Megaelectron volt secondary-ion mass spectrometry - yield ...
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) Bombardment of a sample surface with a primary ion beam ( I p...
-
Upload
quentin-cannon -
Category
Documents
-
view
263 -
download
1
Transcript of Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS) Bombardment of a sample surface with a primary ion beam ( I p...

Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS)Bombardment of a sample surface with a primary ion beam (Ip) followed by mass spectrometry of the emitted secondary ions (Is) constitutes secondary ion mass spectrometry. SIMS is a surface analysis technique used to characterize the surface and sub-surface region of materials and based on m/e ratio measurement of ejected particles under ion bombardment.
Basic Principles
Instrumentation
Mass Resolution
Modes of Analysis
Applications
http://www.eaglabs.com/mc/sims-theory.htmlhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QTjZutbLRu0
Is
IpPrimary ion beam
To mass spectrometer
Depth Profiling
(Trace) element analysis
Imaging and mapping
1 m l l
Solid sample and stable in a vacuum
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-7gSbaslRCU to~0:50 SIMS sputteringhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UDFfEUZJ-Jo

Basic Principles: I. Ion Beam Sputtering
Primary ion beam:Cs+, O2
+, Ar+ and Ga+ at energies ~ a few keV.
sample
Bombarding Ip (sputtering) produces monoatomic and polyatomic particles of sample material and resputtered primary ions, along with electrons and photons. The secondary particles carry negative, positive, and neutral charges and they have kinetic energies ranging from zero to a few hundred eV.
Is
Sputter rates in typical SIMS experiments vary between 0.5 and 5 nm/s. Sputter rates depend on primary beam intensity, sample material, and crystal orientation.
Neutral & charged (+/-) species
Ip
Of ejected particles some are ionized (<10%), these are the secondary ions.Only ions ejected from the surface are employed for analysis.

Al+ from Al2O3 versus Al+ from Al metal
http://www.eaglabs.com/mc/sims-seconday-ion-yields-elemental.html#next
The ion sputtering yield of any considered element varies with the alternation of other components within the specimen surface.


Matrix Effects
Absolute secondary ion yields as a function of atomicnumber, under high vacuum conditions (a) and under oxygen saturation (b): 3keV Ar+, incident angle 60o,
beam density 10-3 A/cm-2 pressure 10-10 Torr.
I = I - ICLEAN


Selection of Primary Ions
Oxygen works as a medium which strips off electrons from the speeding sputtered atoms when they leave surface, while Cesium prefers to load an electron on the sputtered atoms.


Instrumentation
SIMS CAMECA 6F
Ion Sources• Ion sources with electron impact ionization - Duoplasmatron: Ar+, O2
+, O-
• Ion sources with surface ionization - Cs+ ion sources• Ion sources with field emission - Ga+ liquid metal ion sources
Mass Analyzers• Magnetic sector analyzer• Quadrupole mass analyzer• Time of flight analyzer
Ion Detectors• Faraday cup• Dynode electron multiplier
IpIs Ion sources
Ion detectors
Mass analyzers
http://www.eaglabs.com/mc/sims-instrumentation.html
Vacuum < 10−6 torr
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IO-KCjxznLs to~2:00

Basic Overview
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QTjZutbLRu0 at~0:45-1:45

Cameca SIMS

Duoplasmatron ion source
(O2)
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Duoplasmatron

Cs Ion SourceCs ion sources are used to enhance negative ion yield, such as C, O, and S etc. which is based on the surface ionization of vapors on hot surfaces and extraction of ions by an electric field.
In general Cs beams are smaller than those generated by the duoplasmatron and sputter material more effectively due to their greater mass. However, the Cs gun is expensive to operate and is only routinely used for O, S or C isotopic analysis.

Liquid metal ion source (LMIS), operates with metals or metallic alloys, which are liquid at room temperature or slightly above. The liquid metal covers a W tip and emits ions under influence of an intense electric field. The LMIS provides a tightly focused ion beam (<50 nm) with moderate intensity, i.e., high spatial resolution, which is important for mapping chemical elements over the specimen surface.
Liquid Metal Ion Source (Ga or metal alloys)
W

Magnetic Sector Analyzer
High transmission efficiencyHigh mass resolution R 2000Imaging capability
ESA bends lower energy ions more strongly than higher energy ions. The sputtering process produces a range of ion energies. An energy slit can be set to intercept the high energy ions. Sweeping the magnetic field in MA provides the separation of ions according to mass-to-charge ratios in time sequence.
Mass Analyzer (MA)
Magnet Sector
Electrostatic Sector
E
r - radius of curvature of the path of the ion in the B fieldhttp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tOGM2gOHKPc&feature=relmfu http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lxAfw1rftIA
EnergyFocal plane
Degree (r) of deflection of ions by the magnetic filed depends on m/q ratio.
mv2/r = qBv Capable: R ~ 105
at~1:00-4:15



