Single Board Computer GPIO Interface Bringup Guide
Transcript of Single Board Computer GPIO Interface Bringup Guide

Thundercomm TurboX™ S605 Single Board Computer GPIO Interface Bringup Guide
Rev. V01
Jan 04, 2019
DN: TC_S605_161401
Empowering Every IoT Device with Our Technology

REVISION PAGES
0.1
1 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
1
Version Date Description
V0.1 2019-1-4 Initial Version

REVISION PAGES
0.1
2 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
2
Contents
1 Introduction .............................................................................................................................................................. 3
1.1 Purpose ........................................................................................................................................................... 3
1.2 Acronyms ........................................................................................................................................................ 3
2 GPIO Programming Guide .................................................................................................................................... 5
2.1 GPIO And PMIC GPIO/MPP Examples ......................................................................................................... 5
2.2 Configure Chipset GPIO ................................................................................................................................. 5
2.3 Configure PM670IC GPIO/MPP .................................................................................................................... 7
2.4 GPIO Setting For IRQ .................................................................................................................................... 8
3 QUPs: Qualcomm universal peripherals .................................................................................................................. 10
3.1 QUPs AS UART EXAMPLE ....................................................................................................................... 11
3.2 QUPs AS I2C EXAMPLE ............................................................................................................................ 16

REVISION PAGES
0.1
3 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
3
1 Introduction
1.1 Purpose
The purpose of this document is guide to user how to configure GPIO.
1.2 Acronyms
Acronyms or term Definition
SDK Software Development Kit
BT Bluetooth
RF Radio Frequency
DSI Display Serial Interface
CSI Camera Serial Interface
SOM System On Module
GPIO General Purpose Input Output
QHD Quarter High Definition
SPMI System Power Management Interface (Qualcomm PMIC / baseband proprietary
protocol)
UIM User Identity Module
HDMI High Definition Multimedia Interface
I2C Inter-Integrated Circuit
I2S Inter-IC Sound
NFC Near Field Communication
EMMC Embedded Multimedia Card
UFS Universal Flash Storage
USB HS USB High Speed
USB SS USB Super Speed
MIPI Mobile Industry processor interface
ANC Audio Noise Cancellation
AMIC Analog Microphone
DMIC Digital Microphone

REVISION PAGES
0.1
4 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
4
MSM Mobile Station Modem
JTAG Joint Test Action Group
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter
QUP Qualcomm® universal peripherals
SLIMBUS Serial Low-power Inter-chip Media Bus
MPP Multi-Purpose Pin
GPS Global Positioning system
SSBI Single wire serial bus interface (Qualcomm proprietary mostly PMIC /
Companion chip and baseband processor protocol)
PMIC Power Management IC
PWM Pulse-Width Modulation
DC Direct Current
WLAN Wireless Local Area Networks
HSIC High Speed Inter Connect Bus
LNA Low Noise Amplifier
EEPROM Electrically Erasable Programmable Read only memory
LED Light-Emitting Diode
LCD Liquid Crystal Display

REVISION PAGES
0.1
5 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
5
2 GPIO Programming Guide
The purpose of this chapter is to provide information for configuring Thundercomm TurboXTM GPIOs and
QUP.
2.1 GPIO And PMIC GPIO/MPP Examples
This section describes the configure registers for GPIO in the Thundercomm TurboXTM chipset using device
tree.
The official documentation for configuring Thundercomm TurboXTM GPIOs pins alternate function present in
your BSP.
<android-source-tree>/kernel/msm-4.9/Documentation/devicetree/bindings/pinctrl/qcom,sdm670-pinctrl
2.2 Configure Chipset GPIO
Take an example you want to configure GPIO12 as GPIO and change drive strength to 2mA.
Step 1: Add the pin-controller node in
<android-source-tree>/ msm-4.9/arch/arm64/boot/dts/qcom/sdm670-pinctrl.dtsi
Step 2: Snippet
&soc {
tlmm: pinctrl@03400000 {
nfc {
nfc_enable_active: nfc_enable_active {
/* active state */
mux {
/* 12: NFC ENABLE 116:ESE Enable */
pins = "gpio12", "gpio62", "gpio116";
function = "gpio";
};
config {
pins = "gpio12", "gpio62", "gpio116";
drive-strength = <2>; /* 2 MA */

