REVOLUTIONS AND ENLIGHTENMENT WORLD HISTORY MR. ALLEN.
-
Upload
samantha-perry -
Category
Documents
-
view
229 -
download
2
Transcript of REVOLUTIONS AND ENLIGHTENMENT WORLD HISTORY MR. ALLEN.
REVOLUTIONS REVOLUTIONS AND AND
ENLIGHTENMENTENLIGHTENMENTWORLD HISTORYWORLD HISTORY
MR. ALLENMR. ALLEN
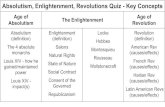
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONSESSENTIAL QUESTIONS FOR FOR UNITS 1 AND 2 –DEVELOPMENT UNITS 1 AND 2 –DEVELOPMENT
OF MODERN POLITICAL OF MODERN POLITICAL THOUGHTTHOUGHT
1) Why do people form societies?1) Why do people form societies? 2) What is more important, the good of the 2) What is more important, the good of the
individual or the good of society?individual or the good of society? 3) Should people be able to choose who 3) Should people be able to choose who
governs them?governs them? 4) What type of government would be best 4) What type of government would be best
for you?for you? 5) Is religion a force for good in society? 5) Is religion a force for good in society?
(We will revisit) –Enlightenment/Jesus(We will revisit) –Enlightenment/Jesus
THE REVOLUTIONSTHE REVOLUTIONS
3 Great political events at the end of the 3 Great political events at the end of the 1717thth and 18 and 18thth centuries centuries
Glorious Revolution-King held accountable Glorious Revolution-King held accountable to the people’s representative body to the people’s representative body (Constitutional Monarchy)(Constitutional Monarchy)
American Revolution - “No taxation American Revolution - “No taxation without…”without…”
French Revolution – Anarchy to French Revolution – Anarchy to DictatorshipDictatorship
Louis XIV bankrupted Louis XIV bankrupted France!!!France!!!
King Louis King Louis XIVXIV of of
France (r. 1643- France (r. 1643- 1715 1715
““The Sun King”The Sun King”
DIVINE RIGHT OF DIVINE RIGHT OF KINGSKINGS
Monarchs did not consider Monarchs did not consider themselves accountable to their themselves accountable to their citizens, but only to godcitizens, but only to god
““I am the State”I am the State”
-Louis XIV-Louis XIV
Palace of VersaillesPalace of Versailles
Built 1671-1682 byBuilt 1671-1682 byKing Louis XIVKing Louis XIV
Shows how out of touch and Shows how out of touch and insincere King Louis XIV was insincere King Louis XIV was towards his subjectstowards his subjects
Magna Carta 1215 – The Magna Carta 1215 – The King’s power is not King’s power is not
absolute!absolute! King King John IJohn I fought costly unsuccessful wars fought costly unsuccessful wars
with France and these wars led to raised taxes with France and these wars led to raised taxes in Englandin England
Angry English nobles rebelled and forced John Angry English nobles rebelled and forced John to recognize their political and civil rightsto recognize their political and civil rights
The Magna Carta recognized right to trial and The Magna Carta recognized right to trial and no taxation without consentno taxation without consent
England’s legislative branch.Elected law makers who discussAnd vote on potential laws; work
with the King.
Glorious Revolution 1689-Glorious Revolution 1689-Battle Battle over which institution over which institution
would dominate Englandwould dominate England
● ● English did not want a Catholic king. English lords English did not want a Catholic king. English lords invited William of Orange to take throne without invited William of Orange to take throne without bloodshedbloodshed
1689 Parliament crowns 1689 Parliament crowns William and MaryWilliam and Mary co-rulers co-rulers of England of England
● ● Turning point in England’s history: Turning point in England’s history:
● ● Proves that power is now in Proves that power is now in
the hands of Parliamentthe hands of Parliament, ,
not the king!not the king!
Constitutional MonarchyConstitutional Monarchy● ● England was now a England was now a Constitutional MonarchyConstitutional Monarchy: a kingdom : a kingdom
with awith a
constitution to check the powers of the king and protect the constitution to check the powers of the king and protect the rights ofrights of
the citizensthe citizens
ENGLISH BILL OF RIGHTS STATED:
No royal interference with parliament
Freedom of speech
John LockeJohn Locke 1632-17041632-1704 British PhilosopherBritish Philosopher
Believed all people wereBelieved all people were
born with 3 natural rightsborn with 3 natural rights
((Life, Liberty, PropertyLife, Liberty, Property))
John LockeJohn Locke
In the State of nature people could not In the State of nature people could not protect their rights well.protect their rights well.
Humans agreed to a Humans agreed to a Social ContractSocial Contract where government would protect the where government would protect the rights of the people, and the people would rights of the people, and the people would act reasonably toward the government. act reasonably toward the government.
If government broke these agreement, the If government broke these agreement, the people could rebelpeople could rebel
The Age of Enlightenment The Age of Enlightenment 1700s-1800s1700s-1800s
"New opinions are always "New opinions are always suspected, and usually opposed, suspected, and usually opposed,
without any other reason but without any other reason but because they are not already because they are not already
common.“common.“-Locke -Locke
The Age of EnlightenmentThe Age of Enlightenment The EnlightenmentThe Enlightenment, a philosophical movement , a philosophical movement
beginning in France that advocated beginning in France that advocated ReasonReason and and logiclogic as the basis of authority and all decisions as the basis of authority and all decisions and using reason and logic to solve social and using reason and logic to solve social problemsproblems
THE ENLIGHTENMENTTHE ENLIGHTENMENT
Centered in Paris, in salons, drawing Centered in Paris, in salons, drawing rooms of the wealthiest urban classes.rooms of the wealthiest urban classes.
