals ndash hand bonesbull phalanges ndash fingersbull pelvis ndash 3 bones (ilium ischium and pubis)bull femur ndash upper leg longest and strongest bone in bodybull tibia and fibula ndash lower legbull patella ndash kneecapbull tarsal bones ndash anklebull calcaneus ndash heel bonebull metatarsals ndash foot bones
Teamwork
Working in pairs assemble and label a
model skeleton Be creative and choose
from materials provided Also you may
provide any materials for the activity
Learning Activity
JOINTS
Joints are points of contact between 2 or more bonesand classified according to movement
BALL AND SOCKET JOINT ndash bone with ball-shaped head fits into concave socket of 2nd bone Shoulders and hips
HINGE JOINTS ndash move in one direction or plane Knees elbows outer joints of fingers
PIVOT JOINT ndash those with an extension rotate on a 2nd arch shaped bone Radius and ulna atlas and axis
GLIDING JOINTS ndash flat surfaces glide across each other Vertebrae of spine
SUTURE ndash immovable joint
SYNOVIAL FLUID ndash lubricating substance in joints
Types of Motion
1048707 FLEXION- decreasing angle
1048707 EXTENSION- increasing angle
1048707 ABDUCTION- moving away
1048707 ADDUCTION- moving towards
1048707 CIRCUMDUCTION-
1048707 ROTATION- turning on an axis
1048707 PRONATION- turning palm down
1048707 SUPINATION- turning palm up
Disorders of the Bones and Joints FRACTURE ndash a crack or break in bone
Types of fractures ( see table pp )
Treated by CLOSED REDUCTION ndash cast or splint applied OPEN REDUCTION ndash surgical intervention with devices such as wires
metal plates or screws to hold the bones in alignment (internal fixation) TRACTION ndash pulling force used to hold the bones in place ndash used for
fractures of long bones
DISLOCATION ndash bone displaced from proper position in joint
SPRAIN ndash sudden or unusual motion ligaments torn but joint not dislocated
STRAIN ndash overstretching or tearing muscle
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
STRUCTURE OF LONG BONEDIAPHYSIS ndash shaft
EPIPHYSES ndash ends
MEDULLARY CAVITY ndash center of shaft filled with yellow bone marrow which is mostly fat cells also cells that form white blood cells
ENDOSTEUM ndash lines marrow cavity
Shaft is made of COMPACT BONE ndash ends are SPONGYBONE Ends contain red marrow where red blood cells aremade
PERIOSTEUM ndash tough outside covering of bone ndashcontains blood vessels lymph vessels and nerves
AlertLong Bone Anatomy Quiz on Day 2
Label as structures of the long bone
AlertSkeletal Chapter Test on Day 5
Structure of a Long Bone Gross Anatomy
1 _________________ 7 ____________________ 13 _______________________
2 _________________ 8 _____________ 14 _______________________ 3_________________ 9 ____________________ 15 _______________________ 4 _________________ 10 ____________________ 16 _______________________
5 _________________ 11 _____________ 17 _______________________ 6 _________________ 12 ____________________ 18 _______________________ 4 10 1 11 5 12 6 7 13 8 9 2 14 15 16 17 18 3 Word Bank Articular cartilage Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Periosteum Medullary cavity Yellow bone marrow Endosteum Nutrient arteries Distal epiphysis Proximal epiphysis Diaphysis Perforating fibers
AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
AXIAL ndash skull spinal column ribs sternum hyoid
APPENDICULAR ndash shoulder girdle arms pelvis legs
Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
Eight Cranial Bones1 frontal2 parietal2 temporal1 occipital 1 ethmoid1 sphenoid
Fourteen Facial Bones2 nasal1 vomer2 inferior concha2 maxilla2 lacrimal2 zygomatic2 palatine1 mandible
Facial
Cranium
Spine ndash Vertebral Column26 Bones
Encloses the spinal cord
Vertebrae ndash separated by pads of cartilage = intervertebral discs
Cervical vertebrae (7)
Thoracic vertebrae (12)
Lumbar vertebrae (5)
Sacrum Coccyx
26 Bones
Ribs and Sternum Sternum divided into 3 parts ndash bottom tip isXIPHOID PROCESS
12 pairs of ribs ndash first 7pairs are true ribs ndash connected to sternum by cartilage
-next 5 pairs are false ribs ndash first 3 attach to cartilage connects them to 7th rib
(not sternum) next 2 are floating (not attached on front of body)
Appendicular Skeleton
