Questions 1.What is Full form Of TCP/IP 2.Which are the layers in TCP/IP Model ? 3.Task of...
-
Upload
roberto-binkley -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of Questions 1.What is Full form Of TCP/IP 2.Which are the layers in TCP/IP Model ? 3.Task of...

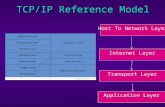
Questions1. What is Full form Of TCP/IP2. Which are the layers in TCP/IP Model ?3. Task of Application Layer4. Task Of Host – to – Network Layer 5. Task of Internet layer 6. Host to network is combination of which layers ?7. task of transport layer 8. Protocol in Application layer 9. Protocol in transport layer 10. What is TCP ?11. What is UDP ?12. Which one is connection oriented & Connection Less?13. Example of TCP , Example Of UDP 14. Protocol in internet layer?15. Which are designing issues in Layers?16. Difference Between TCP/IP & OSI
1

Network Examples2

The ARPANET
Developed By ARPA in 1968.
Designed To service nuclear Attack.
Before ARPANET only Telephone Networks were there.
Before ARPANET the network works on circuit switching principle.
It was vulnerable because failure in one switch will fail whole Conversion.
ARPANET use concept of PACKET SWITCHING ,contains subnets and Hosts.
Host will send Message to subnet and subnet will divide the message in packets and Forward it.
Each Packet was stored Before it was forwarded.
3

The ARPANET
(a) Structure of the telephone system.
(b) Baran’s proposed distributed switching system.
4

The ARPANET (2)
The original ARPANET design.
IMP : interface Message Processor
5

The Internet Not A specific network but collection of
networks.
Not planned and controlled by anyone.
Possible Because of TCP/IP Model.
6

Internet Services
Traditional applications (1970 – 1990)
• E-mail• News• Remote login• File transfer
7

Internet8

Internet address
To identify each computer on the net it requires a proper addressing scheme.
For identification each system will have Name ( Domain Name)
Address ( IP Address)
9

IP Address
Each computer on the internet is identify by unique IP
Address.
It is made of four number each of 256 bits.
Each will have value from 1 to 255
Example : 202.65.10.155
The numbers between . Are called OCTETS
Leftmost octet represent Largest Network.
Right most octet represent a particular machine.
10

Questions 1. What is ARPANET ?
2. Two main parts in ARPANET ?
3. Task of host ?
4. Task of subnet ?
5. Which are two types of switching ?
6. What is circuit switching ?
7. What is packet switching ?
8. Define
9. Internet Services ?
10. IP address is Of how many bits ?
11. Name for the numbers in IP address ?
12.Range of OCTET ?
13.Left Most Octet Represent ?
14.Right Most Octet Represent ?
11

Domain Name Addressing A small Network Having many computers is called
Domain.
It may also represent the behaviour of the Network or
the location of the network.Domain Name Description
.com Company or Commercial
.edu Educational
.gov Government
.mil Military site
.net Internet service provide or network resource
Domain Name Description
.au Australia
.in India
.uk United kingdom
.ca canada
12

Wireless LAN
Uses wireless transmission media.
Less popular because of high price , low data rate.
The typical Coverage area is 300 to 1000 feet.
Must provide security.
The MAC(Medium Access Control) addressing should
permit dynamic and automated
addition,deletion,relocation of end system.
13

Application of wireless LAN
LAN EXTENSION :
WLAN saves the cost of installation of LAN cabling
and eases the task of relocation and modification.
Cross Building interconnect :
To connect two LAN in different building , it may be
wired or wireless.
Ad hoc Networking :
Is a peer to peer connection for temporarily purpose.
14

Wireless LANs
(a) Wireless networking with a base station.
(b) Ad hoc networking.
15

Types of WLAN
It Depends Upon Transmission technique
Used.
Infrared(IR) LAN : Limited To Single Room
Spread Spectrum LAN : Spread Spectrum
Transmission.
Narrow Band Microwave : Microwave
Frequency .
16

Types of WLAN IEEE 802.11X
802.11 refers to a family of specification
developed by IEEE(Institute of Electrical and
Electronics Engineers) 802.11 :
Provide 1 Mbps or 2 Mbps transmission in 2.4 GHz Band
802.11a : Provide 5 Mbps transmission in 5 GHz Band
802.11b (wifi) : Provide 11 Mbps transmission in 2.4 GHz Band
802.11g : Provide 20 Mbps transmission in 2.4 GHz Band
17

Frame Relay
Frame Relay (FR) is a high-performance WAN
protocol that operates at the physical and data link
layers of the OSI reference model.
FR originally was designed for use across Integrated
Service Digital Network (ISDN) interfaces.
Today, it is used over a variety of other network
interfaces as well.
FR is an example of a packet-switched technology.
18

19Frame Relay Devices
Devices attached to a Frame Relay WAN fall into the following two general categories: Data terminal equipment (DTE)
DTEs generally are considered to be terminating equipment for a specific network and typically are located on the premises of a customer.
Example of DTE devices are terminals, personal computers, routers, and bridges.
Data circuit-terminating equipment (DCE) DCEs are carrier-owned internetworking devices. The purpose of DCE equipment is to provide clocking
and switching services in a network, which are the devices that actually transmit data through the WAN.

20Frame Relay Devices

21
Packet-Switching Networks
Basic technology the same as in the 1970s
One of the few effective technologies for long distance data communications
Advantages: Flexibility, resource sharing, robust,
responsive
Disadvantages: Time delays in distributed networks Need for routing and congestion control

22
Definition of Packet Switching
Refers to protocols in which messages are divided into packets
before they are sent. Each packet is then transmitted
individually and can even follow different routes to its
destination. Once all the packets forming a message arrive at
the destination, they are recompiled into the original message.
Most modern Wide Area Network (WAN) protocols, including
TCP/IP, X.25, and Frame Relay, are based on packet-
switching technologies.

23
Circuit Switching
In contrast, normal telephone service is based on a circuit-
switching technology, in which a dedicated line is allocated for
transmission between two parties.
Circuit-switching is ideal when data must be transmitted quickly
and must arrive in the same order in which it's sent. This is the
case with most real-time data, such as live audio and video.
Packet switching is more efficient and robust for data that can
withstand some delays in transmission, such as e-mail
messages and Web pages.

NDSL, Chang Gung University
24 The Use of Packets

25
Packet Switching: Datagram Approach

26
Advantages with compared to Circuit-Switching
Greater line efficiency (many packets can go over shared link)
Non-blocking under heavy traffic (but increased delays). When traffic becomes heavy on a circuit-switching network, some calls are blocked.
Priorities can be used.

27
Disadvantages relative to Circuit-Switching
Packets Add additional delay with every node they pass through
Jitter: variation in packet delay Data overhead in every packet for routing
information, etc Processing overhead for every packet at
every node traversed

NDSL, Chang Gung University
28
Simple Switching Network

29
Switching Technique
Large messages broken up into smaller packets
Datagram Each packet sent independently of the
others No call setup More reliable (can route around failed
nodes or congestion) Virtual circuit
Fixed route established before any packets sent
No need for routing decision for each packet at each node

NDSL, Chang Gung University
30
Packet Switching: Virtual-Circuit Approach