Pressure Vessel Design Manual - PVManagepvmanage.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/Appendices-2.pdf ·...
Transcript of Pressure Vessel Design Manual - PVManagepvmanage.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/Appendices-2.pdf ·...

778 Appendices
Appendix L Vessel Surge Capacities and Hold-Up Times
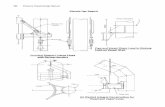
Figure L-2 Nomograph to find shell length for desired holding time Reprinted by permission of Gulf Publishing Co
Figure L-1 Nomograph to find drum size for holding time Reprinted by permission of Gulf Publishing Co
Appendices 779
Appendix M Minor Defect Evaluation Procedure
780 Appendices
Appendix N Tolerances
Appendices 781
Tolerance for Vertical Vessels
Notes
1 Minimum thickness as specified2 Out of roundness is defined by ASME VIII-1 Para
UG 80 and is +- 1 of the diameter The followingtolerances are recommended to provide strictercontrol of diametral difference
3 Distance from reference tangent line and top flangeFace 0015 in Ft (1mm 1m) lt 05 in (12mm)
4 Shell amp skirt tolerance Max slope from straightline is 0125 in 10 feet (3mm 3050mm) The totalmaximum deviation allowed is as follows (also seetable for maximum permissible bow)
5 Out of levelness over a horizontal plane
SHELL DIA lt48 (1200) 48 - 84 (1200 - 2100) 84- 180 (2100- 4800) gt180 (4800)
TOLERANCE 125 (3mm) 188 (45mm) 25 (6mm) 313(75mm)
Tan-Tan Length Total Max Deviation
lt50rsquo (15240 mm) 5 (13 mm)
50rsquo - 100rsquo
(15240 mm - 30480 mm)
75 (19 mm)
gt100rsquo (30480 mm) 1 (25 mm)
VESSEL DIAMETER lt48 (1200 mm) 48 -84 (1200-2100) 84 - 120 (2100-3000) gt120 ( 3000 mm)
TOLERANCE 06 (15 mm) 125 (3 mm) 188 (5 mm) 25 (6 mm)
inches mm
6 Height of Skirt or Support
Legs
+ 0 (-) 125 + 0 (-) 3
7 Levelness of Support
Lugs
0125 3
8 Bolt Circle Diameter for
Anchor Bolts
0125 3
9 Height of Anchor Chairs 0125 3
782 Appendices
10 Nozzle projection 0125 3
11 Projection of Manhole 025 6
12 Location of Nozzle 0125 3
13 Location of Manhole 025 6
14 Distance beween
matched instrument
connections
004 1
15 Tilt of Nozzle +- 5 Degree
16 Tilt of Manhole +- 1 Degree
17 Permissible deviation of
bolt holes from CL
006 15
18 Orientation of Nozzle 0125 3
19 Orientation of Manhole 025 6
20 Orientation of Clips amp
Gussets
0125 3
21 Location of Stiffening
rings
025 6
22 C-C location of bolt holes
in clips
0125 3
23 Elevation of Tray
Supports from Ref Tan
Line
025 6
24 Location of Downcomer
Support bars from CL
+ 375 (-) 125 + 9 (-) 3
25 Out of level of Tray
Support Rings
See Tolerances for Trays
26 Distance beween trays or
DC Clearance
0125 3
27 Weir height 006 15
28 Levelness of Downcomer
Supports
0125 3
Appendices 783
784 Appendices
Tolerance for Horizontal Vessels
Notes
1 Minimum thickness as specified2 Out of roundness is defined by ASME VIII-1 Para
UG 80 and is +- 1 of the diameter The followingtolerances are recommended to provide strictercontrol of diametral difference
3 Distance between Reference Line and far end ofshell
4 Deviation from horizontal plane
5 Maximum Permissible Bow lt15 of lengthlt15 (40 mm) (See also Table for Maximum Bow)
6 Out of levelness of supports
Shell dia lt48 (1200) 48 - 84 (1200 - 2100) gt84 (2100)
Tolerance 125 (3) 188 (45) 25 (6)
Vessel Diameter lt 48 (1200 mm) 48 -84 (1200-2100) 84 - 120 (2100-3000) gt120 (3000 mm)
Tolerance 06 (15 mm) 125 (3 mm) 188 (5 mm) 25 (6 mm)
Shell Length lt 50rsquo (15000) gt50rsquo (15000)
Tolerance 015Ft (1 mmM) 01Ft (8 mm M)
+- inches +- mm
7 Height of supports 013 3
8 Distance between hole centers for Anchor Bolts 006 15
9 Distance between supports 013 3
10 Distance from CL Support to Reference Tangent Line 013 3
11 Nozzle projection 013 3
12 Projection of Manhole 025 6
13 Location of Nozzle 013 3
14 Location of Manhole 025 6
15 Distance beween matched instrument connections 004 1
16 Tilt of Nozzle +- 5 Degree
17 Tilt of Manhole +- 1 Degree
(Continued)
Appendices 785
Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
