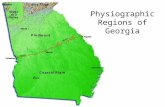
Section 2: Geographic Regions of Georgia -- Appalachian Plateau Region -- Ridge and Valley Region --...
-
Upload
tamsyn-mccoy -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
3
Transcript of Section 2: Geographic Regions of Georgia -- Appalachian Plateau Region -- Ridge and Valley Region --...
Section 2: Geographic Regions Section 2: Geographic Regions of Georgiaof Georgia
-- Appalachian Plateau Region
-- Ridge and Valley Region
-- Blue Ridge Region
-- Piedmont Plateau
-- Coastal Plain Region
-- Okefenokee Swamp
Appalachian Plateau Region• Georgia’s smallest region• TAG corner (Tennessee, Alabama,
Georgia meet)• Many limestone caves, deep canyons,
rock formations• Cumberland Plateau (
Lookout Mountain and Sand Mountain separated by limestone ridges)
• Limestone, shale, and sandstone soils• Chickamauga & Chattanooga National
Military Parks• Cloudland Canyon with waterfalls• Ellison Cave
Ridge and Valley Region• Between Blue Ridge Mountains
and Appalachian Plateau • Low open valleys parallel to
narrow ridges• Elevations ranges from 700 to
1600 feet above sea level• Forests and pastures dominate
the region • Limestone and clay soils in the
valley• Shale and sandstone on the
ridges• Taylor Ridge and Pigeon
Mountain• Textile and carpet industry
(Dalton)
Blue Ridge Region • Northeastern part of state• Contains state’s highest and
largest group of mountains (create barrier to warm moist air from Gulf of Mexico)
• Brasstown Bald, Georgia’s highest mountain
• Mountains provide much precipitation (water) for the state (80 inches)
• Sandy loam and clay soils• Hardwood forests, vegetable
farming, and apples• Amicalolo Falls, Tallulah
Gorge, Helen are here.
Piedmont Plateau • Begins in mountain foothills and
goes to state’s central part• Gently sloping hills in north,
flatlands in the south• Hardwood timber, pine, and
agriculture• Red clay and granite base• Chattahoochee, Flint,
Ocmulgee, and Oconee rivers • Over ½ population live here.• Atlanta, Athens, Madison,
Milledgeville, Stone Mountain
Coastal Plain Region • Largest region, three-fifths of
state• Inner Coastal Plain: Mild
climate, good underground water supply, state’s major agriculture region (Vidalia onion)
• Outer Coastal Plain (southwest corner): naval stores,Okefenokee Swamp, and Barrier islands, rich soil for peanuts, pecans, corn, and pulp production
• Low-lying freshwater wetlands
Okefenokee Swamp• 681 square miles• Located south of Waycross• Largest swamp in North
America• Freshwater wetland• Water lies close to the
surface(2 to 4 feet) • President Franklin
Roosevelt established Okefenokee Wildlife Refuge in 1927 in order to protect swamp
Barrier Islands• Spanish explorers called the
barrier islands “islands of gold”
• Protect beaches by blocking sand, winds, and water that could erode the mainland
• Two-thirds remains wilderness areas
• Much recreation, seafood gathering
• Deep water ports for shipping • St. Simons, Jekyll, and Tybee
Fall Line Features • Separates Piedmont Plateau
and Coastal Plain• Hilly or mountainous lands
meet the coastal plain• Runs from Columbus (west)
through Macon to Augusta (east)
• Many waterfalls caused by water from the hills cutting channels into the softer soil of the plains
• Fall Line waterfalls provide power source for several Georgia communities
Savannah River*boundary between Georgia and
South Carolina.*empties into Atlantic Ocean*has nation’s busiest ports
*hydroelectric dams provide power
*provides drinking water for Savannah, Augusta, and South
Carolina
Chattahoochee River• Flows into Gulf of Mexico and
forms part of border with Alabama
• Goes through Fall Line• Provides hydroelectric power• Provides drinking water for
Georgia, Florida, and Alabama• Flows into Gulf of Mexico and
forms part of border with Alabama
• Provides flood control and recreation
Appalachian Mountain• Southernmost part is the Blue
Ridge Mountain chain• Highest peak in GA is here
(Brasstown Bald is 4,786 feet above sea level).
• Highest and wettest part of GA. (80 inches a year) This rain leads to rivers that provide drinking water for most of GA.
• Brings tourists, kayakers, canoeists, and whitewater rafters
• Crest (top) forms Continental Divide-a line that divides the direction in which rivers drain. Rivers west of divide flow west into Gulf of Mexico. Rivers east of divide flow east into Atlantic Ocean.