REVISION PAGES
0.1
6 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
6
bias-pull-up;
};
};
nfc_enable_suspend: nfc_enable_suspend {
/* sleep state */
mux {
/* 12: NFC ENABLE 116:ESE Enable */
pins = "gpio12", "gpio62", "gpio116";
function = "gpio";
};
config {
pins = "gpio12", "gpio62", "gpio116";
drive-strength = <2>; /* 2 MA */
bias-disable;
};
};
};
};
};
Above device tree code is the configuration for GPIO12, it has both active and suspend node.
“nfc” device node is the node which configures the GPIO12 as gpio, sets the drive strength as 2ma, sets PULL
UP for active, and disable PULL UP while in suspend. For more details about options refer to above document
( <android-source-tree>/kernel/ msm-4.9/Documentation/devicetree/bindings/pinctrl/qcom,sdm670-pinctrl ).
Using the Thundercomm TurboXTM GPIO in device tree of any driver, for example:
&mydriver {
compatible = “mydriver”;
qcom,my-gpio = “<&tlmm 12 0x00>;
pinctrl-0 = <&nfc_int_active
&nfc_enable_active
&nfc_clk_default>;
pinctrl-1 = <&nfc_int_suspend &nfc_enable_suspend>};
Step 3: To get the gpio in your driver use below api,

REVISION PAGES
0.1
7 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
7
platform_data->dis_gpio = of_get_named_gpio(np, "qcom,my-gpio ", 0);
Step 4: If you want to set gpio that you got from dts, use below api in your code
gpio_direction_output(platform_data->dis_gpio, 1); //set it high
or
gpio_direction_output(platform_data->dis_gpio, 0); //set it high
2.3 Configure PM670IC GPIO/MPP
For example, to configure PM670 GPIO16 as GPIO and change drive strength to highest.
Step 1 : Open the GPIO node in
<android-source-tree>/kernel/msm-4.9/arch/arm64/boot/dts/qcom/sdm670-pinctrl.dtsi
Step 2 : Add the GPIO node
&pm660_gpios {
gpio16_dig_out {
gpio16_dig_out_default: gpio16_dig_out_default {
pins = "gpio16"; /* GPIO 16 */
function = "normal"; /* normal output */
power-source =<0> ; /* VIN0 */
output-low; /* digital output, no invert */
input-disable; /* prevent GPIO from being set to DIO */
};
};
};
Configure the GPIO in device tree of any driver, for example:
&mydriver {
compatible = "qcom,test";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&gpio16_dig_out_default>;
qcom,my-gpio = <&pm660_gpios 16 GPIO_ACTIVE_LOW>; };

REVISION PAGES
0.1
8 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
8
Step 3: build the boot.img and flash to board, get the GPIO in your driver with the following API,
platform_data->dis_gpio = of_get_named_gpio(np, "qcom,my-gpio ", 0);
Step 4: If you want to set gpio , use the following API in your code
gpio_direction_output(platform_data->dis_gpio, 1); //set it high
or
gpio_direction_output(platform_data->dis_gpio, 0); //set it high
2.4 GPIO Setting For IRQ
Make sure the IRQ in your driver with parent controller correctly, and your GPIO is configured as input.
Here is an example for touch screen controller driver.
<android-source-tree>/kernel/msm-4.9/arch/arm/boot/dts/qcom/sdm670-mtp.dtsi
&qupv3_se9_i2c {
status = "ok";
himax-ts@48 {
compatible = "tshimax,hxcommon";
reg = <0x48>;
interrupt-parent = <&tlmm>;
interrupts = <5 0x2>;
vdd-supply = <&pm660l_l6>;
avdd-supply = <&pm660_l11>;
himax,display-coords = <0 720 0 1280>;
himax,panel-coords = <0 720 0 1280>;
himax,rst-gpio = <&tlmm 134 0x00>;
himax,irq-gpio = <&tlmm 5 0x00>;
report_type = <1>;