18 Permissible deviation of bolt holes from CL 004 1
19 Location of Nozzle from CL 013 3
20 Location of Manhole from CL 025 6
21 Location of bolt holes of clip from CL 013 3
22 Location of clips and stiffening rings from Reference
Tangent Line
025 6
23 Projection of bolt holes in clips from CL 013 3
786 Appendices
Maximum Permissible Bow
Table N-1Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
Note Item DescriptionNotes
Tolerance
INCHES mm
1 Sub-Assy Length
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 6
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 6
gt15 gt4575 +- 5 +- 6
2 Manways From Reference Tangent Line +-0375 +- 10
3 First Tray Elevation +- 25 +- 6
4 Tray Spacing Non-Cumulative +- 125 +- 3
5 Nozzle Above Tray +- 125 +- 3
6 Tray Spacing At Girth Seam Sub-Assembly +- 375 +- 10
7 Nozzle Clips amp
Elevations
LENGTH
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 3
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 10
15-20 4575-6100 +- 5 +- 13
20-40 6100-12200 +- 75 +- 19
40-80 12200-24400 +- 1 +- 25
80-160 24400-48800 +- 15 +- 38
gt160 gt48800 +- 75 +- 75
8 Out of level Slope For Skirt Diameter gt20rsquo (6 M) 1500 1500
9 Anchor Bolt Circle 5 (12 mm) Max Total +- 25 +- 6
10 Bolt Hole Location-
Clips
Non-Cumulative +- 25 +- 6
Appendices 787
Table N-2US units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (Ft)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bow
lt48 48 to 72 72 to 96 gt96
lt10 012 009 006 006
10-20 025 018 015 01
20-30 035 025 023 015
30-40 05 034 03 02
40-50 06 04 035 025
50-60 07 05 04 03
60-70 085 06 045 035
70-80 1 067 053 04
80-90 11 08 06 045
90-100 12 09 067 05
gt100 15 1 075 055
Table N-3Metric units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (mm)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bows
lt1200 1200-1800 1800-2400 gt2400
lt3000 4 24 16 16
3000-6000 8 47 4 24
6000-9000 11 8 55 4
9000-12000 15 10 8 47
12000-15000 19 13 95 6
15000-18000 23 15 11 8
18000-21000 27 17 135 9
21000-24000 30 21 15 10
24000-27000 34 23 17 11
gt27000 38 25 19 13
788 Appendices
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
Appendices 789
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
1 The Master Reference Line (MRL) shall be estab-lished by the vessel manufacturer and clearlymarked inside and outside of the vessel prior toattaching the bottom head It shall be parallel to theroot land of the bottom seam weld and perpendic-ular to the longitudinal axis of the vessel
2 The working elevation of a tray support ring shall bethe elevation specified on the outline drawing Itshall be a level plane parallel to the MRL
3 The distance from the MRL to the working elevationof any tray support ring shall be within +- 14 in(6mm) of the nominal distance
4 The distance between the working elevations ofany two adjacent tray support rings shall be within+- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance and theaccumulated tolerances between tray support ringsshall not exceed the tolerances in Note 3
5 The highest and lowest points of a tray support ringmeasured adjacent to the vessel shell shall notexceed the following deviations from the workingelevations
6 Tray support rings shall not have a wavinessexceeding 116 in (15mm) for any 1 foot(300mm) of circumferential length
7 Tilt of a tray support ring over its width shall notexceed 116 in (15mm)
8 Orientation of the downcomer centerline shall bewithin 18 in (3mm) of its nominal distance fromthe Vessel Reference Centerline VRC for vesselsup to 72 in (1800mm) dia and within frac14rdquo (6mm)for vessels over 72 in (1800mm) dia
9 Distance from downcomer support bar toVRC shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) of thenominal distance On a multipass tray the distance
between downcomer support bars shall also bewithin +- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance
10 Deviation from nominal distance between down-comer support bars shall be subject to vessel out-of-roundness tolerance Facility for adjustmentmust be provided in the downcomer and weirplates