bull clavicle ndash collar bonebull scapula ndash shoulder bladebull humerus ndash upper armbull radius and ulna ndash lower armbull carpals ndash wrist bones ndash held together by ligamentsbull metalcarpals ndash hand bonesbull phalanges ndash fingersbull pelvis ndash 3 bones (ilium ischium and pubis)bull femur ndash upper leg longest and strongest bone in bodybull tibia and fibula ndash lower legbull patella ndash kneecapbull tarsal bones ndash anklebull calcaneus ndash heel bonebull metatarsals ndash foot bones
Teamwork
Working in pairs assemble and label a
model skeleton Be creative and choose
from materials provided Also you may
provide any materials for the activity
Learning Activity
JOINTS
Joints are points of contact between 2 or more bonesand classified according to movement
BALL AND SOCKET JOINT ndash bone with ball-shaped head fits into concave socket of 2nd bone Shoulders and hips
HINGE JOINTS ndash move in one direction or plane Knees elbows outer joints of fingers
PIVOT JOINT ndash those with an extension rotate on a 2nd arch shaped bone Radius and ulna atlas and axis
GLIDING JOINTS ndash flat surfaces glide across each other Vertebrae of spine
SUTURE ndash immovable joint
SYNOVIAL FLUID ndash lubricating substance in joints
Types of Motion
1048707 FLEXION- decreasing angle
1048707 EXTENSION- increasing angle
1048707 ABDUCTION- moving away
1048707 ADDUCTION- moving towards
1048707 CIRCUMDUCTION-
1048707 ROTATION- turning on an axis
1048707 PRONATION- turning palm down
1048707 SUPINATION- turning palm up
Disorders of the Bones and Joints FRACTURE ndash a crack or break in bone
Types of fractures ( see table pp )
Treated by CLOSED REDUCTION ndash cast or splint applied OPEN REDUCTION ndash surgical intervention with devices such as wires
metal plates or screws to hold the bones in alignment (internal fixation) TRACTION ndash pulling force used to hold the bones in place ndash used for
fractures of long bones
DISLOCATION ndash bone displaced from proper position in joint
SPRAIN ndash sudden or unusual motion ligaments torn but joint not dislocated
STRAIN ndash overstretching or tearing muscle
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
AlertLong Bone Anatomy Quiz on Day 2
Label as structures of the long bone
AlertSkeletal Chapter Test on Day 5
Structure of a Long Bone Gross Anatomy
1 _________________ 7 ____________________ 13 _______________________
2 _________________ 8 _____________ 14 _______________________ 3_________________ 9 ____________________ 15 _______________________ 4 _________________ 10 ____________________ 16 _______________________
5 _________________ 11 _____________ 17 _______________________ 6 _________________ 12 ____________________ 18 _______________________ 4 10 1 11 5 12 6 7 13 8 9 2 14 15 16 17 18 3 Word Bank Articular cartilage Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Periosteum Medullary cavity Yellow bone marrow Endosteum Nutrient arteries Distal epiphysis Proximal epiphysis Diaphysis Perforating fibers
AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
AXIAL ndash skull spinal column ribs sternum hyoid
APPENDICULAR ndash shoulder girdle arms pelvis legs
Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
Eight Cranial Bones1 frontal2 parietal2 temporal1 occipital 1 ethmoid1 sphenoid
Fourteen Facial Bones2 nasal1 vomer2 inferior concha2 maxilla2 lacrimal2 zygomatic2 palatine1 mandible
Facial
Cranium
Spine ndash Vertebral Column26 Bones
Encloses the spinal cord
Vertebrae ndash separated by pads of cartilage = intervertebral discs
Cervical vertebrae (7)
Thoracic vertebrae (12)
Lumbar vertebrae (5)
Sacrum Coccyx
26 Bones
Ribs and Sternum Sternum divided into 3 parts ndash bottom tip isXIPHOID PROCESS
12 pairs of ribs ndash first 7pairs are true ribs ndash connected to sternum by cartilage
-next 5 pairs are false ribs ndash first 3 attach to cartilage connects them to 7th rib
(not sternum) next 2 are floating (not attached on front of body)
Appendicular Skeleton
bull clavicle ndash collar bonebull scapula ndash shoulder bladebull humerus ndash upper armbull radius and ulna ndash lower armbull carpals ndash wrist bones ndash held together by ligamentsbull metalcarpals ndash hand bonesbull phalanges ndash fingersbull pelvis ndash 3 bones (ilium ischium and pubis)bull femur ndash upper leg longest and strongest bone in bodybull tibia and fibula ndash lower legbull patella ndash kneecapbull tarsal bones ndash anklebull calcaneus ndash heel bonebull metatarsals ndash foot bones