REVISION PAGES
0.1
9 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
9
pinctrl-names = "himax_irq";
pinctrl-0 = <&himax_irq>;
};
};
If use PM670 GPIOs:
&qupv3_se9_i2c {
status = "ok";
himax-ts@48 {
compatible = "tshimax,hxcommon";
reg = <0x48>;
interrupt-parent = <&tlmm>;
interrupts = <5 0x2>;
vdd-supply = <&pm660l_l6>;
avdd-supply = <&pm660_l11>;
himax,display-coords = <0 720 0 1280>;
himax,panel-coords = <0 720 0 1280>;
himax,rst-gpio = <&tlmm 134 0x00>;
himax,irq-gpio = <&pm660_gpios 13 0x00>;
report_type = <1>;
pinctrl-names = "himax_irq";
pinctrl-0 = <&himax_irq>;
};
};
Using the following API to request IRQ:
Int irqn = gpio_to_irq(platform_data->irq_gpio);
request_irq(....,irqn,...);

REVISION PAGES
0.1
10 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
10
3 QUPs: Qualcomm universal peripherals
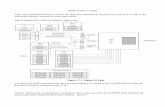
Thundercomm TurboXTM has 13 QUPs ports grouped in 2 QUPs groups.
a) QUPs for AP
b) QUPs for SPLI
There are 19 Qualcomm® universal peripherals (QUPs) on QCS605, of which 6 QUPs are dedicated to SLPI
and 16 QUPs in GPIOs. Each port can be configured as I2C, SPI, or UART. The block diagram of QUPs is as
follow.
Figure 2.4-1 QUPs Block Diagram in Thundercomm TurboXTM
The supported assignments are listed in the table for each QUP. Only one protocol can be selected in one
QUP engine at a time.

REVISION PAGES
0.1
11 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
11
Table 2.4-1 the supported assignment of QUPs
QUP GPIO Assignment are listed in the following table (GPIOs 31–34 are muxed on QUP_11 and QUP_14).
Table 2.4-2 QUP GPIO Assignment
3.1 QUPs AS UART EXAMPLE
The UART core is used for transmitting and receiving data through a serial interface. It is used for
communicating with other UART protocol devices. Configuration of this mode is primarily defined by the
UART_DM_MR1 and UART_DM_MR2 registers.
UART can configure as Low-speed UART vs High Speed UART. Low-speed UART is a FIFO-based UART driver

REVISION PAGES
0.1
12 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
12
designed for small data transfers at a slow rate, such as console debugging. If a large amount of data is
transferred or for a high-speed transfer, is recommended using the high-speed UART driver.
For Low speed FIFO based UART driver :
o Use compatible = " qcom,msm-geni-console", "qcom,msm-geni-uart "; in your UART device node
For High Speed DMA based UART driver :
o Use compatible = " qcom,msm-geni-serial-hs", "qcom,msm-geni-uart "; in your UART device
node
For High speed DMA based UART driver you need to supply
Low-speed UART example driver in kernel
We will use QUPs9 GPIO4、GPIO5 as UART. Low speed UART with two pins is very common. So we will
configure as bellow:
QUPs9 – GPIO4 will be UART_TX
QUPs9 – GPIO5 will be UART_RX
Creating a device tree node for QUPs9
The official documentation about all parameters about low speed UART refer to
<android-soruce-tree>/kernel/ msm-4.9/Documentation/devicetree/bindings/serial/qcom,msm-geni-uart.txt
Declare QUPs9 UART as qupv3_se9_2uart in
<android-source-tree>/kernel/ msm-4.9/arch/arm64/boot/dts/qcom/sdm670-qupv3.dtsi
/* 2-wire UART */
/* Debug UART Instance for CDP/MTP platform */
qupv3_se9_2uart: qcom,qup_uart@0xa84000 {
compatible = "qcom,msm-geni-console", "qcom,msm-geni-uart";
reg = <0xa84000 0x4000>;
reg-names = "se_phys";
clock-names = "se-clk", "m-ahb", "s-ahb";
clocks = <&clock_gcc GCC_QUPV3_WRAP1_S1_CLK>,
<&clock_gcc GCC_QUPV3_WRAP_1_M_AHB_CLK>,

