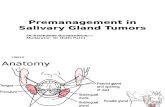
Salivary Gland Tumors Slide Seminar
Transcript of Salivary Gland Tumors Slide Seminar
Case 1 –video 1 attached
A 15 yrs. old young lady
with a parotid mass
https://www.dropbox.com/s/l9tqx9ya6wgmmeq/1.mp4?dl=0
To see video #1, please find the attached video or, click
the below link to open it in the browser:
What is your diagnosis?
• A. Cystadenocarcinoma
• B. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
• C. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
• D. Low grade salivary duct carcinoma
Mucoepidermoid carcinomaIntermediate grade
• 3 cell types
• No myoepithelial cells
• Solid and cystic spaces
• Sialomucin
IHC panel for MEC• CK7 (Strong +)• CK14 (Scattered +)• P63 +( striated ductal phenotype, basal cells origin, Exclude Metastatic RCC)• MUC1, MUC4, MUC5AC +
• Myoepithelial markers-> Negative
• Mucicarmine staining
Prognosis for MEC
Correlate strongly with clinical stageTumor site
Adequacy of surgical procedure
Adjuvant therapy
• Importance of early diagnosis
Tumor size Tumor invasion Vascular/ perineural invasion Surgical margins
Case 2- video 2 attached
A 44 yrs. old woman with a submandibular
masshttps://www.dropbox.com/s/nkpxhabnkjeh2p5/2.mp4?dl=0
To see video #2, please find the attached video or, click
the below link to open it in the browser:
What is your diagnosis?
• A. Salivary duct carcinoma
• B. Adenoid cystic carcinoma
• C. Basal cell adenocarcinoma
• D. Polymorphous adenocarcinoma (PAC)
Sieve-like pattern
of small malignant basaloid cells
2 cell types: luminal and abluminal
3 growth patterns
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
Case 3- video 3 attached
A 55 yrs. old woman with a parotid mass
https://www.dropbox.com/s/73puz6564xbcrqw/3.mp4?dl=0
To see video #3, please find the attached video or, click
the below link to open it in the browser:
What is your diagnosis?
• A. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
• B. Acinic cell carcinoma
• C. Secretory carcinoma
• D. Metastatic thyroid carcinoma
• Well-differentiated ACC associated with lymphoid stromaMicrocystic growth pattern + dense lymphoid stroma
Low Ki-67 labelling index
Thin pseudocapsule
• High grade transformation (dedifferentiation) Conventional low-grade ACC + high grade ACC
High Ki-67 labelling
ACC diagnosis and treatmentDOG1 staining for ACC diagnosis (acinar differentiation) MUC3 positive in ACC ( not in MEC, ADCC)Always negative for P63 ( MEC is always +)
• Histological grade is stronger predictor of survival than TNM stage.• Surgical resection -> excellent results• Best survival rate of all salivary gland carcinomas
Immunohistochemistry
Plays a limited, even though important rolein diagnosing salivary gland tumors
Assist the final diagnosis! CK7+/CK20-