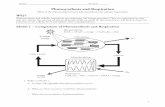
Respiration & photosynthesis
-
Upload
wja10255 -
Category
Technology
-
view
903 -
download
4
description
Transcript of Respiration & photosynthesis

Energy Energy Transformations: Transformations: Photosynthesis & Photosynthesis & RespirationRespiration

Read pages 218-220Read pages 218-220
1.1. What is energy?What is energy?
2.2. List 2 processes (in the cell) that require List 2 processes (in the cell) that require energy (the ability to do work).energy (the ability to do work).
3.3. What is the difference between an What is the difference between an autotroph and a chemotroph?autotroph and a chemotroph?
4.4. What is metabolism?What is metabolism?

ATP & ADPATP & ADPATP: Adenosine triphosphateATP: Adenosine triphosphate adenine + ribose + 3 phosphatesadenine + ribose + 3 phosphates Energy storing molecule, only stores energy for a Energy storing molecule, only stores energy for a
few minutesfew minutes Source of all cell energySource of all cell energy When one phosphate group breaks off, energy is When one phosphate group breaks off, energy is
releasedreleased
Adenine
Ribose
3 Phosphate groups

ADP: Adenosine diphosphate
Adenine + ribose + 2 phosphates
Molecule that results from ATP losing one P
Another P may be added later
ADP ATP
Energy
Energy
Partiallychargedbattery
Fullychargedbattery
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) + Phosphate Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)

Describe organelles Describe organelles involved in energy involved in energy transformationtransformation Energy transformation is when Energy transformation is when
energy is converted from one energy is converted from one form to another.form to another.
Energy transformations involve Energy transformations involve photosynthesis and respiration.photosynthesis and respiration.

PhotosynthesisPhotosynthesis

• CHLOROPLASTS:
•Found in plant cells, some protists & bacteria not animal cells
•Contain pigment called chlorophyll (green)
•Allows plants to go through photosynthesis by converting light into energy for the cell

Overview PhotosynthesisOverview Photosynthesis Photosynthesis:Photosynthesis: process process
using energy from sunlight using energy from sunlight to convert water and COto convert water and CO2 2
into oxygen and into oxygen and carbohydrates (sugar)carbohydrates (sugar)
Two parts:Two parts: Light dependent reactions: Light dependent reactions:
produce Oproduce O2 2 & converts ADP & converts ADP
to ATPto ATP Calvin cycle (dark Calvin cycle (dark
reactions): use ATP from reactions): use ATP from light reactions to produce light reactions to produce sugarssugars
Light Energy
CO2 + H2O Sugars + O2
Chloroplast

Chlorophyll: green pigment in cells that absorbs blue & red light energy
Moves energy to electrons that drive reactions
Equation for photosynthesis:
6CO2 +6H2O + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2

• MITOCHONDRIA: “powerhouse” of cell
•Releases energy from food molecules
•Found in both animal and plant cells
•A cell that needs more energy has more mitochondria
•Ex: muscles, growing cells, areas of repair

Overview cellular Overview cellular respirationrespiration
Respiration:Respiration: process that releases energy by process that releases energy by breaking down food when oxygen is presentbreaking down food when oxygen is present
Equation for Respiration:Equation for Respiration:
CC66HH1212OO66 + 6O + 6O22 6CO 6CO22 + 6H + 6H22O + energyO + energy

Anaerobic respiration: (fermentation) occurs without oxygen present
Two types:
Alcoholic: form ethyl alcohol and CO2 as waste products; used to make bread rise
Lactic acid: produces lactic acid in muscles when exercising without enough oxygen

PhotosynthesisPhotosynthesis RespirationRespiration
FunctionFunction Energy storageEnergy storage Energy releaseEnergy release
LocationLocation ChloroplastsChloroplasts MitochondriaMitochondria
ReactantsReactants Carbon dioxideCarbon dioxide
waterwater
GlucoseGlucose
oxygenoxygen
ProductsProducts GlucoseGlucose
oxygenoxygen
Carbon dioxideCarbon dioxide
waterwater
EquationEquation 6CO2 +6H2O + energy C6H12O6 + 6O2
C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 +6H2O + energy