Teamwork
Working in pairs assemble and label a
model skeleton Be creative and choose
from materials provided Also you may
provide any materials for the activity
Learning Activity
JOINTS
Joints are points of contact between 2 or more bonesand classified according to movement
BALL AND SOCKET JOINT ndash bone with ball-shaped head fits into concave socket of 2nd bone Shoulders and hips
HINGE JOINTS ndash move in one direction or plane Knees elbows outer joints of fingers
PIVOT JOINT ndash those with an extension rotate on a 2nd arch shaped bone Radius and ulna atlas and axis
GLIDING JOINTS ndash flat surfaces glide across each other Vertebrae of spine
SUTURE ndash immovable joint
SYNOVIAL FLUID ndash lubricating substance in joints
Types of Motion
1048707 FLEXION- decreasing angle
1048707 EXTENSION- increasing angle
1048707 ABDUCTION- moving away
1048707 ADDUCTION- moving towards
1048707 CIRCUMDUCTION-
1048707 ROTATION- turning on an axis
1048707 PRONATION- turning palm down
1048707 SUPINATION- turning palm up
Disorders of the Bones and Joints FRACTURE ndash a crack or break in bone
Types of fractures ( see table pp )
Treated by CLOSED REDUCTION ndash cast or splint applied OPEN REDUCTION ndash surgical intervention with devices such as wires
metal plates or screws to hold the bones in alignment (internal fixation) TRACTION ndash pulling force used to hold the bones in place ndash used for
fractures of long bones
DISLOCATION ndash bone displaced from proper position in joint
SPRAIN ndash sudden or unusual motion ligaments torn but joint not dislocated
STRAIN ndash overstretching or tearing muscle
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
Structure of a Long Bone Gross Anatomy
1 _________________ 7 ____________________ 13 _______________________
2 _________________ 8 _____________ 14 _______________________ 3_________________ 9 ____________________ 15 _______________________ 4 _________________ 10 ____________________ 16 _______________________
5 _________________ 11 _____________ 17 _______________________ 6 _________________ 12 ____________________ 18 _______________________ 4 10 1 11 5 12 6 7 13 8 9 2 14 15 16 17 18 3 Word Bank Articular cartilage Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Periosteum Medullary cavity Yellow bone marrow Endosteum Nutrient arteries Distal epiphysis Proximal epiphysis Diaphysis Perforating fibers
AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
AXIAL ndash skull spinal column ribs sternum hyoid
APPENDICULAR ndash shoulder girdle arms pelvis legs
Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
Eight Cranial Bones1 frontal2 parietal2 temporal1 occipital 1 ethmoid1 sphenoid
Fourteen Facial Bones2 nasal1 vomer2 inferior concha2 maxilla2 lacrimal2 zygomatic2 palatine1 mandible
Facial
Cranium
Spine ndash Vertebral Column26 Bones
Encloses the spinal cord
Vertebrae ndash separated by pads of cartilage = intervertebral discs
Cervical vertebrae (7)
Thoracic vertebrae (12)
Lumbar vertebrae (5)
Sacrum Coccyx
26 Bones
Ribs and Sternum Sternum divided into 3 parts ndash bottom tip isXIPHOID PROCESS
12 pairs of ribs ndash first 7pairs are true ribs ndash connected to sternum by cartilage
-next 5 pairs are false ribs ndash first 3 attach to cartilage connects them to 7th rib
(not sternum) next 2 are floating (not attached on front of body)
Appendicular Skeleton
bull clavicle ndash collar bonebull scapula ndash shoulder bladebull humerus ndash upper armbull radius and ulna ndash lower armbull carpals ndash wrist bones ndash held together by ligamentsbull metalcarpals ndash hand bonesbull phalanges ndash fingersbull pelvis ndash 3 bones (ilium ischium and pubis)bull femur ndash upper leg longest and strongest bone in bodybull tibia and fibula ndash lower legbull patella ndash kneecapbull tarsal bones ndash anklebull calcaneus ndash heel bonebull metatarsals ndash foot bones
Teamwork
Working in pairs assemble and label a
model skeleton Be creative and choose
from materials provided Also you may
provide any materials for the activity
Learning Activity
JOINTS
Joints are points of contact between 2 or more bonesand classified according to movement
BALL AND SOCKET JOINT ndash bone with ball-shaped head fits into concave socket of 2nd bone Shoulders and hips
