Q1680 Pediatric Elimination Disorders - cdn.ymaws.com · Hirschsprung’s disease Emotional...
Transcript of Q1680 Pediatric Elimination Disorders - cdn.ymaws.com · Hirschsprung’s disease Emotional...

10/6/2016
1
PEDIATRIC ELIMINATION DISORDERS
S O P H I A L . T H O M A S M N , A P R N , F N P - B C , P P C N P - B C , F N A P , F A A N P
I HAVE NO KNOWN CONFLICTS OR DISCLOSURES
Objectives:
1. Define elimination disorders
2. Discuss diagnostic criteria for enuresis and encopresis
3. Differentiate classifications of these disorders
4. Discuss treatments for these disorders

10/6/2016
2
ELIMINATION DISORDERS
Elimination disorders are disorders that concern the elimination of feces or urine from the body.
The American Psychiatric Association recognizes two elimination disorders:
Enuresis F98.0
Encopresis F98.1
NORMAL DEVELOPMENT
Toddler Phase (18 months- 3 years)
Bowel Continence
Bladder Continence
TOILET TRAINING 101
Readiness for Toilet TrainingMajor milestone in physical and social development that is often
achieved during the day by 36 months although accidents may continue through 5 yearsReadiness CriteriaBladder control (should empty completely and stay dry)Physical readiness (fine- and gross-motor coordination) Instructional readiness (ability to follow directions)

10/6/2016
3

10/6/2016
4
Enuresis (urinary incontinence) is the persistent inability to control urination that is not consistent with one’s development age.
‘Enuresis’ is derived from the Greek word ‘enourein’, which means ‘to void urine’.
2-10% of children affected
Nocturnal enuresis is more commonly known as bedwetting
ENURESIS CLASSIFICATIONS Nocturnal Enuresis
Monosymptomatic
Polysymptomatic
Diurnal Enuresis
Primary Enuresis
Secondary Enuresis
TYPES OF ENURESIS Regressive Enuresis
Monosymptomatic Nocturnal Enuresis
Polysymptomatic Nocturnal Enuresis
Functional Enuresis
Nonfunctional Enuresis
Revenge Enuresis
Enuresis due to lack of training
Detrusor Dependent Enuresis
Volume-Dependent Enuresis

10/6/2016
5
PREVALENCE 30% of US children achieve continence by age 2
More common in males. Age 7: 9% boys and 6% girls
Mortality: only due to fatal abuse
At age 4, 25% of kids wet the bed; 5-10% of 7 year olds
15% of enuretic children have spontaneous resolution of symptoms each year
8% of boys/4% girls age12 years meet criteria for nocturnal enuresis
1% of 18 year olds still have enuretic symptoms
Resolution of 15% per year
30% of children with ADHD
Health and Psychological Consequences
Could be marker for medical conditions such as urinary tract infections Psychosocial consequences result from
shaming, blaming and characterological attributions that are directed to incontinent children in addition to increased risk of child abuse secondary to incontinence
Evidence-based Assessment No widely used tools Most research using instruments that
incorporate items into larger constellation of items on psychosocial issues Dysfunctional Voiding Scoring System
assesses enuresis and other co-morbid voiding and/or elimination symptoms Domains of interest include wet or dry
days or nights and size of urine spot
ENURESIS

10/6/2016
6
ENURESIS DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIADSM-5 Diagnostic Criteria for Enuresis F98.0
A. Repeated voiding of urine into bed or clothes (whether involuntary or intentional).
B. The behavior is clinically significant as manifested by either a frequency of twice a week for at least 3 consecutive months or the presence of clinically significant distress or impairment in social, academic (occupational), or other important areas of functioning.
C. Chronological age is at least 5 years (or equivalent developmental level).
D. The behavior is not due exclusively to the direct physiological effect of a substance (e.g., a diuretic) or a general medical condition ( e.g., diabetes, spina bifida, a seizure disorder).Specify type:Nocturnal OnlyDiurnal OnlyNocturnal and Diurnal