REVISION PAGES
0.1
13 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
13
<&clock_gcc GCC_QUPV3_WRAP_1_S_AHB_CLK>;
pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep";
pinctrl-0 = <&qupv3_se9_2uart_active>;
pinctrl-1 = <&qupv3_se9_2uart_sleep>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 354 0>;
qcom,wrapper-core = <&qupv3_1>;
status = "disabled";
};
Setting pins for qupv3_se9_2uart in
<android-kerne-tree>/kernel/msm-4.9/ arch/arm64/boot/dts/qcom/sdm670-pinctrl.dtsi
&soc {
tlmm: pinctrl@03400000 {
qupv3_se9_2uart_pins: qupv3_se9_2uart_pins {
qupv3_se9_2uart_active: qupv3_se9_2uart_active {
mux {
pins = "gpio4", "gpio5";
function = "qup9";
};
config {
pins = "gpio4", "gpio5";
drive-strength = <2>;
bias-disable;
};
};
qupv3_se9_2uart_sleep: qupv3_se9_2uart_sleep {
mux {
pins = "gpio4", "gpio5";

REVISION PAGES
0.1
14 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
14
function = "gpio";
};
config {
pins = "gpio4", "gpio5";
drive-strength = <2>;
bias-disable;
};
};
};
High-speed UART example in kernel
UART_DM can be configured as a BAM-based UART. This driver is designed for high-speed, large data
transfers such as Bluetooth® communication, or application requiring large data transfer, and requires DMA.
We recommend to use CTS/RTS lines to avoid any data transfer errors between devices.
Creating device tree node
We will use QUPs6 GPIO45, GPIO46, GPIO47, GPIO48 as UART. Declare QUPs6 UART as qupv3_se6_4uart in
<android-source-tree>/kernel/msm-4.9/arch/arm64/boot/dts/qcom/sdm670-qupv3.dtsi
For detailed information, refer to the device tree documentation at
<android-source-tree>/kernel/ msm-4.9/arch/arm64/boot/dts/qcom/sdm670-qupv3.dtsi
The following elements are the minimum requirement:
qupv3_se6_4uart: qcom,qup_uart@0x898000 {
compatible = "qcom,msm-geni-serial-hs", "qcom,msm-geni-uart";
reg = <0x898000 0x4000>;
reg-names = "se_phys";
clock-names = "se-clk", "m-ahb", "s-ahb";
clocks = <&clock_gcc GCC_QUPV3_WRAP0_S6_CLK>,
<&clock_gcc GCC_QUPV3_WRAP_0_M_AHB_CLK>,
<&clock_gcc GCC_QUPV3_WRAP_0_S_AHB_CLK>;
pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep";

REVISION PAGES
0.1
15 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
15
pinctrl-0 = <&qupv3_se6_4uart_active>;
pinctrl-1 = <&qupv3_se6_4uart_sleep>;
interrupts-extended = <&pdc GIC_SPI 607 0>,
<&tlmm 48 0>;
status = "disabled";
qcom,wakeup-byte = <0xFD>;
qcom,wrapper-core = <&qupv3_0>;
};
Setting pins for qupv3_se9_2uart in
<android-kerne-tree>/kernel/msm-4.9/ arch/arm64/boot/dts/qcom/sdm670-pinctrl.dtsi
&soc {
tlmm: pinctrl@03400000 {
qupv3_se6_4uart_pins: qupv3_se6_4uart_pins {
qupv3_se6_4uart_active: qupv3_se6_4uart_active {
mux {
pins = "gpio45", "gpio46", "gpio47",
"gpio48";
function = "qup6";
};
config {
pins = "gpio45", "gpio46", "gpio47",
"gpio48";
drive-strength = <2>;
bias-disable;
};
};
qupv3_se6_4uart_sleep: qupv3_se6_4uart_sleep {
mux {

REVISION PAGES
0.1
16 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
16
pins = "gpio45", "gpio46", "gpio47",
"gpio48";
function = "gpio";
};
config {
pins = "gpio45", "gpio46", "gpio47",
"gpio48";
drive-strength = <2>;
bias-disable;
};
};
};
3.2 QUPs AS I2C EXAMPLE
Supports standard (100 Khz), fast (400 Khz) and Fast+ (1 MHz)
Supports 7-bit device addressing
Maximum length of single transfer is 2^16 – 1
Read / write data is transferred between QUP FIFO and I2C data path
Interrupts are not generated for every i2c/read / write
Uses Tagging mechanism to identify FIFO contents
o Purpose of tag – sends control signal / data to the mini QUP engine
o Length of the tag – 8 bits
o QUP core processes each i2c transaction based on TAG
o Output FIFO is provided with tagged data by software
o For read operations, incoming byte is tagged by QUP and placed in input FIFO

