Anatomy and Physiology Respiratory System [Tab 2] Respiratory System.
Respiratory System
description
Transcript of Respiratory System

Respiratory System

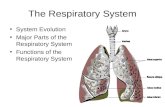
Structures & Functions• The organs of the respiratory system include–Nose–Pharynx–Larynx–Trachea–Bronchi–Lungs
• Accessory organs –Diaphragm–Thorax

Structures & Functions• The process of respiration involves the
inspiration of air that contains O2 for use by the cells of the body and the expiration of CO2, which is a waste product from the cells of the body.
• The respiratory system relies on the circulatory system to complete the respiratory cycle.

Structures & Functions•O2 is inhaled into the lungs and
transported by the blood.
•The blood then transports waste products back to the lungs to be exhaled.

Nose•Naso or rhino mean nose•Acts as an entrance for air and exit for
CO2.•Mucous membrane lines the nose.
▫Acts as a filter for dust and other foreign matter
•The nose also warms and moistens the entering air.
•Contains olfactory receptors.•Bloodhound

Nose•The nostrils are paired external openings
to the airways.▫Very in pliability and expandability
Horse – expandable nostrils Pig – rigid nostrils


Importance of Concha• Responsible for bringing air temperature
to an acceptable level.• Bulldog

Pharynx• AKA the throat• The upper portion of the pharynx is attached to
the base ok the skull and the lower portion unites with the esophagus.
• Divided into three parts–Nasopharynx• Opening into the back of nasal chambers
– Oropharynx• Opening into the back of the mouth
– Laryngopharynx• Opening into the larynx and esophagus

Pharynx•The pharynx is used by both the
respiratory and the digestive tracts as a passageway for air and food
•Depending on the species, it may also have a role in vocalization.

Larynx•The larynx is commonly called the voice
box and is located just below the pharynx. (Adams apple)
•Firm cartilage structure at the opening to major airways.
▫Epiglottis a lid like cartilage structure that prevents
food from entering the airway during swallowing
Main sound organ in mammals

Larynx•The larynx contains the vocal folds
•Opening between the vocal folds is the glottis.

Trachea•Series of cartilage rings joined by
connective tissues.▫Rings are C shaped, not complete circles
Why?
•Supports a rigid airway, allows for movement.

Trachea•Lined with epithelium containing cilia.
▫Particles that get past the nasal membranes are caught in the cilia.
▫Worked toward pharynx where it is swallowed.

Trachea•Trachea branches into 2 bronchi.
▫Right and left lung•Trachea
▫Bronchus Bronchioles
Alveolar Sacs▫Aveoli

RESPIRATORY RATES OF VARIOUS ANIMALS HORSE: 10-14 BPM MEAN 12
DAIRY COW: 26-35 BPM MEAN 29
PIG: 32-58 BPM MEAN 40
DOG: 18-34 BPM MEAN 24
CAT: 20-40 BPM MEAN 31
SHEEP: 20-34 BPM MEAN 25
![Anatomy and Physiology Respiratory System [Tab 2] Respiratory System.](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/56649ebd5503460f94bc631f/anatomy-and-physiology-respiratory-system-tab-2-respiratory-system.jpg)