HINGE JOINTS ndash move in one direction or plane Knees elbows outer joints of fingers
PIVOT JOINT ndash those with an extension rotate on a 2nd arch shaped bone Radius and ulna atlas and axis
GLIDING JOINTS ndash flat surfaces glide across each other Vertebrae of spine
SUTURE ndash immovable joint
SYNOVIAL FLUID ndash lubricating substance in joints
Types of Motion
1048707 FLEXION- decreasing angle
1048707 EXTENSION- increasing angle
1048707 ABDUCTION- moving away
1048707 ADDUCTION- moving towards
1048707 CIRCUMDUCTION-
1048707 ROTATION- turning on an axis
1048707 PRONATION- turning palm down
1048707 SUPINATION- turning palm up
Disorders of the Bones and Joints FRACTURE ndash a crack or break in bone
Types of fractures ( see table pp )
Treated by CLOSED REDUCTION ndash cast or splint applied OPEN REDUCTION ndash surgical intervention with devices such as wires
metal plates or screws to hold the bones in alignment (internal fixation) TRACTION ndash pulling force used to hold the bones in place ndash used for
fractures of long bones
DISLOCATION ndash bone displaced from proper position in joint
SPRAIN ndash sudden or unusual motion ligaments torn but joint not dislocated
STRAIN ndash overstretching or tearing muscle
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
AXIAL ndash skull spinal column ribs sternum hyoid
APPENDICULAR ndash shoulder girdle arms pelvis legs
Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
Eight Cranial Bones1 frontal2 parietal2 temporal1 occipital 1 ethmoid1 sphenoid
Fourteen Facial Bones2 nasal1 vomer2 inferior concha2 maxilla2 lacrimal2 zygomatic2 palatine1 mandible
Facial
Cranium
Spine ndash Vertebral Column26 Bones
Encloses the spinal cord
Vertebrae ndash separated by pads of cartilage = intervertebral discs
Cervical vertebrae (7)
Thoracic vertebrae (12)
Lumbar vertebrae (5)
Sacrum Coccyx
26 Bones
Ribs and Sternum Sternum divided into 3 parts ndash bottom tip isXIPHOID PROCESS
12 pairs of ribs ndash first 7pairs are true ribs ndash connected to sternum by cartilage
-next 5 pairs are false ribs ndash first 3 attach to cartilage connects them to 7th rib
(not sternum) next 2 are floating (not attached on front of body)
Appendicular Skeleton
bull clavicle ndash collar bonebull scapula ndash shoulder bladebull humerus ndash upper armbull radius and ulna ndash lower armbull carpals ndash wrist bones ndash held together by ligamentsbull metalcarpals ndash hand bonesbull phalanges ndash fingersbull pelvis ndash 3 bones (ilium ischium and pubis)bull femur ndash upper leg longest and strongest bone in bodybull tibia and fibula ndash lower legbull patella ndash kneecapbull tarsal bones ndash anklebull calcaneus ndash heel bonebull metatarsals ndash foot bones
Teamwork
Working in pairs assemble and label a
model skeleton Be creative and choose
from materials provided Also you may
provide any materials for the activity
Learning Activity
JOINTS
Joints are points of contact between 2 or more bonesand classified according to movement
BALL AND SOCKET JOINT ndash bone with ball-shaped head fits into concave socket of 2nd bone Shoulders and hips
HINGE JOINTS ndash move in one direction or plane Knees elbows outer joints of fingers
PIVOT JOINT ndash those with an extension rotate on a 2nd arch shaped bone Radius and ulna atlas and axis
GLIDING JOINTS ndash flat surfaces glide across each other Vertebrae of spine
SUTURE ndash immovable joint
SYNOVIAL FLUID ndash lubricating substance in joints
Types of Motion
1048707 FLEXION- decreasing angle
1048707 EXTENSION- increasing angle
1048707 ABDUCTION- moving away
1048707 ADDUCTION- moving towards
1048707 CIRCUMDUCTION-
1048707 ROTATION- turning on an axis
1048707 PRONATION- turning palm down
1048707 SUPINATION- turning palm up
Disorders of the Bones and Joints FRACTURE ndash a crack or break in bone
Types of fractures ( see table pp )
Treated by CLOSED REDUCTION ndash cast or splint applied OPEN REDUCTION ndash surgical intervention with devices such as wires
metal plates or screws to hold the bones in alignment (internal fixation) TRACTION ndash pulling force used to hold the bones in place ndash used for
fractures of long bones
DISLOCATION ndash bone displaced from proper position in joint
SPRAIN ndash sudden or unusual motion ligaments torn but joint not dislocated
STRAIN ndash overstretching or tearing muscle
