repaso de ciencia .docx
-
Upload
maria-isabel-blanco -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of repaso de ciencia .docx

7/23/2019 repaso de ciencia .docx
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/repaso-de-ciencia-docx 1/10
ELEMENTS, COMPUNDS AND MIXTURES
• Element- is a pure substance that cannot be separated intosimpler substances by physical or chemical means.
o To ID the elements you need characteristic propertieso An ELEMENT is a PURE SUSTAN!E because it contains
only one type o" particle.• Pure Substance# a substance in $hich there is only one type o"
particle.o Simplest particles. o Elements are made o" particles called atoms.
Characterstc Pr!"ertes
# Use t! ID matter
# Can be "h#scal !r chemcal
# Am!unt !$ matter %!es n!t chan&e the characterstc"r!"ert#
# A set !$ characterstc s nee%e% t! %ent$#, n!t !nl# !ne
PROPERTIES O' ELEMENTS
• Each element can be identi%ed by its uni&ue set o" properties. Anelement may share a property $ith another element' but otherproperties can help you tell the elements apart.
• Usin( their physical properties and their chemical properties canidenti"y elements.
CLASSI'(IN) ELEMENTS *( T+EIR PROPERTIES
# !ate(ories o" Elements) Three ma*or cate(ories are)• Cate&!res Are Smlar *# +no$in( the cate(ory to $hich an
un"amiliar element belon(s' you can predict some o" itsproperties.
• Each element has a uni&ue set o" physical and chemicalproperties.
Metals Metall!%s N!n Metal
Shiny !an be shiny or not Dull ,not shiny-
ood conductors o"Ener(y ,heat andelectricity currents-
Semiconductor Poor conductors o"ener(y
Malleable ,sheets- !an be malleable Not malleableDuctile ,$ire- !an be ductile Not ductile
!an be brittle rittleE/) cooper' tin' lead E/) boron' silicon' E/) neon' sul"ur'

7/23/2019 repaso de ciencia .docx
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/repaso-de-ciencia-docx 2/10
antimony iodine
COMPOUNDS MADE O' ELEMENTS
# C!m"!un%s- pure substance composed o" t$o or moreelements that are chemically combined. A particle o" acompound is a molecule. Molecules o" compounds are "ormed$hen atoms o" t$o or more elements *oin to(ether. Eachcompound has its o$n physical properties.
Some compounds can be bro+en do$n into their elements by chemicalchan(es. 0ther compounds brea+ do$n to "orm simpler compoundsinstead o" elements. These simpler compounds can then be bro+endo$n into elements throu(h more chemical chan(es. The only $ay to
brea+ do$n a compound is throu(h a chemical chan(e.
1 Elements are combined in a speci%c ratio accordin( to theirmasses to "orm a compound.
1 Each compound can also be identi%ed by their di2erent chemicaland physical properties.
1 There are more than 3 million compounds that e/ist' carbon is"ound in 435 o" them.
1 !6EMI!AL MEANS 0NL7 can brea+ do$n !0MP0UNDS intoelements or simpler compounds8
1 Sometimes ener(y is needed "or a chemical chan(e to happen.
This is done by applyin( heat or electric current ,electrolysis-.
1 A compound has properties that di2er "rom those o" theelements that "orm it.
E/ample) Table Salt
Elements)# 0nly one
particleatom
!ompounds)# T$o or more
particlessubstances
# Atom ormolecule
PureSubstanc
e

7/23/2019 repaso de ciencia .docx
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/repaso-de-ciencia-docx 3/10
Na 9 Cl :NaCl#So"t #Poisonous # Sa"eto eat#Sil;ery $hite metal #reenish yello$ (as #
<hite solid#Reacts ;iolently # Dissol;eseasily<ith 6=0 in 6=0
PROPERTIES O' COMPOUNDS
• A compound is a pure substance composed o" t$o or moreelements that are chemically combined. Elements combine byreactin( $ith one another.
• A particle o" a compound is a called a molecule. Molecules o"compounds are "ormed $hen atoms o" t$o or more elements *oin
to(ether.
PROPERTIES O' COMPOUNDS
• Each compound can be identi%ed by its physical and chemicalproperties.
• Pr!"ertes C!m"!un%s s. Elements A compound hasproperties that di2er "rom those o" the elements that "orm it.
*REAIN) DO/N COMPOUNDS
• !ompounds can be bro+en do$n into their elements or intosimpler compounds by chemical chan(es.
• Meth!%s !$ *rea0n& D!1n C!m"!un%s Sometimes' ener(yis needed "or a chemical chan(e to happen. T$o $ays to addener(y are to apply heat and to apply an electric current.Electrolysis
• C!m"!un%s n Nature Some compounds "ound in nature areproteins' carbon dio/ide' and carbohydrates.
• C!m"!un%s n In%ustr# Some compounds must be bro+endo$n "or use in industry. 0ther compounds are made in industry"or use as medicines' "ood preser;ati;es' and synthetic "abrics.
PROPERTIES O' MIXTURE
• m2ture- a combination o" t$o or more substances that are notchemically combined.

