Radionuclide imaging in infection and inflammation.
-
Upload
bernice-susanna-robbins -
Category
Documents
-
view
224 -
download
8
Transcript of Radionuclide imaging in infection and inflammation.

Radionuclide imaging in infection and inflammation

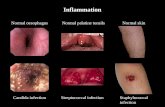
Inflammation
A basic way in which the body reacts to infection, irritation or other injury
Inflammation is now recognized as a type of nonspecific immune response

Morfology of inflammation
Blood hyperperfussionIncreased cappilars permeabilityExudationSwellingLeukocytes migrationDysfunction of organ or tissue

Diagnosis of inflammation
Physical examinationLaboratory testsX-rayUltrasoundMRI

Symptoms
DolorRuborTumorCalor
Hallmarks of inflammation were first described by Aulus (Aurelius) Cornelius Celsus, a Roman physician and medical writer, who lived from about 30 B.C. to 45 A.D.

X-ray and ultrasound
Do we really need other modalities?What we see in X-ray or ultrasound?Is X-ray or ultrasound specific technique for inflammatory process?

Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis in a peadriatric patient

Hematogenous osteomyelitisin a peadriatric patient

Hematogenous osteomyelitisin a peadriatric patient

Diagnosis of inflammation
Physical examinationLaboratory testsX-rayUltrasoundMRI
Scintigraphy

Specific radionuclide techniques
In vitro labelled leukocytesIn vivo labelled leukocytesLabelled poliklonal IgGLabelled antibioticsGallium-67 scan

Non specific radiomuclide techniques
Bone scintigraphyRenal static scintigraphySalivary gland scintigraphyBrain perfussion scan

In vitro labelled leukocytes
Indium-111 oxinTechnetium-99m – HmPAOLabelling process outside of bodySeparation of leucocytes in centrifugal machineLabelling by diffusion of radioactive complex into a cell

In vitro labelling

In vitro labelling

In vivo labelled leucocytes
ImmunoscintigraphyMonoclonal IgG antibody Fab’ fragment labeled with Technetium-99mInjected targets NCA-90, found on the cell membrane of graunlocytes

In vivo labelling

In vivo labelling

After injection

Indications
Abscess in abdomen (appendicitis)Fever of unknown originArtery graft infectionsInfection ortopaedic prothesisBowel inflamatory disease

Tc99m-HmPAO labelled leukocytes – normal abdominal scan

Atypical presentation of acute appendicitis in high-risk populations, such as children, make correct diagnosis difficult.
Rate of complications, including death, is directly correlated with delay in diagnosis and surgery.
Appendicitis

Tc99m-HmPAO labelled leukocytes scintigraphy is a rapid and very accurate method for detecting acute appendicitis in patients with acute lower abdominal pain and equivocal clinical findings.
Appendicitis

Appendicitis

Fever of Unknown Origin (FUO)
30% of patiens with FUO have silent infectionAfter surgery 60%Very often negative X-ray and USTc99m-HmPAO labelled scintygraphy is method of choice

Arterial graft infections
2-6% of graftsMortality very high 25-75%The highest sensitivity of Tc99m-HmPAO labelled leukocytes scintigraphy100% !Early diagnosis saves live

Bowel inflamatory diseases
Crohn diseaseColitis ulcerosaNon specific bowel inflamationThe same efficacy that colonoscopy with mucosa biopsyControl of treatement

Crohn disease

Colitis ulcerosa

Gallium-67 citrate
Labelling in vivo leucocytesBinds to transport protein laktoferrinExpensiveLess specific than labelled leucocytesAlso binds transferrine in tumours cells (lymphoma, HCC, leucemia)

Gallium-67 scan
Spondyllitis VTh5

Pericarditis

Ga-67 - Acute pulmonary infection

Policlonal human immunoglobins IgG labelled with Tc99m
Accumulation in focus of inflammationCirculating IgG`s are premeabling to intercellular spaceEasy to preparation and cost effectiveNo differentiation between inflamation and infection

Policlonal IgG-Tc99m - normal

Policlonal IgG-Tc99m - normal

Policlonal IgG-Tc99m

Policlonal IgG-Tc99m

Bone scintigraphy
Three-phase scintigraphyEarly phase: perfussionLate phase: bone metabolismUsefull in incection and inflammationNon specific

Bone scan - normal

Bone scan - three phase

Osteomyelitis

Osteomyelitis

Otitis media complication

Septic arthritis

Rheumatoid artritis
99mTc-MDP RA 99mTc-MDP Normal

Entesopaties
Achilles Tendinitis
99mTc-MDP

Seronegative arthritis

Pyelonephritis
High incidence in children1% leads to renal failure and transplantation10% asymptomaticRenal scars

DMSA-Tc99m scan
99m Tc - DMSA-

Static renal scintygraphy
Gold standard in detection of inflammatory scars!Method of choice

Pyelonephritis
In acute pyelonephritis DMSA scan is ALWAYS abnormal!

Inflamatory scars
Sens Spec.
DMSA 92.1 93.8
ECHO-
74.3 56.7DOPPLER
CT 86.8 87.5
MR 89.5 87.5

Brain vasculitis
Antiphospholipide Antybody SyndromLupus cerebri and other colagenosesHigh mortality!Needs agressive treatement with cytostatics and high doses of steroidsrCBF=Brain perfussion scanSPECT

Normal perfussion

Cerebral vasculitis

Cerebral vasculitis

Salivary gland function

Sjoegrens disease