10/6/2016
7
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
MaturationalAnatomical AbnormalitiesEndocrineUrinary Tract DiseaseNeurologicalMedicationsPsychological
DIAGNOSTIC WORKUPChild’s AgeOnset of Symptoms (Primary/Secondary)Timing (Nocturnal/Diurnal/Both)FrequencyFamily HistoryDevelopmental HistoryHydration and nutrition historyDaytime voiding patternToilet training historySleep historyBehavior, personality, and emotional status
PHYSICAL EXAM
Neurological Exam
Throat and Neck Exam
Skin Exam
Abdominal Exam
CMP (but blood tests usually not necessary)
UA

10/6/2016
8
COMMON UNDERLYING PROBLEMS
• Overactive bladder or dysfunctional voiding
• Cystitis or UTI
• Constipation
• Neurogenic bladder
• Sleep-disordered breathing
• Urethral obstruction
• Major motor seizure
• Ectopic ureter
• Diabetes mellitus or insipidus
CONSULTS
• Pediatric Urology• Ultrasound of Genitourinary system• Voiding Cystourethrogram• Renal Ultrasound• Pediatric Neurology• Sleep Study
TREATMENT• Education
• Watchful Waiting
• Non-pharmacological Management
• Pharmacological Management
• Therapeutic Interventions

10/6/2016
9
NON-PHARMACOLOGICAL INTERVENTIONS
Education
Behavioral Modification
Bell and Pad
NON-PHARMACOLOGICAL INTERVENTIONS Bladder-Volume Alarm
Star Chart System
Nightlifting
Timed Night Awakening
Bladder Training Exercises/Overlearning
Evidence-based Interventions
Bell-and-Pad or Urine-Alarm Training treatment success is higher and relapse rate lower than any other method, especially when combined with Desmopressin
ENURESIS

10/6/2016
10
Medications Desmopressin AcetateOxybutynin Chloride Imipramine
Other Treatment Approaches Hypnosis Sphincter exercises Restriction of fluids before bed
ENURESIS
PHARMACOLOGICAL INTERVENTIONS
Desmopressin
Oxybutynin
Imipramine
TCAs, SSRIs & Psychostimulants
NSAIDs
PATHYPHYSIOLOGY, CLASSIFICATION, & TREATMENT STRATEGIES
Wright, A. (2016) Childhood enuresis. Paediatrics and Child Health, 26( 8) 353-359

10/6/2016
11
DESMOPRESSIN (DDAVP)
• For polyuria• A synthetic analogue of ADH• Increases water uptake of the renal distal tubules ===
diminishes urine production• Must restrict fluids 1 hr before and 8 hrs after administration
(risk of hyponatremia)• May use in conjunction with the alarm• 1/3 of children don’t respond – most have small nocturnal
bladder capacity• Dose age 6 and older: tablets 0.2mg q hs, max 0.6mg• *nose spray no longer indicated for primary enuresis due to
hyponatremia risk• Not all children will respond; not all kids with enuresis have
low ADH or overproduce urine
PATHYPHYSIOLOGY, CLASSIFICATION, & TREATMENT STRATEGIES
Wright, A. (2016) Childhood enuresis. Paediatrics and Child Health, 26( 8) 353-359
OXYBUTYNIN
Anticholinergic
Beneficial for children who have small bladder capacity, daytime symptoms of frequency and urgency, or those who wet more than once at night
Does not decrease urine production
For detrusor overactivity: Relaxes bladder smooth muscle: Allows the bladder to hold more urine
Start in ages over 5 years old 5mg BID
Maximum dose is a total of 15 mg per day
Onset 1 hr, t1/2 2‐3 hrs
Extended release for children older than 6 at 5mg po daily
Maximum is 20 mg po daily (increase by 5mg weekly)