7/23/2019 repaso de ciencia .docx
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/repaso-de-ciencia-docx 4/10
N! Chemcal Chan&es n a M2ture No chemicalchan(es happen $hen a mi/ture is made. So' eachsubstance has the same chemical ma+eup it had be"orethe mi/ture $as "ormed.
Usn& "h#scal chan&es can se"arate Se"aratn&
M2tures Thr!u&h Ph#scal Meth!%s M2tures.Physical chan(es do not chan(e the identities o" thesubstances.
The Rat! !$ C!m"!nents n a M2ture the components o" a mi/ture do not need to be mi/ed in ade%nite ratio.
!lassi%cations o" mi/tures)• homogeneous: no ;isible di;ision and uni"orm composition
• heterogeneous: ;isible di;ision and are not uni"orms
6etero(eneous1 6a;e one or more ;isible boundaries bet$een the components.1 !omposition is not uni"orm.1 E/amples) Roc+s' mil+ and blood ,you need a microscope to see
the parts-' and others.
6omo(eneous1 6a;e no ;isible boundaries because the components are mi/ed
as indi;idual atoms' ions and molecules.1 !omposition is uni"orm.1 E/ample) su(ar and $ater
>- s!lut!n- mi/ture that appears to be a sin(le substance. Iscomposed o" particles o" t$o or more substances that aredistributed e;enly amon( each other. A solution is homo(eneous.Solutions ha;e the same appearance and properties throu(houtthe mi/ture. The particles in solutions are so small that theyne;er settle out. They cannot be remo;ed by %lterin(. Theparticles are so small that they don?t e;en scatter li(ht.
=- %ss!l3n&- The process in $hich particles o" substancesseparate and spread e;enly throu(hout a mi/ture
@- s!lute- the substance that is dissol;ed.
3- s!l3ent# the substance in $hich the solute is dissol;ed
- s!lublt## the ability o" the solute to dissol;e in a sol;ent at acertain temperature and pressure.

7/23/2019 repaso de ciencia .docx
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/repaso-de-ciencia-docx 5/10
B- all!#s- are solid solutions o" metals or nonmetals dissol;ed inmetals.
C- c!ncentrat!n- measure o" the amount o" solute dissol;ed in a
sol;ent.
- %lute less solute then sol;ent
4- c!ncentrate% more solute than sol;ent
S!lut!ns C!ll!%s Sus"ens!ns
• h!m!&ene!us • hetero(eneous • hetero(eneous
• N! 4ltrat!n • No %ltration • %ltration
• D! n!t scatterl&ht
• Scatter li(ht • Scatter li(ht
• D! n!t settle%!1n
• Do not settledo$n
• Settles do$n
Se"aratn& M2tures
Mi/tures can be separated by physical means' such as>. y hand=. iltration#passin( mi/tures throuht a %lterF. Trasps solids
@. E;aporation# occurs in sur"ace o" a li&uid3. distillation# process that separates a mi/ture based on the
boilin( points o" the components. ma(net# a ma(net can be used to separate a mi/ture o"
the elements iron and aluminumB. centri"u(e# separates mi/tures by the densities o" the
components.• Less dense (oes on top
Dissol;in( ases in Li&uids
Most s!l%s are more s!luble in l5u%s at h&her tem"eratures.ut (ases become less soluble in li&uids as the temperature is raised.
C!m"!un%s M2tures
Pure substance Not pure substance6 !r m!re substanceschemcall# c!mbne%
= or more substances n!tchemically combined

