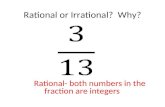Rational Numbers. Some Definitions Rational Number: Any number that can be converted into a fraction...
-
Upload
julian-cole -
Category
Documents
-
view
213 -
download
0
Transcript of Rational Numbers. Some Definitions Rational Number: Any number that can be converted into a fraction...

Rational Numbers

Some Definitions
• Rational Number: Any number that can be converted into a fraction ( Examples: ¼, 3, 4.25, 0).
• Fraction: A part of a whole ( ¼ , ¾).• Mixed Number: A whole number and a fraction (1 ¼
)• Terminating Decimal: A decimal number that stops
(3.75, 4.3, 8.3245).• Repeating Decimal: A decimal number that has a
repeating pattern (3.757575… , 2.345345… )

Adding Decimal Numbers
• To add decimal numbers, line up the addends by the decimal place and add.
• Make sure the place values line up properly.

Complete #1-5

Applying Integer Rules
• We can apply the same rules for integers to rational decimal numbers.
• Rule 1: If the signs are the same, add and keep the sign the same.
• Rule 2: If the signs are different, subtract and keep the sign of the larger number.

Complete #6-10

Adding Fractions and Mixed Numbers
• When you add fractions, you must first find a common denominator.
• We find a common denominator by finding the least common multiple for the denominators of our addends.
• Make sure your answer is always in lowest terms.

Complete #11-15

Applying Integer Rules
• We can also apply our integer rules to fractions and mixed numbers.
• If we need to borrow, take one away from the whole number and add the appropriate amount to the numerator.

Complete #16-20

Subtracting Rational Numbers

Use your subtraction rules:
• Change subtraction to addition and find the opposite of the second number.
• Go back to addition rules.

Multiplying Rational Numbers

Multiplying Decimals
• Line up the numbers justified right. • Multiply the factors.• Count the decimal places in each factor and
add. • Move the decimal place that many times to
the left.

Multiplying Fractions
• Change mixed numbers to improper fractions.– Cross cancel and multiply OR– Multiply and reduce

Dividing Rational Numbers

Dividing Decimals
• Set it up. (First in)• Move the decimal on the outside.• Move the decimal on the inside the same
number of times.• Rewrite and divide.

Dividing Fractions
• Change mixed numbers to improper fractions.
•KFC