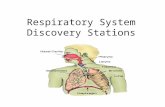
Respiratory System. Functions of the Respiratory System 1.Pulmonary ventilation – movement of...
-
Upload
abraham-mccarthy -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Respiratory System. Functions of the Respiratory System 1.Pulmonary ventilation – movement of...

Respiratory System

Functions of the Respiratory System
1. Pulmonary ventilation – movement of gases into/out of lungs for exchange
2. Gas conditioning3. Sound production4. Olfaction5. Defense

Divisions of the Respiratory System
• Structurally divided into: upper and lower respiratory tracts
• Functionally divided into:– Conducting portion– Respiratory portions

Upper Respiratory Tract1. Nose and nasal cavities– Nasal conchae – condition air
2. Paranasal sinuses3. Pharynx– Nasopharynx contains:• Opening of eustachian tube• Pharyngeal tonsil
– Oropharynx contains:• Palatine tonsils• Lingual tonsils
– Laryngopharynx• All are part of conducting
portion

Lower Respiratory Tract
• Conducting portion– Larynx– Trachea– Bronchi– Bronchioles
• Respiratory portion– Respiratory bronchioles– Alveolar ducts– Alveoli

Larynx• Connects pharynx to trachea• Three major cartilages:– Thyroid cartilage – Cricoid cartilage– Epiglottis• Covers opening to airway when swallowing

Larynx• Arytenoid cartilages - important in sound
production

Sound Production• vocal ligaments – covered by mucous membrane– Ligaments + membrane = vocal folds (“true”
vocal cords)• vestibular ligaments– Vestibular folds (“false” vocal cords)
• Opening between vocal folds - rima glottidis– vocal folds + rima glottidis = glottis
• Air forced thru rima glottidis vibration of vocal folds sound– Muscles pivot arytenoid cartilages – abduct or
adduct folds• Vocal folds in action

Trachea• Supported by C-shaped tracheal
cartilages– Keep airway open– Posteriorly, connected by trachealis
muscle• Lined with PSCC and goblet cells
trachealis

Bronchial Tree• primary bronchi
secondary bronchi tertiary bronchi– All bronchi lined with
PSCC– Rings of cartilage get
smaller and smaller• Bronchi bronchioles– < 1 mm diameter– No cartilage– Lining simple ciliated
columnar cuboidal

Bronchioles• Walls composed of relatively thick layer
of smooth muscle– Allows for bronchoconstriction/dilation
• Bronchioles terminal bronchioles – last part of conducting portion
• Terminal bronchioles respiratory bronchioles alveolar ducts alveoli– Primary location of gas exchange between
blood and air– Surface area of each lung is approx. half a
tennis court

Alveoli1. Alveolar type I cells –
simple squamous ET– rapid diffusion of gases
2. Alveolar type II cells– produce pulmonary
surfactant • decreases surface tension w/in
alveolus • prevents collapse of alveoli

Alveolar Macrophages
• Third type of cell, alveolar macrophage (dust cell)– engulfs microorganisms or particulate matter

Lungs and Pleura• Lungs located in pleural cavities• serous membrane called pleura– Visceral pleura – Parietal pleura

Left Lung
• Slightly smaller than right lung – b/c of heart– cardiac notch
• Oblique fissure divides lung into superior and inferior lobes

Right Lung
• oblique and horizontal fissures – divide lung into superior,
middle and inferior lobes

Thoracic Wall Dimensional Changes During Respiration
1. Vertical – movement of diaphragm
2. Lateral – muscles attached to ribs3. Anterior/Posterior – muscles
attached to ribs• Expansion of cavity inhalation• Compression of cavity
exhalation

Muscles Attached to Ribs
• Muscles attached to ribs:1. Scalenes (inhalation)• Elevate ribs 1 &2
2. External intercostal (inhalation)• Elevate ribs
3. Internal intercostal (forced exhalation)• Depress ribs

Respiratory Control Centersin the Brainstem
• Respiratory rhythmicity center in medulla oblongata– controls rate and depth of
breathing– Dorsal respiratory group
(DRG)• stimulates muscles of
inspiration– Ventral respiratory group
(VRG)• controls forced exhalation
– Inactive during normal breathing

• Read about asthma, smoking, emphysema, and lung cancer