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
Eight Cranial Bones1 frontal2 parietal2 temporal1 occipital 1 ethmoid1 sphenoid
Fourteen Facial Bones2 nasal1 vomer2 inferior concha2 maxilla2 lacrimal2 zygomatic2 palatine1 mandible
Facial
Cranium
Spine ndash Vertebral Column26 Bones
Encloses the spinal cord
Vertebrae ndash separated by pads of cartilage = intervertebral discs
Cervical vertebrae (7)
Thoracic vertebrae (12)
Lumbar vertebrae (5)
Sacrum Coccyx
26 Bones
Ribs and Sternum Sternum divided into 3 parts ndash bottom tip isXIPHOID PROCESS
12 pairs of ribs ndash first 7pairs are true ribs ndash connected to sternum by cartilage
-next 5 pairs are false ribs ndash first 3 attach to cartilage connects them to 7th rib
(not sternum) next 2 are floating (not attached on front of body)
Appendicular Skeleton
bull clavicle ndash collar bonebull scapula ndash shoulder bladebull humerus ndash upper armbull radius and ulna ndash lower armbull carpals ndash wrist bones ndash held together by ligamentsbull metalcarpals ndash hand bonesbull phalanges ndash fingersbull pelvis ndash 3 bones (ilium ischium and pubis)bull femur ndash upper leg longest and strongest bone in bodybull tibia and fibula ndash lower legbull patella ndash kneecapbull tarsal bones ndash anklebull calcaneus ndash heel bonebull metatarsals ndash foot bones
Teamwork
Working in pairs assemble and label a
model skeleton Be creative and choose
from materials provided Also you may
provide any materials for the activity
Learning Activity
JOINTS
Joints are points of contact between 2 or more bonesand classified according to movement
BALL AND SOCKET JOINT ndash bone with ball-shaped head fits into concave socket of 2nd bone Shoulders and hips
HINGE JOINTS ndash move in one direction or plane Knees elbows outer joints of fingers
PIVOT JOINT ndash those with an extension rotate on a 2nd arch shaped bone Radius and ulna atlas and axis
GLIDING JOINTS ndash flat surfaces glide across each other Vertebrae of spine
SUTURE ndash immovable joint
SYNOVIAL FLUID ndash lubricating substance in joints
Types of Motion
1048707 FLEXION- decreasing angle
1048707 EXTENSION- increasing angle
1048707 ABDUCTION- moving away
1048707 ADDUCTION- moving towards
1048707 CIRCUMDUCTION-
1048707 ROTATION- turning on an axis
1048707 PRONATION- turning palm down
1048707 SUPINATION- turning palm up
Disorders of the Bones and Joints FRACTURE ndash a crack or break in bone
Types of fractures ( see table pp )
Treated by CLOSED REDUCTION ndash cast or splint applied OPEN REDUCTION ndash surgical intervention with devices such as wires
metal plates or screws to hold the bones in alignment (internal fixation) TRACTION ndash pulling force used to hold the bones in place ndash used for
fractures of long bones
DISLOCATION ndash bone displaced from proper position in joint
SPRAIN ndash sudden or unusual motion ligaments torn but joint not dislocated
STRAIN ndash overstretching or tearing muscle
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
Spine ndash Vertebral Column26 Bones
Encloses the spinal cord
Vertebrae ndash separated by pads of cartilage = intervertebral discs
Cervical vertebrae (7)
Thoracic vertebrae (12)
Lumbar vertebrae (5)
Sacrum Coccyx
26 Bones
Ribs and Sternum Sternum divided into 3 parts ndash bottom tip isXIPHOID PROCESS
12 pairs of ribs ndash first 7pairs are true ribs ndash connected to sternum by cartilage
-next 5 pairs are false ribs ndash first 3 attach to cartilage connects them to 7th rib
(not sternum) next 2 are floating (not attached on front of body)
Appendicular Skeleton
bull clavicle ndash collar bonebull scapula ndash shoulder bladebull humerus ndash upper armbull radius and ulna ndash lower armbull carpals ndash wrist bones ndash held together by ligamentsbull metalcarpals ndash hand bonesbull phalanges ndash fingersbull pelvis ndash 3 bones (ilium ischium and pubis)bull femur ndash upper leg longest and strongest bone in bodybull tibia and fibula ndash lower legbull patella ndash kneecapbull tarsal bones ndash anklebull calcaneus ndash heel bonebull metatarsals ndash foot bones
Teamwork
Working in pairs assemble and label a
model skeleton Be creative and choose
from materials provided Also you may
provide any materials for the activity
Learning Activity
JOINTS
Joints are points of contact between 2 or more bonesand classified according to movement