Guests gathered to discuss ideas-Coffee Guests gathered to discuss ideas-Coffee replaces beer as the daytime drink of replaces beer as the daytime drink of choice. Growth of readingchoice. Growth of reading
Philosophies wanted to be like Isaac Philosophies wanted to be like Isaac Newton, who’s discoveries in math and Newton, who’s discoveries in math and astronomy suggested natural lawsastronomy suggested natural laws
Voltaire Voltaire 1694-17781694-1778 French PhilosopherFrench Philosopher Was opposed to Was opposed to
organized religions organized religions criticizing other criticizing other faiths and faiths and practitionerspractitioners
Did believe in Did believe in freedom of religionfreedom of religion
Staunch supporter Staunch supporter
of individual of individual
liberties, after his liberties, after his exile to Englandexile to England
VoltaireVoltaire Staunch supporter of right to a fair trialStaunch supporter of right to a fair trial
Heavily influencedHeavily influenced
leaders of the Frenchleaders of the French
RevolutionRevolution
Was opposed to censorship: "I disapprove of what you say, but I Was opposed to censorship: "I disapprove of what you say, but I will defend, to the death, your right to say it." will defend, to the death, your right to say it."
Baron MontesquieuBaron Montesquieu 1689-17551689-1755 French PhilosopherFrench Philosopher Believed government’s Believed government’s
power needs to be power needs to be checkedchecked
Baron MontesquieuBaron Montesquieu Separation of PowersSeparation of Powers Believed power in government Believed power in government
had to be divided amongst had to be divided amongst different branchesdifferent branches
Believed checks and balances Believed checks and balances are necessary to keep one are necessary to keep one branch from becoming too branch from becoming too powerfulpowerful
Believed the people needed Believed the people needed safeguards from government safeguards from government becoming too powerfulbecoming too powerful
Heavily influenced America’s Heavily influenced America’s founding fathers 1770’s-1780’founding fathers 1770’s-1780’
Thomas HobbesThomas Hobbes Believed human Believed human
beings were beings were naturally wickednaturally wicked
Believed human beings Believed human beings could not be trusted to could not be trusted to make decisions to benefit make decisions to benefit all, only to benefit all, only to benefit themselvesthemselves
Believed an absolute monarch Believed an absolute monarch was necessary to protect was necessary to protect human beings from each human beings from each other (Humans not capable of other (Humans not capable of self rule)self rule)
Hobbes: Hobbes: Leviathan Leviathan and Social and Social ContractContract
Argued that the only way to Argued that the only way to avoid war, chaos, disarray avoid war, chaos, disarray was a strong central rulerwas a strong central ruler
Argued that the people Argued that the people and the leader had a and the leader had a Social ContractSocial Contract
Hobbes’ Social ContractHobbes’ Social Contract: : people give up their rights to an people give up their rights to an absolute ruler in exchange for absolute ruler in exchange for protection, law, and order. People protection, law, and order. People do notdo not have the right to rebel have the right to rebel
Wrote Wrote LeviathanLeviathan 16511651
TURN TO A PARTNERTURN TO A PARTNER
Hobbes believed human beings were Hobbes believed human beings were self interested and could not make self interested and could not make decisions to benefit society. decisions to benefit society. Therefore, we need an absolute Therefore, we need an absolute ruler.ruler.
Do you agree?Do you agree?
Jean Jacque RousseauJean Jacque Rousseau
Believed in EducationBelieved in Education
Wrote that an Wrote that an informed society could informed society could make good decisionsmake good decisions
Blamed societies' evil Blamed societies' evil on the uneven on the uneven distribution of distribution of property in the worldproperty in the world
THE SOCIAL CONTRACTTHE SOCIAL CONTRACT Built on Locke’s Social contract-Man Built on Locke’s Social contract-Man
adopted laws to preserve their property. In adopted laws to preserve their property. In doing so they become enslaved by doing so they become enslaved by government and tricked by the wealthy.government and tricked by the wealthy.
People should not be able to follow their People should not be able to follow their own self interests, and society should be own self interests, and society should be governed by the general will (Majority will)governed by the general will (Majority will)
The General will is always right, so citizens The General will is always right, so citizens should be forced to obey.should be forced to obey.
Rousseau’s Social ContractRousseau’s Social Contract The Social ContractThe Social Contract: :
published 1762published 1762 Believed that the people Believed that the people
are the source of are the source of government powersgovernment powers
Believed government’s Believed government’s job was to help people be job was to help people be happy and needs cared happy and needs cared forfor
Believed if government did Believed if government did not do its job people had not do its job people had the right to remove leaders, the right to remove leaders, rebelrebel
Mary WollstonecraftMary Wollstonecraft Argued that society Argued that society
trains women to be trains women to be weak and more weak and more concerned with their concerned with their superficial looks than superficial looks than contributions to societycontributions to society
Argued that women Argued that women should receive the same should receive the same type and quality of type and quality of education as meneducation as men
Argued it was a problem that Argued it was a problem that men were so comfortable with men were so comfortable with treating women as inferiorstreating women as inferiors
Mary WollstonecraftMary Wollstonecraft Argued that society Argued that society
trains women to be trains women to be weak and more weak and more concerned with their concerned with their superficial looks than superficial looks than contributions to societycontributions to society
Argued that women Argued that women should receive the same should receive the same type and quality of type and quality of education as meneducation as men
Argued it was a problem that Argued it was a problem that men were so comfortable with men were so comfortable with treating women as inferiorstreating women as inferiors