Quadrupole Mass FilterIn a QMS the quadrupole is the component of the instrument responsible for filtering sample ions. It consists of 4 circular rods with a direct current voltage and a superimposed radio-frequency (RF) potential. The A rods are connected and are at the same DC and superimposed RF voltages. The same is true of the B rods but in the opposite DC voltage with respect to the A rods, and RF field is phase shifted by 180o. Ions travel down the quadrupole between the rods. Only ions of a certain mass-to-charge ratio m/z will reach the detector for a given ratio of voltages: other ions have unstable trajectories and will collide with the rods. This permits selection of an ion with a particular m/z or allows the operator to scan for a range of m/z-values by continuously varying the applied voltage.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GSYueQzo2n8&feature=related

Time of Flight (TOF) SIMS - Reflectron
(TOF) SIMS enables the analysis of an unlimited mass range with high sensitivity and quasi-simultaneous detection of all secondary ions collected by the mass spectrometer.
TOF SIMS is based on the fact that ions with the same energy but different masses travel with different velocities. Basically, ions formed by a short ionization event are accelerated by an electrostatic field to a common energy and travel over a drift path to the detector. The lighter ones arrive before the heavier ones and a mass spectrum is recorded. Measuring the flight time for each ion allows the determination of its mass.
Schematic of time of flight (TOF) spectrometer - reflectron
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TsxsVLcAGFY&feature=endscreen&NR=1http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZoAUxsEBUnk
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KAWu6SmvHjc

Ion Detectors
Faraday Cup
Secondary electron Multiplier20 dynodes Current gain 107
A Faraday cup measures the ion current hitting a metal cup, and is sometimes used for high current secondary ion signals. With an electron multiplier an impact of a single ion starts off an electron cascade, resulting in a pulse of 108 electrons which is recorded directly.
Usually it is combined with a fluorescent screen, and signals are recorded either with a CCD-camera or with a fluorescence detector.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k4mKDFPiBj8&list=PL212AE426663B340D at~2:10-3:50
http://www.eaglabs.com/mc/sims-secondary-ion-detectors.html#next


SIMS can do trace element analysis
Detection limit is affected by

1 and 2 Static SIMS
3 Dynamic SIMS




Surface Analysis of Silicon Wafers

Dynamic SIMS involves the use of a much higher energy primary beam (larger amp beam current). It is used to generate sample depth profiles. The higher ion flux eats away at the surface of the sample, burying the beam steadily deeper into the sample and generating secondary ions that characterize the composition at varying depths. The beam typically consists of O2
+ or Cs+ ions and has a diameter of less than 10 μm. The experiment time is typically less than a second. Ion yield changes with time as primary particles build up on the material effecting the ejection and path of secondary ions.
Dynamic Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry

Dynamic SIMS – Depth Profiling
Factors affecting depth resolution
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-7gSbaslRCU&feature=related


Crater Effect
(a)
(b)
(a) Ions sputtered from a selected central area (using a physical aperture or electronic gating) of the crater are passed into the mass spectrometer.
(b) The beam is usually swept over a large area of the sample and signal detected from the central portion of the sweep. This avoids crater edge effects.
The analyzed area is usually required to be at least a factor of 3 3 smaller than the scanned area.

Sample Rotation Effect

Gate Oxide Breakdown
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IO-KCjxznLs&NR=1&feature=endscreen 2:10-2:45

Dynamic SIMS vs Static SIMS

http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IO-KCjxznLs at~2:45-3:18

http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cspfWxnFwiM 3D TOF-SIMS

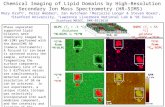
Mapping Chemical Elements
The example (microbeam) images show a pyrite (FeS2) grain from a sample of gold ore with gold located in the rims of the pyrite grains. The image numerical scales and associated colors represent different ranges of secondary ion intensities per pixel.
Some instruments simultaneously produce high mass resolution and high lateral resolution. However, the SIMS analyst must trade high sensitivity for high lateral resolution because focusing the primary beam to smaller diameters also reduces beam intensity. High lateral resolution is required for mapping chemical elements.
34 S197 AU

SIMS can be used to determine the composition of organic and inorganic solids at the outer 5 nm of a sample.
To determine the composition of the sample at varying spatial and depth resolutions depending on the method used. This can generate spatial or depth profiles of elemental or molecular concentrations.
These profiles can be used to generate element specific images of the sample that display the varying concentrations over the area of the sample.
To detect impurities or trace elements, especially in semi-conductors and thin filaments.
Secondary ion images have resolution on the order of 0.5 to 5 μm. Detection limits for trace elements range between 1012 to 1016
atoms/cc. Spatial resolution is determined by primary ion beam widths, which
can be as small as 100 nm.
Summary
SIMS is the most sensitive elemental and isotopic surface microanalysis technique (bulk concentrations of impurities of around 1 part-per-billion). However, very expensive.

Review Questions for SIMS
• What are matrix effects?• What is the difference between ion yield
and sputtering yield?• When are oxygen and cesium ions used as
primary ions?• What is mass resolution?• How can depth resolution be improved?

Next two lectures• AES• XPS
By Prof. Paul Chu