BALL AND SOCKET JOINT ndash bone with ball-shaped head fits into concave socket of 2nd bone Shoulders and hips
HINGE JOINTS ndash move in one direction or plane Knees elbows outer joints of fingers
PIVOT JOINT ndash those with an extension rotate on a 2nd arch shaped bone Radius and ulna atlas and axis
GLIDING JOINTS ndash flat surfaces glide across each other Vertebrae of spine
SUTURE ndash immovable joint
SYNOVIAL FLUID ndash lubricating substance in joints
Types of Motion
1048707 FLEXION- decreasing angle
1048707 EXTENSION- increasing angle
1048707 ABDUCTION- moving away
1048707 ADDUCTION- moving towards
1048707 CIRCUMDUCTION-
1048707 ROTATION- turning on an axis
1048707 PRONATION- turning palm down
1048707 SUPINATION- turning palm up
Disorders of the Bones and Joints FRACTURE ndash a crack or break in bone
Types of fractures ( see table pp )
Treated by CLOSED REDUCTION ndash cast or splint applied OPEN REDUCTION ndash surgical intervention with devices such as wires
metal plates or screws to hold the bones in alignment (internal fixation) TRACTION ndash pulling force used to hold the bones in place ndash used for
fractures of long bones
DISLOCATION ndash bone displaced from proper position in joint
SPRAIN ndash sudden or unusual motion ligaments torn but joint not dislocated
STRAIN ndash overstretching or tearing muscle
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
Ribs and Sternum Sternum divided into 3 parts ndash bottom tip isXIPHOID PROCESS
12 pairs of ribs ndash first 7pairs are true ribs ndash connected to sternum by cartilage
-next 5 pairs are false ribs ndash first 3 attach to cartilage connects them to 7th rib
(not sternum) next 2 are floating (not attached on front of body)
Appendicular Skeleton
bull clavicle ndash collar bonebull scapula ndash shoulder bladebull humerus ndash upper armbull radius and ulna ndash lower armbull carpals ndash wrist bones ndash held together by ligamentsbull metalcarpals ndash hand bonesbull phalanges ndash fingersbull pelvis ndash 3 bones (ilium ischium and pubis)bull femur ndash upper leg longest and strongest bone in bodybull tibia and fibula ndash lower legbull patella ndash kneecapbull tarsal bones ndash anklebull calcaneus ndash heel bonebull metatarsals ndash foot bones
Teamwork
Working in pairs assemble and label a
model skeleton Be creative and choose
from materials provided Also you may
provide any materials for the activity
Learning Activity
JOINTS
Joints are points of contact between 2 or more bonesand classified according to movement
BALL AND SOCKET JOINT ndash bone with ball-shaped head fits into concave socket of 2nd bone Shoulders and hips
HINGE JOINTS ndash move in one direction or plane Knees elbows outer joints of fingers
PIVOT JOINT ndash those with an extension rotate on a 2nd arch shaped bone Radius and ulna atlas and axis
GLIDING JOINTS ndash flat surfaces glide across each other Vertebrae of spine
SUTURE ndash immovable joint
SYNOVIAL FLUID ndash lubricating substance in joints
Types of Motion
1048707 FLEXION- decreasing angle
1048707 EXTENSION- increasing angle
1048707 ABDUCTION- moving away
1048707 ADDUCTION- moving towards
1048707 CIRCUMDUCTION-
1048707 ROTATION- turning on an axis
1048707 PRONATION- turning palm down
1048707 SUPINATION- turning palm up
Disorders of the Bones and Joints FRACTURE ndash a crack or break in bone
Types of fractures ( see table pp )
Treated by CLOSED REDUCTION ndash cast or splint applied OPEN REDUCTION ndash surgical intervention with devices such as wires
metal plates or screws to hold the bones in alignment (internal fixation) TRACTION ndash pulling force used to hold the bones in place ndash used for
fractures of long bones
DISLOCATION ndash bone displaced from proper position in joint
SPRAIN ndash sudden or unusual motion ligaments torn but joint not dislocated
STRAIN ndash overstretching or tearing muscle
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
Appendicular Skeleton
bull clavicle ndash collar bonebull scapula ndash shoulder bladebull humerus ndash upper armbull radius and ulna ndash lower armbull carpals ndash wrist bones ndash held together by ligamentsbull metalcarpals ndash hand bonesbull phalanges ndash fingersbull pelvis ndash 3 bones (ilium ischium and pubis)bull femur ndash upper leg longest and strongest bone in bodybull tibia and fibula ndash lower legbull patella ndash kneecapbull tarsal bones ndash anklebull calcaneus ndash heel bonebull metatarsals ndash foot bones