REVISION PAGES
0.1
17 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
17
Figure 3.2-1 I2C Core and TARGET data transfer
The QUP engine provides a general purpose data path engine to support multiple minicores. Each minicore
implements protocol-specific logic. The common FIFO provides a consistent system I/O buffer and system
DMA model across widely varying external interface types, e.g., one pair of FIFO buffers can support SPI and
I2C minicores independently.
The I2C core supports High Speed mode (up to 3.4 MHz). The following key features have been added for
Thundercomm TurboXTM:
BAM integration
Support for I2C tag version 2
Add a new device tree node
File: <android-source-tree>/kernel/msm-4.9/arch/arm64/boot/dts/qcom/sdm670-qupv3.dtsi
For details, see <android-tree>/kernel/ msm-4.9/Documentation/devicetree/bindings/i2c/i2c-msm-v2.txt.
qupv3_se5_i2c: i2c@894000 {
compatible = "qcom,i2c-geni";
reg = <0x894000 0x4000>;
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 606 0>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
clock-names = "se-clk", "m-ahb", "s-ahb";
clocks = <&clock_gcc GCC_QUPV3_WRAP0_S5_CLK>,

REVISION PAGES
0.1
18 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
18
<&clock_gcc GCC_QUPV3_WRAP_0_M_AHB_CLK>,
<&clock_gcc GCC_QUPV3_WRAP_0_S_AHB_CLK>;
dmas = <&gpi_dma0 0 5 3 64 0>,
<&gpi_dma0 1 5 3 64 0>;
dma-names = "tx", "rx";
pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep";
pinctrl-0 = <&qupv3_se5_i2c_active>;
pinctrl-1 = <&qupv3_se5_i2c_sleep>;
qcom,wrapper-core = <&qupv3_0>;
status = "disabled";
};
Setting up pins
For details, refer to
<android-source-tree>/kernel/ msm-4.9/Documentation/devicetree/bindings/pinctrl/qcom,sdm670-pinctrl
File: <android-source-tree>/kernel/msm-4.9/arch/arm/boot/dts/qcom/sdm670-pinctrl.dtsi
Add the following to set up the pins:
&soc {
tlmm: pinctrl@03400000 {
/* SE 5 pin mappings */
qupv3_se5_i2c_pins: qupv3_se5_i2c_pins {
qupv3_se5_i2c_active: qupv3_se5_i2c_active {
mux {
pins = "gpio85", "gpio86";
function = "qup5";
};
config {
pins = "gpio85", "gpio86";
drive-strength = <2>;

REVISION PAGES
0.1
19 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
19
bias-disable;
};
};
qupv3_se5_i2c_sleep: qupv3_se5_i2c_sleep {
mux {
pins = "gpio85", "gpio86";
function = "gpio";
};
config {
pins = "gpio85", "gpio86";
drive-strength = <2>;
bias-pull-up;
};
};
};
};
Registering slave device using device tree
Once the I2C bus is properly verified, you can create a slave device driver and register it with the I2C bus in
<android-source-tree>/kernel/msm-4.9/arch/arm64/boot/dts/qcom/sdm670-mtp.dtsi
&qupv3_se5_i2c {
status = "ok";
himax-ts@48 {
compatible = "tshimax,hxcommon";
reg = <0x48>;
interrupt-parent = <&tlmm>;
interrupts = <5 0x2>;
vdd-supply = <&pm660l_l6>;
avdd-supply = <&pm660_l11>;

REVISION PAGES
0.1
20 of 22 STATE TITLE
Thundercomm TurboXTM 605 GPIO Configure Guide
20
himax,display-coords = <0 720 0 1280>;
himax,panel-coords = <0 720 0 1280>;
himax,rst-gpio = <&tlmm 134 0x00>;
himax,irq-gpio = <&tlmm 5 0x00>;
report_type = <1>;
pinctrl-names = "himax_irq";
pinctrl-0 = <&himax_irq>;
};
};