10/6/2016
12
IMIPRAMINE (TOFRANIL)
Tricyclic antidepressant
Facilitates urine storage by decreasing bladder contractility and increasing outlet resistance
Inhibits reuptake of norepinephrine and seratonin at the presynaptic neuron
First prescribed for enuresis when psych causes of enuresis were considered common
Dose 1 hr before bed: 6-12 years 10-25 mg qhs, max 50 mg
12+ years 10-25 mg qhs, max 75 mg
Dose earlier in early night wetters
Black box warning – suicide risk, worsening MDD
Caution in cardiovascular disease, possibility of arrhythmias
Baseline EKG
TREATMENT ALGORHYTHM FOR NOCTURNAL ENURESIS

10/6/2016
13
ADDITIONAL TREATMENTSCognitive Behavioral Therapy
Psychodynamic Psychotherapy
Biofeedback
Acupuncture
Encopresis is a repeated passage of feces into inappropriate places, such as on clothing or the floor.
Usually involuntary in nature, often related to constipation, impaction and retention with a resultant overflow
May be intentional in some cases

10/6/2016
14
ENCOPRESISPrimary Encopresis
Secondary Encopresis
Retentive Encopresis
Nonretentive encopresis
ENCOPRESIS PREVALENCESecondary encopresis is more common
Between ages 7-8 prevalence is 1.5%
3:1 male to female ratio
Retentive type is 80-95% of cases
25% of encopretic kids have enuresis
ENCOPRESIS RISK FACTORS
Abuse or neglect;
Diet that is rich in fat and/or sugar;
Inadequate water intake;
Presence of chaos or unpredictability in the patient’s life;
Lack of physical exercise;
Refusal to use the bathroom, especially public restrooms;
Presence of a neurological impairment;
History of constipation or painful defecation;
Cognitive delays, such as autism or mental retardation;
Presence of obsessive/compulsive disorders;
ADHD or difficulty focusing;
Learning disabilities

10/6/2016
15
ENCOPRESIS ETIOLOGYDelay in Maturation
Underlying Medical Condition
Psychological/Behavioral
Constipation
Etiology Biological Variables Genetics
Developmental Delay?
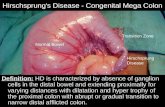
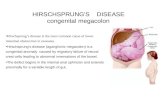
Hirschsprung’s disease
Emotional Variables Early theories assumed
psychodynamic etiology (e.g., unconsious conflict, personality profiles)
Etiology (Cont) Learning Variables Most useful view considers types Manipulative
Stress-induced
Constipation (80-95% of cases)
Manipulative soiling follows reinforcement model
Chronic diarrhea and loose bowels
Chronic Constipation Diet
Toilet habits/Withholding
School bathroom conditions
ENCOPRESIS
ENCOPRESIS
DSM-V Diagnostic Criteria for Encopresis
A. Repeated passage of feces into inappropriate places (e.g., clothing or floor) whether involuntary or intentional.
B. At least 1 event a month for at least 3 months.
C. Chronological age is at least 4 years (or equivalent developmental level).
D. The behavior is not due exclusively to the direct physiological effects of a substance (e.g., laxatives) or a general medical condition except through a mechanism involving constipation.

10/6/2016
16
DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIAThe DSM-IV recognizes 2 subtypes:1. constipation and overflow incontinence• Feces poorly formed, leakage continuous, occurs sleeping
and waking hours2. without constipation and overflow incontinence• the feces are usually well-formed, soiling is intermittent, and
feces are usually deposited in a prominent location. This form may be associated with oppositional defiant disorder or conduct disorder, or may be the consequence of large anal insertions, or more likely due to chronic encopresis that has radically desensitized the colon and anus
ENCOPRESIS
SYMPTOMS
• Occasional passage of very large stools;
• Secretive behavior associated with the act of having a bowel movement;
• Inability to retain feces (bowel incontinence);
• The passage of stool in inappropriate places (for example in the child’s clothing);
• Constipation and/or hard stools

10/6/2016
17
PRIMARY RETENTIVE ENCOPRESIS
Delayed Physical Maturation
Inappropriate Toilet Training