11 Tilt of downcomer support bars over its width shallnot exceed 116 in (15mm)
12 Distance between top of downcomer (weir) supportbar and top of tray support ring shall be within+- 116 in (15mm) of the nominal distance
13 Tray decks shall have a flat surface within 116 in(15mm) measured across a 1 ft (300mm) squaresurface
14 The difference in height between the highest andlowest points of the weir measured to a levelplane shall not exceed
15 Clearance between bottom of downcomer and topof tray or seal pan below shall not deviate from thenominal clearance by more than
16 The bowing of a downcomer in a horizontal planeshall not deviate from the straight by more than+- 18 in (3mm)
17 Downcomer horizontal clearances measured fromthe bottom edge of downcomer to recessed seal panor inlet weir shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) ofnominal
Vessel Dia Tolerance
48rdquo (1200 mm) and smaller 116rdquo (15 mm)
48rdquo to 84rdquo (1200 e 2100 mm) 332rdquo (25 mm)
Over 84rdquo 18rdquo (3 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo 14rdquo (6 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller +- 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) +- 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo +- 14rdquo (6 mm)
790 Appendices
Figure N-1 Maximum permissible deviation from a circular form e for vessels under external pressure SourceReprinted by permission of ASME
Figure N-2 Example of differences between maximum and minimum inside diameters in cylindrical conical andspherical shells Source Reprinted by permission of ASME
Appendices 791
Tolerances for Shape of Heads
792 Appendices
Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Appendix L Vessel Surge Capacities and Hold-Up Times
Figure L-2 Nomograph to find shell length for desired holding time Reprinted by permission of Gulf Publishing Co
Figure L-1 Nomograph to find drum size for holding time Reprinted by permission of Gulf Publishing Co
Appendices 779
Appendix M Minor Defect Evaluation Procedure
780 Appendices
Appendix N Tolerances
Appendices 781
Tolerance for Vertical Vessels
Notes
1 Minimum thickness as specified2 Out of roundness is defined by ASME VIII-1 Para
UG 80 and is +- 1 of the diameter The followingtolerances are recommended to provide strictercontrol of diametral difference
3 Distance from reference tangent line and top flangeFace 0015 in Ft (1mm 1m) lt 05 in (12mm)
4 Shell amp skirt tolerance Max slope from straightline is 0125 in 10 feet (3mm 3050mm) The totalmaximum deviation allowed is as follows (also seetable for maximum permissible bow)
5 Out of levelness over a horizontal plane
SHELL DIA lt48 (1200) 48 - 84 (1200 - 2100) 84- 180 (2100- 4800) gt180 (4800)
TOLERANCE 125 (3mm) 188 (45mm) 25 (6mm) 313(75mm)
Tan-Tan Length Total Max Deviation
lt50rsquo (15240 mm) 5 (13 mm)
50rsquo - 100rsquo
(15240 mm - 30480 mm)
75 (19 mm)
gt100rsquo (30480 mm) 1 (25 mm)
VESSEL DIAMETER lt48 (1200 mm) 48 -84 (1200-2100) 84 - 120 (2100-3000) gt120 ( 3000 mm)
TOLERANCE 06 (15 mm) 125 (3 mm) 188 (5 mm) 25 (6 mm)
inches mm
6 Height of Skirt or Support
Legs
+ 0 (-) 125 + 0 (-) 3
7 Levelness of Support
Lugs
0125 3
8 Bolt Circle Diameter for
Anchor Bolts
0125 3
9 Height of Anchor Chairs 0125 3
782 Appendices
10 Nozzle projection 0125 3
11 Projection of Manhole 025 6
12 Location of Nozzle 0125 3
13 Location of Manhole 025 6
14 Distance beween
matched instrument
connections
004 1
15 Tilt of Nozzle +- 5 Degree
16 Tilt of Manhole +- 1 Degree
17 Permissible deviation of
bolt holes from CL
006 15
18 Orientation of Nozzle 0125 3
19 Orientation of Manhole 025 6
20 Orientation of Clips amp
Gussets
0125 3
21 Location of Stiffening
rings
025 6
22 C-C location of bolt holes
in clips
0125 3
23 Elevation of Tray
Supports from Ref Tan
Line
025 6
24 Location of Downcomer
Support bars from CL
+ 375 (-) 125 + 9 (-) 3
25 Out of level of Tray