7/23/2019 repaso de ciencia .docx
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/repaso-de-ciencia-docx 6/10
Separatin() !hemical Means Separatin() Physical means only!ombined in speci%c ratios N!t speci%c ratiosNe1 substance $!rme% N! ne$ substance "ormed
CONCENTRATIONS O' SOLUTIONS• S!lut!n- is a mi/ture that appears to be a sin(le substance.
The process in $hich particles o" substances separate and spreade;enly throu(hout a mi/ture is +no$n as dissolving.
S!l3ent S!lute
1 Substance in $hich thesolute is dissol;ed.
1 Substance that is dissol;ed.1
1 I" it in;ol;es t$o ,=- li&uidsor t$o ,=- (ases' thesubstance $ith (reater
amount is the sol;ent.
1 Must be soluble in thesol;ent.
• Partcles n S!lut!ns The particles in solutions are so smallthat they ne;er settle out. They also cannot be remo;ed by%lterin(.
• The particles in solutions are so small that they don?t e;enscatter li(ht.
• A measure o" the amount o" solute dissol;ed in a sol;ent isc!ncentrat!n.
• C!ncentrate% !r Dlute7 Solutions can be described as bein(concentrated or dilute. ut these t$o terms do not tell you theamount o" solute that is dissol;ed.
• S!lublt# is the ability o" a solute to dissol;e in a sol;ent at acertain temperature.
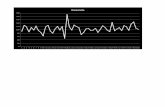
• The solubility o" most solids in $ater increases $ithtemperature. The (raph on the ne/t slide sho$s this relationship.
• Dss!l3n& )ases n L5u%s ases become less soluble in
li&uids as the temperature is raised.• Dss!l3n& S!l%s 'aster n L5u%s Three $ays to ma+e a
solute dissol;e "aster are mi/in( the solution' heatin( thesolution' and crushin( the solute into smaller particles.
S0LUILIT7 RAP6) ,important-

7/23/2019 repaso de ciencia .docx
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/repaso-de-ciencia-docx 7/10
SUSPENSIONS
•
Sus"ens!n# a mi/ture in $hich particles o" a material aredispersed throu(hout a li&uid or a (as but are lar(e enou(h thatthey settle out.
• The particles in a suspension are lar(e enou(h to scatter orbloc+ li(ht.
• Passin( it throu(h a %lter can separate a suspension.
COLLOID
•
!!ll!%# a mi/ture in $hich the particles are dispersedthrou(hout but are not hea;y enou(h to settle out.
• Particles in a colloid are lar(e enou(h to scatter li(ht. Passin( itthrou(h a %lter cannot separate a colloid.
Three t#"es !$ m2ture8s S!lut!ns 9small"artcles:
C!ll!%s 9me%um"artcles:
Sus"ens!n 9lar&e"artcles:
6omo(eneous 6etero(eneous 6etero(eneousNo %ltration No %ltration iltrationDo not scatter li(ht Scatter li(ht Scatter li(htDo not settle do$n Do not settle do$n Settles do$n!an be)>. Solid# alloys ,metal 9
metal-
E/amples)o Nature clouds'
blood' mil+' opals'
E/amples)• Sno$ (lobe
• Paint

7/23/2019 repaso de ciencia .docx
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/repaso-de-ciencia-docx 8/10
=. Li&uids# sea $ater'lemonade
@. as# air $e breatheN=# C5G=# =>5
Ar# >50thers# >5!o=' 6=G ;aporH etc.
pearls
o Manma%emayo' (elatin'stic+ deodorant'
$hipped cream'+etchup
Solution)S!lute S!l3ent
Itdissol;es
Substances in$hichsolute isdissol;ed
Smaller
&uantity
Lar(er
uantitySolid isal$aysthesolute ina solid#li&uidmi/ture
Li&uid isal$aysthesol;entin asolid#li&uidmi/ture
;: Can be
S!lut!n ; s"!!n
=- C!ncentrate%m!re salute
Saturate% ;< s"!!ns

7/23/2019 repaso de ciencia .docx
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/repaso-de-ciencia-docx 9/10
=: Dlute%- lesssalute;.; S"!!ns
SATURATED--->

7/23/2019 repaso de ciencia .docx
http://slidepdf.com/reader/full/repaso-de-ciencia-docx 10/10
MIXTURES PROPERTIES O' MIXTURES
1 A MIXTURE is a combination o" t$o or more substances that areN0T !6EMI!ALL7 !0MINED.1 Substances in mi/tures +eep their identities because no chemical
chan(e ta+es place $hen a mi/ture is made.1 E/amples) air' sea$ater' soil' or(anisms' (ranite ,combination o"
minerals-. The components o" a mi/ture D0 N0T need to be mi/ed in ade%nite ratio li+e the components o" a compound.