Teamwork
Working in pairs assemble and label a
model skeleton Be creative and choose
from materials provided Also you may
provide any materials for the activity
Learning Activity
JOINTS
Joints are points of contact between 2 or more bonesand classified according to movement
BALL AND SOCKET JOINT ndash bone with ball-shaped head fits into concave socket of 2nd bone Shoulders and hips
HINGE JOINTS ndash move in one direction or plane Knees elbows outer joints of fingers
PIVOT JOINT ndash those with an extension rotate on a 2nd arch shaped bone Radius and ulna atlas and axis
GLIDING JOINTS ndash flat surfaces glide across each other Vertebrae of spine
SUTURE ndash immovable joint
SYNOVIAL FLUID ndash lubricating substance in joints
Types of Motion
1048707 FLEXION- decreasing angle
1048707 EXTENSION- increasing angle
1048707 ABDUCTION- moving away
1048707 ADDUCTION- moving towards
1048707 CIRCUMDUCTION-
1048707 ROTATION- turning on an axis
1048707 PRONATION- turning palm down
1048707 SUPINATION- turning palm up
Disorders of the Bones and Joints FRACTURE ndash a crack or break in bone
Types of fractures ( see table pp )
Treated by CLOSED REDUCTION ndash cast or splint applied OPEN REDUCTION ndash surgical intervention with devices such as wires
metal plates or screws to hold the bones in alignment (internal fixation) TRACTION ndash pulling force used to hold the bones in place ndash used for
fractures of long bones
DISLOCATION ndash bone displaced from proper position in joint
SPRAIN ndash sudden or unusual motion ligaments torn but joint not dislocated
STRAIN ndash overstretching or tearing muscle
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
Teamwork
Working in pairs assemble and label a
model skeleton Be creative and choose
from materials provided Also you may
provide any materials for the activity
Learning Activity
JOINTS
Joints are points of contact between 2 or more bonesand classified according to movement
BALL AND SOCKET JOINT ndash bone with ball-shaped head fits into concave socket of 2nd bone Shoulders and hips
HINGE JOINTS ndash move in one direction or plane Knees elbows outer joints of fingers
PIVOT JOINT ndash those with an extension rotate on a 2nd arch shaped bone Radius and ulna atlas and axis
GLIDING JOINTS ndash flat surfaces glide across each other Vertebrae of spine
SUTURE ndash immovable joint
SYNOVIAL FLUID ndash lubricating substance in joints
Types of Motion
1048707 FLEXION- decreasing angle
1048707 EXTENSION- increasing angle
1048707 ABDUCTION- moving away
1048707 ADDUCTION- moving towards
1048707 CIRCUMDUCTION-
1048707 ROTATION- turning on an axis
1048707 PRONATION- turning palm down
1048707 SUPINATION- turning palm up
Disorders of the Bones and Joints FRACTURE ndash a crack or break in bone
Types of fractures ( see table pp )
Treated by CLOSED REDUCTION ndash cast or splint applied OPEN REDUCTION ndash surgical intervention with devices such as wires
metal plates or screws to hold the bones in alignment (internal fixation) TRACTION ndash pulling force used to hold the bones in place ndash used for
fractures of long bones
DISLOCATION ndash bone displaced from proper position in joint
SPRAIN ndash sudden or unusual motion ligaments torn but joint not dislocated
STRAIN ndash overstretching or tearing muscle
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
JOINTS
Joints are points of contact between 2 or more bonesand classified according to movement
BALL AND SOCKET JOINT ndash bone with ball-shaped head fits into concave socket of 2nd bone Shoulders and hips
HINGE JOINTS ndash move in one direction or plane Knees elbows outer joints of fingers
PIVOT JOINT ndash those with an extension rotate on a 2nd arch shaped bone Radius and ulna atlas and axis
GLIDING JOINTS ndash flat surfaces glide across each other Vertebrae of spine
SUTURE ndash immovable joint
SYNOVIAL FLUID ndash lubricating substance in joints
Types of Motion
1048707 FLEXION- decreasing angle
1048707 EXTENSION- increasing angle
1048707 ABDUCTION- moving away
1048707 ADDUCTION- moving towards
1048707 CIRCUMDUCTION-
1048707 ROTATION- turning on an axis
1048707 PRONATION- turning palm down
