Scoliosis (Spine Disorder)
-
Upload
amir-rifaat -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
109 -
download
2
Transcript of Scoliosis (Spine Disorder)
“Scoliosis” comes from Greek word
“skolios” means
crooked.
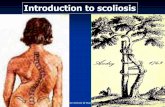
Scoliosis is a deviation of the
spine viewed from coronal or frontal plane, causing a curve, which is
accompanied by abnormal lateral
and rotational curvature (>10o) of
the spine.
10o - 20o of scoliosis is “Mild”
20o - 40o of scoliosis is “Moderate”
> 40o of scoliosis is “Severe”
Scoliosis is a neuro-
muscular condition
influenced by other factors,
although it appears to be a bone condition.
There may be one curve (C-curve) present or two curve (S-curve).
SCOLIOSIS
Congenital scoliosis
• Caused by a bone abnormality present at birth
Neuromuscular or myopathic scoliosis• Result of abnormal
muscles or nerves.• Frequently seen in
people with spina bifida or cerebral palsy or in those with various conditions that are accompanied by, or result in, paralysis.
Degenerative scoliosis
• Result from traumatic (injury or illness) bone collapse, previous major back surgery, or osteoporosis.
• Adult scoliosis that typically occur after age 65
Idiopathic scoliosis• Most common type and no
specific unidentified cause.• There are 4 types of
scoliosis:-• Infantile = affect at birth
and < 3 years old• Juvenile = pre-puberty ( 3
– 9 years old)• Adolescent = puberty to
maturity (10 – 18 years old)
• Adult = after maturity (after age of 18 years old)
CAUSES OF SCOLIOSIS
Classification by anatomic area:
• Cervical curve – apex between C1 and C6• Cervico-thoracic curve - apex between C7 and T1• Thoracic curve - apex between T2 and T11• Thoraco-lumbar curve - apex between T12 and L1• Lumbar curve - apex between L2 and L4• Lumbosacral curve - apex between L5 and S1
SCOLIOSISCC
C-TC
TC
T-LC
LC
LSC
IDIOPATHIC SCOLIOSIS
Infantile scoliosis• Curve may disappear by itself as age increase• Milwaukee brace full time (23 hours)• Surgical correction
Juvenile scoliosis• Milwaukee brace (18-24 months)• With reduction of the curve, time of wearing also reduced from 20 hours to 6 hours
everyday• Surgery
Adolescent scoliosis• Curve under 45 degrees – exercise, bracing, electrical stimulation, manipulation,
biofeedback• Curve over 45-50 degrees - surgical
TREATMENT
44% of bracing attempts are considered failures
Research findings:-• Less than 30 degrees, there were no significant differences between braced and non-
braced patients. Usually, brace is prescribed for scoliosis less than 20 degrees.• 60% felt bracing handicapped their lives• 14% considered bracing left a psychological scar• Bracing significantly decrease lung function, causing respiratory distress (headaches,
anxiety, sleep problem, and cognitive dysfunction)
Facts• Scoliosis braces cause the muscles to weaken or atrophy because not been used• The joints around the spine need movement or other degenerative issues may develop• The brace stress the ribs and often creates a rib hump
SCOLIOSIS BRACING NOT SUPPORTED ?
• To provide rapid pain relief and functional improvement• To create a lifestyle habit for continued improvement and stability• To prevent age and hormone-related declines in bone density and
strength• To stabilize scoliotic curve• Improve fitness, muscle strength and power.• Improve proprioception• Improve range of motion• Improve tolerance for prolonged activities
THE BEST TREAMENT IS EXERCISE
Types of exercises for scoliosis• Symmetrical exercises
• Goals – To strengthen back and abdominal muscles and for functional improvement in ranges of joint motion.
• Breathing exercises• Goals – To increase lung volume and thorax
mobility and flexibility.• Asymmetrical exercises
• Goals – For lengthening muscles on the shortened side, and for contracting muscles on the lengthened side.
• Static exercises body weight (hanging or traction exercises) • Goals – For releasing tension along the spine
THE BEST TREAMENT IS EXERCISE
Consist of a combination of stretching, strengthening, and breathing techniques
Halt curve progression, eliminate pain, and improve posture – for life
Can be done at home and part of daily life
Schroth Therapy Follows a 3-Step Exercise Process:
• 1. First make the proper pelvis position corrections• 2. Do spinal elongation and then rotational angular breathing (RAB) techniques to move
spine and ribs into best possible posture• 3. Tense the trunk muscles isometrically, in order to strengthen weak muscles and
preserve the corrected posture
The goal is to develop the inner muscles of the rib cage in order to change the shape of the upper trunk and to correct any spinal abnormalities.
SCHROTH EXERCISE
Specific exercises are provided based on the curve patterns and severity, as well as the patients function and mobility. The goal is create awareness of the new posture and alignment through position, repetitions and breathing.
Exercises are designed to reduce the flat back and rib prominence and restore alignment of the pelvis.
Schroth program will be based on your individual evaluation.
Treatment sessions are typically 45-55 min long and can range from 5 sessions up to 20 sessions.
SCHROTH EXERCISE
• THE EFFECTIVENESS OF CONSERVATIVE TREATMENTS FOR THE IMPROVEMENT OF SCOLIOSIS CURVES IN AN ADOLESCENT CHILD: A CASE REPORT• Subject: 10 years old female suffer idiopathic scoliosis. Her initial Cobb angles were
measured to be 32° right thoracic curve, with a 19° left lumbar prominence. • Methods: • Initial : Schroth based method of physical therapy - 2 d/w for 6 weeks - 1 hour
duration. Home exercise program (HEP) - 15 min of Schroth based exercises per day, 6 d/w. 23 hours Rosenberger brace.• Phase 2: Decreased frequency – 1d/w for 10 weeks (increased independence in
technique efficiency and accuracy). HEP continued - 15 min/d for 6 d/w. Thoracic Cobb angle improved from 32° to 21°, her lumbar curve remained at 19°• Phase 3: 1d/2 weeks for 20 weeks. Schroth based method postures were progressed
and accessory exercises for core and total body strengthening were further progressed. Thoracic Cobb angle had improved to 17° and her lumbar curvature improved to 15°.
• Conclusion: Schroth based physical therapy method and 23-hour bracing were found to be successful in significantly reducing Cobb angles in this case.
SCOLIOSIS CASE STUDY





















![An introduction to ADOLESCENT SCOLIOSIS - Medacta · Less common forms of adolescent scoliosis[2] are: Congenital Scoliosis: A fairly rare spine abnormality detected at birth Neuromuscular](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/5baaa84309d3f2196d8cf3bc/an-introduction-to-adolescent-scoliosis-medacta-less-common-forms-of-adolescent.jpg)