Signal flow graph
-
Upload
sudhakar-shastri -
Category
Engineering
-
view
64 -
download
7
Transcript of Signal flow graph

SIGNAL FLOW GRAPH
Name: Sudhakar ShastriRegister Number:14MCE1009Submitted to :Prof. Niraj Kumar

Contents
Introduction Basic components Representation of source and load Rules of SFG Construction of SFG Applications

Introduction
SFG is a useful technique for analysis of microwave networks in terms of reflected and transmitted waves.
Signal and Scattering parameters can be described using a graphical technique called Signal Flow Graphs (SFG).

BASIC COMPONETNS
Nodes Branches

REPRESENTATION OF SOURCE AND LOAD
Source representation
Load representation

RULES OF SFG
Series rule
Parallel rule
Recursive rule (self loop)
Node splitting rule

RULE 1:Series Rule
S-parameters for paths in series can be combined into one path by multiplying the s-parameters.
V3=S32S21V1

RULE 2:Parallel Rule
S-parameters for multiple paths connecting the same two nodes can be combined into a single path by adding the s-parameters.
V2=SaV1 + SbV2=V1(Sa + Sb)

RULE 3:Recursion Rule
When a node has a self loop of co-efficient S, the self loop Can be eliminated by multiplying coefficients of the branches feeding that node by 1/(1-S)
V2=S21V1 + S22V2 V3=S32V2
Eliminating V2V3=S32S21V1/1-S22

RULE 4:Node Splitting Rule
A node may be a split into two separate nodes as long as the resulting flow graph contains, once and only once, each combination of separate input and output branches that connect to the original node
V4=S42V2 =S21S42V1

APPLICATIONS
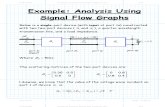
Use signal flow graph to derive expressions for Γin and Γout
For the two port network given below:

CONTD…

CONTD…