1048707 SUPINATION- turning palm up
Disorders of the Bones and Joints FRACTURE ndash a crack or break in bone
Types of fractures ( see table pp )
Treated by CLOSED REDUCTION ndash cast or splint applied OPEN REDUCTION ndash surgical intervention with devices such as wires
metal plates or screws to hold the bones in alignment (internal fixation) TRACTION ndash pulling force used to hold the bones in place ndash used for
fractures of long bones
DISLOCATION ndash bone displaced from proper position in joint
SPRAIN ndash sudden or unusual motion ligaments torn but joint not dislocated
STRAIN ndash overstretching or tearing muscle
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
Types of Motion
1048707 FLEXION- decreasing angle
1048707 EXTENSION- increasing angle
1048707 ABDUCTION- moving away
1048707 ADDUCTION- moving towards
1048707 CIRCUMDUCTION-
1048707 ROTATION- turning on an axis
1048707 PRONATION- turning palm down
1048707 SUPINATION- turning palm up
Disorders of the Bones and Joints FRACTURE ndash a crack or break in bone
Types of fractures ( see table pp )
Treated by CLOSED REDUCTION ndash cast or splint applied OPEN REDUCTION ndash surgical intervention with devices such as wires
metal plates or screws to hold the bones in alignment (internal fixation) TRACTION ndash pulling force used to hold the bones in place ndash used for
fractures of long bones
DISLOCATION ndash bone displaced from proper position in joint
SPRAIN ndash sudden or unusual motion ligaments torn but joint not dislocated
STRAIN ndash overstretching or tearing muscle
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
Disorders of the Bones and Joints FRACTURE ndash a crack or break in bone
Types of fractures ( see table pp )
Treated by CLOSED REDUCTION ndash cast or splint applied OPEN REDUCTION ndash surgical intervention with devices such as wires
metal plates or screws to hold the bones in alignment (internal fixation) TRACTION ndash pulling force used to hold the bones in place ndash used for
fractures of long bones
DISLOCATION ndash bone displaced from proper position in joint
SPRAIN ndash sudden or unusual motion ligaments torn but joint not dislocated
STRAIN ndash overstretching or tearing muscle
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
Fractures WorksheetMatch common fracture types with treatments Write the correct answer ineach blank (An answer may be used more than once)
a greenstick fracture b simple fracturec compound fracture d comminuted fracturee closed reduction f open reductiong traction
_____ 1 Surgical correction of a broken bone_____ 2 Bone is broken completely but ends do not penetrate the
skin_____ 3 Nonsurgical correction of broken bone and application of a
cast_____ 4 A fracture in which the bone splinters but the break is incomplete_____ 5 Bones are broken into many pieces_____ 6 A fracture in which the bone ends penetrate the skin_____ 7 A pulling force used to hold the bones in place_____ 8
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
Diseases of Bones ARTHRITIS ndash inflammation of one or more joints
Abnormal curvatures of the spine KYPHOSIS ndash hunchback LORDOSIS ndash swayback SCOLIOSIS ndash lateral curvature
Diagnosis and Treatment ARTHROSCOPY ndash examination into joint using
arthroscope with fiber optic lens most knee injuries treated with arthroscopy
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
Internet Research ActivityComplete an Internet search on the disorders ldquoarthritisrdquo and ldquoosteoporosisrdquo The goal will be to fill out a summary chart (handout) comparing the two disorders
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-
ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
bull HOSA
Participate in a Biomedical Debate on the topic ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo One group should argue that Osteoporosis is worse and the other that Arthritis is worse
- Skeletal System
- FUNCTIONS
- BONE FORMATION
- STRUCTURE OF LONG BONE
- Slide 5
- Slide 6
- AXIAL amp APPENDICULAR SKELETON
- Skull Composed of cranial and facial bones
- Spine ndash Vertebral Column 26 Bones
- Ribs and Sternum
- Appendicular Skeleton
- Learning Activity
- JOINTS
- Slide 14
- Disorders of the Bones and Joints
- Fractures Worksheet
- Diseases of Bones
- Internet Research Activity
- ldquoOsteoporosis vs Arthritisrdquo
-