Sa Economics
-
Upload
alvaro-mamani-machaca -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of Sa Economics
-
8/22/2019 Sa Economics
1/3
ECONOMICS www.stir.ac.uk/management/about/economics/
Overseas Advisor: Dr Robin Ruffell
Email: [email protected]
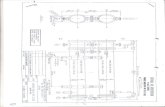
Code Title Availability Prerequisite SCQF
Credit
SCQF
Level
ECN111 Introductory
Microeconomics
Autumn Basic high school
maths
22 8
The economic problem of scarcity; the concept of opportunity cost; the production possibility frontier; how
prices are determined by supply and demand; the concept of market equilibrium; the causes and effects of
changes in supply and demand; the elasticities of supply and demand; government intervention in markets;
the different categories of costs; the short-run pricing and output decisions of firms in perfect competition,
monopolistic competition and monopoly; labour markets and the reasons why wage rates vary for different
types of occupation; the distribution of income; the theory of comparative advantage.
*This is a first year module. Please note that students can only register for one of these modules as part oftheir overall courseload each semester.
ECN211 IntermediateMicroeconomics
Autumn ECN111 22 8
The assumptions of consumer choice theory relating to preferences and constraints on choice; derivation of
the main results about demand; the application of consumer choice theory to payments in kind, subsidies
and lump-sum benefits; consumer welfare measures of welfare and cost-benefit analysis; labour supply;
capital supply; the theory of costs and production; the long-run theory of perfect competition, monopolistic
competition and monopoly; the behaviour of oligopolistic markets.
ECN212 Intermediate
Macroeconomics
Spring ECN112 22 9
Stylized macroeconomic facts and how they relate to theory and policy; income and wealth accounting;
aggregate data analysis trends versus cycles; historical evolution of macroeconomic theory; the classical
approach to aggregate demand and supply; the determinants of savings and investment; new-Keynesian
theory of aggregate supply; the IS-LM model of income and interest rate determination; efficiency versus
sticky wages and unemployment; the trade off between inflation and unemployment; demand and supply of
money; static macroeconomic policy analysis.
ECN213 Introduction to Quantitative
Techniques for Economics
Spring ECN112 AND ECN 211 22 9
The mathematical treatment of the economic problem of optimisation subject to a constraint - elementary
algebra; the concept of a derivative and a partial derivative; rules for calculating derivatives; simple
optimisation and constrained optimisation; the economic application of the mathematical techniques
covered. The econometric estimation of a relationship between two economic variables - the principles and
difficulties of collecting data by sample surveys; methods of summarising and representing data, including
frequency distributions, measures of location and dispersion and index numbers; the basic concepts of
probability theory; the key concepts of statistical inference - point estimation, interval estimation andhypothesis testing; the method of least squares; the economic application of the statistical techniques
covered.
ECN311 Advanced Microeconomics Autumn ECN211 22 10
Choice and rationality; individual welfare changes; the pure exchange model; trading at false prices; Pareto
optimality; social welfare functions and compensation tests; market failure, property rights and public goods;expected utility and the insurance market; games and oligopoly; adverse selection, moral hazard and
principal-agent theory.
-
8/22/2019 Sa Economics
2/3
ECN313 Using Economic Data Autumn ECN213 22 10
Extension of the method of least squares introduced in ECN213 to handle estimation of relationships
between many variables. the problems of econometric estimation, their causes, diagnosis and solutions. the
use of computers for least-squares estimation. The second half will develop skills in two sorts of work: the
critical appraisal of applied econometric results and original applied work involving formulation of an
economic model, data gathering and statistical estimation.
ECN 414 Economic Policy in Britain
and Europe
Autumn ECN311 AND ECN 312 22 10
This module uses the theory discussed in Advanced Microeconomics and Advanced Macroeconomics to
examine major topical policy issues: the current state of the British economy; fiscal and monetary issues of
current concern in the UK, including pension funding and inflation targeting; problems associated with
unemployment in the UK and Europe and policy objectives in the fields of employment, unemployment and
part-time employment; major economic issues of the European Community agriculture, fiscal criteria,
monetary union, central bank independence; the relationship between the UK and the European Monetary
Union.
ECN3BK Domestic and InternationalBanking Autumn ECN212 22 10
The core principles of money and the financial system; the role of financial institutions, financial instruments
and financial markets; risk, return and diversification; the capital asset pricing model; the interest rate and its
determinants; the interest rate and its determinants; the main economi c fundamental of banks activities; on-
balance-sheet and off-balance-sheet activities of banks; demand for money; the supply of money; central
banking: monetary policy instruments; inflation targeting; central bank independence and accountability; issues
in banking: after the crisis.
ECN3EE Energy Economics Autumn ECN211 22 10
This module examines the function of the major markets for energy: oil, coal, natural gas, electric power, and
alternative/renewable energy in a national and international context. It discusses the technologic structure and
parameters of energy supply and use; the principal drivers of supply and demand for energy; basic econometricforecasting of supply or demand for energy; the environmental issues related to energy use and consumption.
ECN3AX Applied Economics I Autumn ECN 211 AND ECN212 22 10
This module will cover a selection of topical issues in applied economics.
ECN3BN Modern Banking Spring ECN212 AND ECN311 22 10
An introduction to modern banking theory and practice from a predominantly microeconomic perspective,
including structure, performance, risks, technology and regulation.
ECN3BP Behavioural Economics and
Public Policy
Spring ECN211 22 10
The overall aim is to provide an overview of the key areas of intersection between economics and psychology.
This area is an exciting field with increasing academic prominence and real-world applications. Students will be
introduced to core areas of economics and psychology such as judgment, rational choice, intertemporal decision
making and emotion-based decision making. The module will also cover emerging areas of economics and
psychology such as neuroeconomics which seeks to examine the biological foundations of economic decision
making.
ECN3IN Industrial Economics Spring ECN311 22 10
-
8/22/2019 Sa Economics
3/3
The structure-conduct-performance model of economic performance; the relevance of non-co-operative game
theory to oligopoly pricing behaviour; the relationships between concentration, mergers, potential competition,
dynamic competition and technical change, entry barriers and strategic deterrence; the economics of marketing
strategies including search theory, optimal advertising, the market for lemons and quality signalling games and
pricing tactics; the economics of global competition and e-commerce.