SESSION 4: PLANT TISSUES - Mindset...
Transcript of SESSION 4: PLANT TISSUES - Mindset...

Life Sciences Grade 10
www.learnxtra.co.za
Brought to you by Page 1
SESSION 4: PLANT TISSUES KEY CONCEPTS:
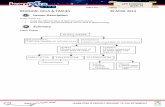
Levels of Organisation
Definition of a tissue
Types of Plant Tissues
Plant Organs - The Leaf TERMINOLOGY: Tissue a group of similar cells adapted for a particular function. XPLANATION TYPES OF PLANT TISSUES:
Meristematic Tissue:
• Cells of meristems divide continuously cells are similar in structure & have thin cellulose cell walls may be spherical, oval, polygonal or rectangular in shape contain few vacuoles
• Found in regions of the plant that grow, mainly at tip of root & stem. According
to their position in the plant, meristems are apical, lateral & intercalary.

Life Sciences Grade 10
www.learnxtra.co.za
Brought to you by Page 2
Simple Permanent Tissue: Epidermis:
• Structure: Transparent, one cell thick and is usually covered with cuticle usually has guard cells with stomata
• Found on the outermost layer of the plant body such as leaves, flowers, stem & roots
• Function is to protect the plant from dessication and infection. Guard cells & cuticle helps to reduce water loss
Parenchyma: • Oval, round or elongated in shape. • Thin cell wall& encloses a dense cytoplasm which contains a small nucleus &
surrounds a large central vacuole. • Intercellular spaces are abundant.
WHERE? • Soft parts of the plant - cortex of roots, ground tissues in stems & mesophyll of
leaves. • Also - pith, medullary rays & packing tissue in xylem & phloem.
WHY? • packing tissue • support to the stem of herbaceous plants water & food storage transport of water
& gases

Life Sciences Grade 10
www.learnxtra.co.za
Brought to you by Page 3
Collenchyma:
• Characterised by the deposition of extra cellulose at the corners of the cells. • Intercellular spaces are generally absent.
WHERE?
• Mainly below the epidermis of dicotyledon stem & petiole.also occur in midribs of dicot leaves.
WHY?
• Provides mechanical support & elasticity. • Allows plant to bend without breaking.

Life Sciences Grade 10
www.learnxtra.co.za
Brought to you by Page 4
Transverse and Longitudinal Section of Collenchyma:
Scelerenchyma:
• Dead cells with no protoplasm. • The walls of cells greatly thickened & lignified. • Due to excessive thickening of the wall of sclerenchyma cells, its cell cavity or
lumen becomes nearly absent. • The cells of are closely packed. • No intercellular spaces.
WHERE?
• Stems, roots, veins of leaves, hard covering of seeds & nuts. • Sclereids form the gritty part of the most of the ripe fruits & contribute
hardness to the seed coat & nutshells. WHY?
• Mainly mechanical & protective in function. • It gives strength, rigidity, flexibility & elasticity to the plant body • Thus, enables it to withstand various strains.

Life Sciences Grade 10
www.learnxtra.co.za
Brought to you by Page 5
Sclereids / Stone Cells:
• Found flesh of fruit like pears. • Also in pips of fruit and shells of nuts
Fibres:
• Make stems & roots tough & rigid Complex Permanent Tissue:
Vascular (Transport)
Tissue:
Xylem
tracheids
vessel elements
Phloem
sieve-tube elements
companion cells

Life Sciences Grade 10
www.learnxtra.co.za
Brought to you by Page 6
Xylem: Composed of cells of four different types:
• Tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma, xylem sclerenchyma. • Except xylem parenchyma, all other xylem elements are dead & bounded by
thick lignified walls. WHERE?
• Vascular bundles of roots, stems and leaves WHY?
• Transport water & minerals salts upward from the root to different parts of shoots.
• Since walls of tracheids, vessels & sclerenchyma of xylem are lignified, they give mechanical strength to the plant body.
Components of Xylem:

Life Sciences Grade 10
www.learnxtra.co.za
Brought to you by Page 7
Vessels Tracheids

Life Sciences Grade 10
www.learnxtra.co.za
Brought to you by Page 8
Phloem:
• Composed of following: 1. Sieve Tubes 2. Companion Cells 3. Phloem Parenchyma 4. Phloem Fibres.
• All phloem cells are living cells, besides fibres. WHERE?
• Vascular bundles of roots, stems and leaves WHY?
• Transport food materials from the leaves to the storage organs & later from storage organs to the growing regions of the plant body
Companion Cells
Sieve - Tube

Life Sciences Grade 10
www.learnxtra.co.za
Brought to you by Page 9
PLANT ORGANS: • Organs:
Consist of a number of tissues that work together to perform a common overall function.
Label the main plant organs:

Life Sciences Grade 10
www.learnxtra.co.za
Brought to you by Page 10
Leaves:
• Leaves - blade or lamina, an edge called the margin of the leaf, the veins
(vascular bundles), a petiole, and two appendages at the base of the petiole called the stipules
Type of Leaves: • Simple - blade not divided into smaller leaflets • Compound - blade divided into smaller leaflets

Life Sciences Grade 10
www.learnxtra.co.za
Brought to you by Page 11
Internal Structure:

Life Sciences Grade 10
www.learnxtra.co.za
Brought to you by Page 12
Guard Cells & Stoma:
Open: Closed:
FUNCTIONS OF LEAVES
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
GASEOUS EXCHANGE
TRANSPIRATION

Life Sciences Grade 10
www.learnxtra.co.za
Brought to you by Page 13
X-AMPLE QUESTIONS: Question 1: Study the following diagram and answer the questions:
1.1 Provide labels for parts labelled A, D, E and G. 1.2 Part labelled C consists of parenchyma tissue. Explain how this tissue is suited
for its functions. 1.3 How do cells labelled B and C differ from ordinary parenchyma tissue? 1.4 Draw a fully labelled diagram to illustrate the structure of part labelled F. 1.5 List TWO functions of the leaf. 1.6 Explain how the leaf is suited to its functions.

Life Sciences Grade 10
www.learnxtra.co.za
Brought to you by Page 14
Question 2: Identify each of the following tissues, provide ONE location, ONE function and ONE structural suitability of each. a)
b)
c)
C