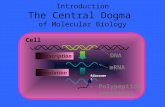
Protein Synthesis. Protein or Polypeptide chain Transcription – Copying the DNA in RNA language....
-
date post
21-Dec-2015 -
Category
Documents
-
view
215 -
download
0
Transcript of Protein Synthesis. Protein or Polypeptide chain Transcription – Copying the DNA in RNA language....

Protein Synthesis

Protein or Polypeptide chain

Transcription – Copying the DNA in RNA language. The resulting mRNA moves out to the cytoplasm.
Translation – At the ribosome, the information encoded in the mRNA is used to assemble a chain of amino acids or protein.

Comparing DNA and RNA
RNA
Ribose sugarUracil instead of
ThymineSingle stranded
DNA
Deoxyribose sugarThymine
Double stranded

Transcription
• RNA polymerase copies the DNA strand, adding the complimentary RNA bases to form the mRNA


The mRNA moves to a ribosome for translation into a protein.


The Triplet Code
• There are four DNA bases• They code for 20 amino acids
• If two bases coded for one amino acid, there wouldn’t be enough, only 16
• Three bases coding for each amino acid is just right, 64 possible combinations.
• A set of 3 DNA bases that code for one amino acid is referred to as a codon.

mRNA genetic code library

There are Three Forms of RNA
• mRNA – messenger RNA carries the information for synthesis of protein
• rRNA – ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes
• tRNA – brings the amino acids to the ribosome for protein synthesis• The triplet code in tRNA is called the
anticodon• Each tRNA and its anticodon is specific for one
amino acid

Translation
• mRNA binds to the ribosome• tRNA arrives, binding to the ribosome• A 2nd tRNA arrives, their amino acids
bond and the 1st tRNA leaves• More tRNA arrive until the mRNA is
completely translated into protein



Mutations
• Mutation – a permanent alteration of a DNA base sequence
• Most have no effect on an organism. Some have a deadly effect, only a slight few have a positive effect.
• Point mutation• When a single base pair is changed.
• Whole chromosome mutations• See chapter 12

• Most mutations happen in somatic cells and are of little or no importance.• Melanoma or skin cancer
• Mutations that happen in gametes can be passed from generation to generation.

A Pedigree of Hemophilia in the Royal Families of Europe
Selected members of the pedigree I-1 = King George III III-1 and III-2 = Prince Albert and Queen Victoria IV-5 and IV-6 = Alice of Hesse and Ludwig IV of Hesse V-13 and V-14 = Alix and Nicholas II (Tsar of Russia) VI-16 = Alexei