Shear Force Full Report
-
Upload
mohd-shafiq -
Category
Documents
-
view
43 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Shear Force Full Report
1
1.0 OBJECTIVE
1.1 Part 1: To plot Shear force influence line.
1.2 Part 2: To verify the use of a shear force influence on a simply supported
beam
INTRODUCTION
Moving loads on beams are common features of design. Many road bridges are constructed from beam, and as such have to be designed to carry a knife edge load, or a string of wheel loads, or a uniformly distributed load, or perhaps the worst combination of all three. The method of solving the problem is to use influence lines.
THEORY
Defination: Shear influence line is defined as a line representing the changes in shear force at a section of a beam when a unit load moves on the beam
Part 1: This Experiment examines how shear force varies at a cut section as a unit load moves from one end to another (see Figure 1). From the diagram, shear force influence line equation can be written. For 0 x a a shear line is given by:
Sy = x/ L (1)
For a x b shear line is given by:
Sy = 1 x L. (2)
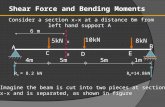
Part 2: If the beam are loaded as shown in Figure 2, the shear force at the cut can be calculated using the influence line. (See diagram 2).
Shear force at cut section = F1 y1 + F2 y2 + F3 y3 (3)
(y1, y2 and y3 are ordinates derived from the influence line in terms of x1, x2, x3, a, b and L)
APPARATUS
Shear Force machine
Weight (Loadings)
Beam
Digital Force Display
Load
PROCEDURES
Part 1
1. Digital Force Display meter reads zero with no load is checking.
2. Hanger with any mass range between 100g to 300g was placed at the first grooved hanger support at the left support and the Digital Force reading recorded in Table 1.
3. The procedure to the next grooved hanger until to the last grooved hanger at the right hand support was repeated.
4. The calculation in Table 1 was completed.
Part 2
1. Three load hangers with 100g. 200g and 300g mass respectively placed at any position between the supports. The positions and the Digital Force Display reading recorded in Table 2.
2. The produce with three other locations was repeated.3. The calculation in Table 2 was completed.
RESULT
Part 1:
Location of load from left hand support (m)Digital Force Display Reading ( N )Shear Force at cut section ( N )Experimental Influence line valueTheoretical Influence lines value
0.040.20.20.102-0.091
0.060.30.30.153-0.136
0.080.40.40.204-0.182
0.100.50.50.255-0.227
0.120.60.60.306-0.273
0.140.70.70.357-0.318
0.160.80.80.408-0.364
0.180.90.90.459-0.409
0.201.01.00.510-0.455
0.221.01.00.510-0.500
0.241.11.10.561-0.545
0.261.21.20.612-0.591
0.34-0.5-0.5-0.2550.227
0.36-0.4-0.4-0.2040.182
0.38-0.3-0.3-0.1530.136
0.40-0.2-0.2-0.0510.091
Part 2:
Position of hanger from left handShear force Digital Reading (N)Theoretical Shear ( Nm )
Locationsupport ( m )
100g200g300g
10.220.240.062.01.962
20.160.080.242.41.581
30.260.040.141.81.156
40.100.240.380.91.000
6.1CALCULATION
Part 1:
1) Experimental Influence line values = Shear Force (N)
Load (N)
Eg. Experimental Influence line values = 0.2 N
= 0.102
200 x 9.81/1000
2) Theoretical Influence lines value; 0.04 x 0.26m
Theoretical value, Sy = -x/L
Eg.Theoretical value, Sy = -0.04/ 0.44
= - 0.091
3) Theoretical Influence lines value; 0.32 x 0.38m
Theoretical value, Sy =1 -x/L
Eg.Theoretical value, Sy = 1 -0.34/ 0.44
= 0.227
Part 2:
Location 1
Y3 Y1 Y2
300g 100g200g
60mm
220mm
140mm
240mm
300mm
a/L
b/L
a/L
=300/440
=0.682
b/L
=140/440
=0.318
y1 / 220=0.682 / 300
y1=0.500
y2 / 240=0.682 / 300
y2=0.546
y3 / 60 =0.682 / 300
y3=0.136
Theoretical Shear = F1y1 + F2y2 + F3y3.
= [(0.1 x 0.5) + (0.2 x 0.546) + (0.3 x 0.136)] x 9.81
=1.962 NmLocation 2
Y2 Y1 Y3
200g 100g300g
80mm
160mm
140mm
240mm
300mm
a/L
b/L
y1 / 160=0.682 / 300
y1=0.248
y2 / 80=0.682 / 300
y2=0.124
y3 / 240=0.682 / 300
y3=0.372
Theoretical Shear = F1y1 + F2y2 + F3y3.
= [(0.1 x 0.248) + (0.2 x 0.124) + (0.3 x 0.372)] x 9.81
=1.581 NmLocation 3
Y2 Y3 Y1
200g 300g100g
40mm
140mm
140mm
260mm
300mm
a/L
b/L
y1 / 200=0.682 / 300
y1=0.403
y2 / 40=0.682 / 300
y2=0.062
y3 / 140=0.682 / 300
y3=0.217
Theoretical Shear = F1y1 + F2y2 + F3y3.
= [(0.1 x 0.403) + (0.2 x 0.062) + (0.3 x 0.217)] x 9.81
=1.156 NmLocation 4
Y1 Y2
Y3
100g 200g
300g100mm
140mm
240mm
60mm
300mm
a/L
b/L
y1 / 100=0.682 / 300
y1=0.155
y2 / 240=0.682 / 300
y2=0.372
y3 / 60=0.682 / 300
y3=0.043
Theoretical Shear = F1y1 + F2y2 + F3y3.
= [(0.1 x 0.155) + (0.2 x 0.372) + (0.3 x 0.043)] x 9.81
=1.008 Nm7.0DISCUSSIONS
Part 1:
1. Derive equation 1 and 2.
Equation 1
Mcut = 0
Fy = 0
(L-x)/L -1 Sy = 0
Sy = -x/L
Equation 2
Mcut = 0
Fy = 0
(L-x)/L Sy = 0
Sy = (L-x)/L
Sy = 1 x/L
2. On the same graph paper, plot the theoretical and experimental values against distance from left hand support.
3. Comment on the shape of graph. What does it tell you about how shear force varies at the cut section as a load moved on the beam?
The experimental result increases with the increasing of the distance of load from the left hand support at the left side of the cut. Based on the result, the values of shear force at cut section (N) increases when a load moves nearer towards the cut.
4. Comment on the experimental result compared to the theoretical result.
Based on the results that we got, shows a totally different result between the theoretical and experimental values. For the experimental influence line value, there are a big different between those experimental and theoretical. Overall, based on the procedure, we followed the right instruction. It might be the error of the machine itself and not in the good condition.
Part 2 :
1. Comment the experimental result and the theoretical result in Table 2.
In this part, we used the load 100g, 200g and 300g. From this experiment, the value for the location 1 to 4, the value for the experimental is bigger than the theoretical value. The value is depend on the location but the value for both results is not so much differences.
8.0CONCLUSION
Part 1 :
From the experiment, we know that the value for the experimental and theoretical values is totally difference. From the graph it shows totally difference result between theoretical and experimental result. Based on the result, the values of shear force at cut section (N) increases when a load moves nearer towards the cut.
Part 2 :
From the experiment, its shows that the location is one of the causes for the differences between the value. We should know that, influence lines can be used to calculate the shear force at the cut section.















![[9] shear force n bending moment](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/553af101550346f92f8b4613/9-shear-force-n-bending-moment.jpg)