10/6/2016
18
RETENTIVE ENCOPRESISRepresents 80-95% of cases
Infrequent Bowel Movements
Large Stools
Painful Defecation
SECONDARY ENCOPRESIS
Birth of sibling
Parental Divorce
Abuse
ODD or CD
MR/Autism/ Psychosis/RAD
Health and Psychological Consequences
Most serious/common involves urinary tract infections from contamination of urinary tract with feces from child’s underwearMost serious social consequence is
teasing and ridicule from peers, classmates, friends, and siblings
Evidence-based AssessmentOne of the available general
parent and teacher rating scales (BASC, CBCL, Connors CBRS) to identify comorbidities such as ODD and ADHD which may interfere with parent’s ability to implement treatment recommendations
ENCOPRESIS

10/6/2016
19
DIAGNOSIS
• Child’s age• Onset (primary/secondary)• Timing (day/night)• Frequency• Location of soiling• Bowel Habits (frequency, stool size, consistency)• Melena/Hematochezia• Pain with Defecation/Fluid and Dietary Habits
PHYSICAL EXAM• Abdominal pain/distention• Height/Weight• Neurological Exam• Skin Exam• Rectal Exam• Abdominal XRAY• Stool Collection• Blood Testing• Rectal Biopsy/Barium Enema
TREATMENT
Advice/Education
Nonpharmacological
Pharmacological Intervention

10/6/2016
20
EDUCATIONDietary Changes (foods high in fiber)
Increase Fluid Intake
Make Toilet Training Non-Threatening
Make Toilet Accessible
Regular Bathroom Times

10/6/2016
21
Other Treatment ApproachesBiofeedback no better than
Medical-BehavioralFor “Manipulative Soiling”Behavioral and family therapyCoping and communication skills emphasizedReward appropriate behaviors and do not reinforce soiling behavior
Other Treatment Approaches (Cont) For “Chronic Diarrhea or Irritable
Bowel Syndrome” Stress reduction and learning
effective coping skills Systematic desensitization and
hypnosis Relaxation training, stress inoculation
training, assertiveness training, general stress management Supportive psychotherapy and
antidiarrheal medications
ENCOPRESIS
NONPHARMACOLOGICAL
CBT
Psychodynamic Psychotherapy
Biofeedback
Acupuncture
PHARMACOLOGICAL
Laxatives
Suppositories
Enemas
Mineral Oil
Stool SoftenersFiber supplements

10/6/2016
22
MAINTENANCE MEDICATIONS
Osmotic laxatives
Mechanism of Action: Retain water in stool, which adds bulk and softness, results in distension and promotes peristalsis
Lactulose (concentration: 10 g / 15 mL)• Lactulose is a synthetic, nonabsorbable disaccharide.• Dose: 1 to 3 mL/kg/day divided doses BID• Tastes sweet• Abdominal cramping, flatus
Sorbitol: 1 to 3 mL per kg per day given in divided doses twice dailyLess costly than lactulose
MAINTENANCE MEDICATIONS
Magnesium hydroxide (MOM, Pedia-Lax)• Magnesium is a divalent cationmaximally absorbed at distal small intestine• Dose: 1 to 3 mL/kg/day divided doses BID for > 2 years old• Thick, chalky. May mix with milk/choc milk• May cause cramping (increased Mag levels stimulate GI motility and secretion)• With OD/renal insufficiency: risk of hypermagnesemia, hypophosphatemia, or
secondary hypocalcemia
Polyethylene glycol powder (Miralax)• Long chain of ethylene glycol, poorly absorbed• Dose: 17 g /240 mL water/juice // 6 months and older: 0.5 -1.5 g/kg/day for no
more than 2 weeks• Titrate dosage at three-day intervals to achieve mushy stool consistency.• Benefits: Solution may be prepared in advance for administration over one to two
days.• Better adherance, tasteless and odorless, dissolve in all liquids
MAINTENANCE MEDICATIONS
Mineral Oil Suspension:Lubricant
Nonabsorbable fat
Softens stool, decreases water absorption from GI tract, and eases passage
Dose: age 6-11 10-25 mL/day, >12 15-45 mL/day
tasteless, chill or give with juice
Don’t use > 1 week
Adherence problems: Leakage may occur if dose is too high or impaction is present.

10/6/2016
23
THANK YOU!