Properties of amino acid side chains report ni lady
-
Upload
aya-chavez -
Category
Documents
-
view
1.052 -
download
1
Transcript of Properties of amino acid side chains report ni lady

PROPERTIES OF AMINO ACID SIDE CHAINS:
CLASSES OF α-AMINO ACIDS

PROPERTIES OF AMINO ACID SIDE CHAINS: CLASSES OF α-AMINO ACIDS
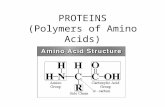
The 20 amino acids contain, in their different side chains, a remarkable collection of chemical groups. It is this diversity of the monomers that allows proteins to exhibit such a great variety of structures and properties.
Many ways have been proposed to group the amino acids into classes, but none is wholly satisfactory.

AMINO ACIDS WITH ALIPHATIC SIDE CHAINS
Glycine, alanine, valine, leucine, and isoleunine have aliphatic, or alkaline, side chains.
Isoleunine for example, has a much greater tendency to transfer from water to a hydrocarbon solvent than does alanine. The more hydrophobic amino acids such as isoleunine are usually found within a protein molecule.

Proline which is difficult to fit in any category, shares many properties with the aliphatic amino acids. Although it is a cyclic amino acid, its side chain has a primarily aliphatic character. However, the rigidity of the ring, compared with the flexibility of most amino acid side chains, often makes the folding of proline residues into protein structures difficult.

AMINO ACIDS WITH HYROXYL- OR SULFUR- CONTAINING SIDE CHAINS
Serine, cystein, threonine, and methionine can be placed in this category.
These amino acids, because of their weakly polar chains, are generally more hydrophilic than their aliphatic analog, although methionine is fairly hydrophobic.

Among the group, cystein is noteworthy in two respects.
First, the side chain can ionize at moderately high pH
Second, oxidation can occur between pairs of cystein side chains to form a disulfide bond.

AROMATIC AMINO ACIDSPhenylalanine, tyrosine, and
tryptophan, carry aromatic side chains. Phenylalanine, together with the aliphatic amino acids. Tyrosine and Tryptophan have some hydrophobic character as well, but it is tempered by the polar groups in there side chains. In addition, tyrosine can ionize at high pH.

The aromatic amino acids, like most compounds carrying conjugated rings, strongly absorbs light in the near-ultraviolet region of the spectrum. This characteristic is frequently used for the analytical detention of proteins, by measuring absorption at 280 nm.

BASIC AMINO ACIDS
Histidine, lysine, and arginine carry basic groups in their side chains.
The basic amino acids are strongly polar, and as consequences they are usually found on the exterior surfaces of proteins, where they can be hydrated by the surrounding aqueous environment.

ACIDIC AMINO ACIDS AND THEIR AMIDES
Aspartic acid and glutamic acids are the only amino acids that carry negative charges at pH 7.
The pKa is values of the acidic amino acids are so low that even when the amino acids are incorporated into proteins, the negative charge on the side chain is retained under physiological conditions. hence, these amino acid residues are often referred to as aspartate and glutamate

Companions to aspartic and glutamic acids are their amides, asparagine and glutamate. Unlike their acidic analogs, asparagine and glutamine have uncharged side chains, although they are decidedly polar. Like the basic and acidic amino acids, they are definitely hydrophilic and tend to be on the surface of a protein molecule, in conatct with the surrounding water.