Sanger Sequencing By D Gnanasingh Arputhadas
-
Upload
gnanasingh-arputhadas -
Category
Health & Medicine
-
view
149 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Sanger Sequencing By D Gnanasingh Arputhadas

DNA Sequencing

DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid )
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a molecule that encodes the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms and many viruses.
DNA is a nucleic acid; alongside proteins and carbohydrates, nucleic acids compose the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life.
Two Strands
Double Helix

DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the precise order of nucleotides within a DNA molecule. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a strand of DNA.
The first DNA sequences were obtained in the early 1970s by academic researchers using laborious methods based on two-dimensional chromatography.

Basic Methods
Maxam-Gilbert sequencing
Chain-termination methods(Sanger sequencing)

Sanger sequencing
Sanger sequencing is a DNA sequencing method in which target DNA is denatured and annealed to an oligonucleotide primer, which is then extended by DNA polymerase using a mixture of deoxynucleotide triphosphates (normal dNTPs) and chain-terminating dideoxynucleotide triphosphates (ddNTPs).

Sanger sequencing
Developed by Frederick Sanger and colleagues in 1977.
It was the most widely used sequencing method for approximately 25 years.

DNA Sequencing (Video)
Video Link : http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6ldtdWjDwes

Sanger Sequencing (Complete Process)
Video Link : http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vK-HlMaitnE




PROCESS

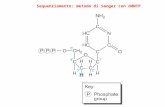
Triphosphates
ATP - Adenosine triphosphateCTP - Cytidine triphosphateTTP - Thiamine triphosphateGTP - Guanosine triphosphate

RESULT
Positive End
Negative End

Need For Sequencing
Evolutionary biologyDNA fingerprintingDetect the presence of known genes for
medical purposes (see genetic testing)Forensic identificationParental testingDetecting mutations

Applications of DNA Sequencing
ForensicsIdentify individualsDetermine the paternity of a childIdentifies endangered and protected species
MedicineDetect genes that are hereditary or cause diseases
AgricultureMap the genome of microorganisms

Future of DNA Sequencing
Projects might focus on researching:The links to develop lifestyleGenomic and cardiovascular diseaseEarly detections of cancer.