Scramble for Africa Imperialism—the total economic, social, & political control of one territory...
-
Upload
tamara-spruce -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
2
Transcript of Scramble for Africa Imperialism—the total economic, social, & political control of one territory...
Scramble for Africa
Imperialism—the total economic, social, & political control of one territory
by another—often used interchangeably with colonialism
Scramble for Africa
• Prior to 1875 little European interest in Africa– Coastal trading villages & remote outposts– Africa, especially the interior, existed as it
always had• Divided by tribal, ethnic, geographic groups• Geography helped keep Europeans back
Travelers Popularize Africa
• Dr. David Livingstone– Scottish missionary– Spent many years
traveling in places Europeans only dreamed about
– Disappeared and no one heard from him for several years
“Dr. Livingstone I presume.”
• Henry Stanley– NY reporter is sent to
find Livingstone– People are fascinated
by his reports, book becomes a best seller, Africa is popularized
• King Leopold of Belgium– Hires Stanley to set up
a colony in Central Africa
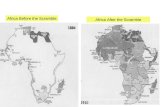
Berlin Conference—1884-1885
• European powers gather to set rules for colonizing– Must communicate where with other
Europeans– Must be able to control
• No Africans present
• Begin carving out territories and setting boundaries
In your notebooks, complete the following statements—
• There were no African rulers present at the Berlin Conference because . . .
• The impact this fact had on the Europeans colonization of Africa was . . .
• http://mappinghistory.uoregon.edu/english/AF/AF01-01.html
Congo Free State(Democratic Republic of the Congo)
worst symbol of European Imperialism• “Free” meaning free trade
– Ivory, rubber, precious metals
• In reality, Leopold set up a brutal colony controlled by force and terror– Leopold never even went there– Small minority of whites dominated blacks in order to
exploit the resources– Belgians monopolized trade– Even other Europeans became critical of the harsh
treatment of the natives
Economic Exploitation
• World wide increase in demand for rubber• Usual high demand for ivory
– Leopold used natives as slaves– Imprisoned and tortured as “incentive” to
produce more– Profit directly to Leopold
• An employee in a British shipping company notices accounting problems
• Campaign begins to end atrocities
Cecil Rhodes—British explorer and businessman, once said: I contend that we [Britons] are the first race in the world, and the more of the world we inhabit, the better it is for the human race.
1.What attitude is expressed in his quote?
1.How do you think people who share this attitude will treat the Africans?
1.Write a caption for the cartoon of Rhodes.
Cecil Rhodes the Social Darwinist
What Africa? All I see is Britain
Africa, you’re welcome
The land of opportunity, for me at least
I’m Cecil and I want Africa
Which slogan best reflects the point of view of Cecil Rhodes?
1. “Embrace African Diversity”
2. “Unite all Africa”
3. “From Constantinople to Cairo”
4. “Imperialism is a Glorious Pursuit”
• Which was a major result of the struggle for Africa by European powers between the 1880’s and WWI?
1. The creation of arbitrary colonial borders
2. The strengthening of local village ties
3. An increase in tribal warfare
4. An increase in the slave trade
African Resistance
• Modern weapons limit success
• Strategic treaties divide rival tribes
• Algerians fight French for 50 years
• Zulu resist Dutch and British
• Menelik defeats Italians– Plays Europeans against each other– Gets modern weapons
Pan Africanism
• 2 world wars and great depression weaken European powers– Can no longer support colonies
• Moral issues of racism & violent suppression also weaken positions
• Leaders educated in the West rise to prominence
• Nationalistic ideas spread to population
Effects of Imperialism
Positive
• Reduced local wars• Improved infrastructure• Improved life, health care,
literacy, water, medicine, education
Negative• undermined traditional tribal
authority• population strains resources• Artificial boundaries
separate tribes, clans, families
• Ethnic tension• Cash crop• Dependent on foreign
markets
Effects of Imperialism
Positive Negative
• Undermined traditional jobs
• European laws and justice systems
• Loss of land• Altered or destroyed
cultures and traditional beliefs
Western Sahara
Sierra Leone
Cote D’Ivorie Dem. Rep. of Congo
South Africa
Rwanda
Somalia
Ethiopia & Eritrea
Sudan
Nigeria
Lasting Effects of Imperialism
• Borders—Nations– Former colonies– No history of democracy– Dictators & corruption– Civil wars– Tribal/ethnic conflict
• Population increases• Resources not evenly
distributed– Geography
– Conflict/wars
• Famine• Little economic
investment in 3rd world nations
• AIDS