Support Rings
See Tolerances for Trays
26 Distance beween trays or
DC Clearance
0125 3
27 Weir height 006 15
28 Levelness of Downcomer
Supports
0125 3
Appendices 783
784 Appendices
Tolerance for Horizontal Vessels
Notes
1 Minimum thickness as specified2 Out of roundness is defined by ASME VIII-1 Para
UG 80 and is +- 1 of the diameter The followingtolerances are recommended to provide strictercontrol of diametral difference
3 Distance between Reference Line and far end ofshell
4 Deviation from horizontal plane
5 Maximum Permissible Bow lt15 of lengthlt15 (40 mm) (See also Table for Maximum Bow)
6 Out of levelness of supports
Shell dia lt48 (1200) 48 - 84 (1200 - 2100) gt84 (2100)
Tolerance 125 (3) 188 (45) 25 (6)
Vessel Diameter lt 48 (1200 mm) 48 -84 (1200-2100) 84 - 120 (2100-3000) gt120 (3000 mm)
Tolerance 06 (15 mm) 125 (3 mm) 188 (5 mm) 25 (6 mm)
Shell Length lt 50rsquo (15000) gt50rsquo (15000)
Tolerance 015Ft (1 mmM) 01Ft (8 mm M)
+- inches +- mm
7 Height of supports 013 3
8 Distance between hole centers for Anchor Bolts 006 15
9 Distance between supports 013 3
10 Distance from CL Support to Reference Tangent Line 013 3
11 Nozzle projection 013 3
12 Projection of Manhole 025 6
13 Location of Nozzle 013 3
14 Location of Manhole 025 6
15 Distance beween matched instrument connections 004 1
16 Tilt of Nozzle +- 5 Degree
17 Tilt of Manhole +- 1 Degree
(Continued)
Appendices 785
Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
18 Permissible deviation of bolt holes from CL 004 1
19 Location of Nozzle from CL 013 3
20 Location of Manhole from CL 025 6
21 Location of bolt holes of clip from CL 013 3
22 Location of clips and stiffening rings from Reference
Tangent Line
025 6
23 Projection of bolt holes in clips from CL 013 3
786 Appendices
Maximum Permissible Bow
Table N-1Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
Note Item DescriptionNotes
Tolerance
INCHES mm
1 Sub-Assy Length
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 6
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 6
gt15 gt4575 +- 5 +- 6
2 Manways From Reference Tangent Line +-0375 +- 10
3 First Tray Elevation +- 25 +- 6
4 Tray Spacing Non-Cumulative +- 125 +- 3
5 Nozzle Above Tray +- 125 +- 3
6 Tray Spacing At Girth Seam Sub-Assembly +- 375 +- 10
7 Nozzle Clips amp
Elevations
LENGTH
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 3
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 10
15-20 4575-6100 +- 5 +- 13
20-40 6100-12200 +- 75 +- 19
40-80 12200-24400 +- 1 +- 25
80-160 24400-48800 +- 15 +- 38
gt160 gt48800 +- 75 +- 75
8 Out of level Slope For Skirt Diameter gt20rsquo (6 M) 1500 1500
9 Anchor Bolt Circle 5 (12 mm) Max Total +- 25 +- 6
10 Bolt Hole Location-
Clips
Non-Cumulative +- 25 +- 6
Appendices 787
Table N-2US units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (Ft)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bow
lt48 48 to 72 72 to 96 gt96
lt10 012 009 006 006
10-20 025 018 015 01
20-30 035 025 023 015
30-40 05 034 03 02
40-50 06 04 035 025
50-60 07 05 04 03
60-70 085 06 045 035
70-80 1 067 053 04
80-90 11 08 06 045
90-100 12 09 067 05
gt100 15 1 075 055
Table N-3Metric units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (mm)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bows
lt1200 1200-1800 1800-2400 gt2400
lt3000 4 24 16 16
3000-6000 8 47 4 24
6000-9000 11 8 55 4
9000-12000 15 10 8 47
12000-15000 19 13 95 6
15000-18000 23 15 11 8
18000-21000 27 17 135 9
21000-24000 30 21 15 10
24000-27000 34 23 17 11
gt27000 38 25 19 13
788 Appendices
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
Appendices 789
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
1 The Master Reference Line (MRL) shall be estab-lished by the vessel manufacturer and clearlymarked inside and outside of the vessel prior toattaching the bottom head It shall be parallel to theroot land of the bottom seam weld and perpendic-ular to the longitudinal axis of the vessel
2 The working elevation of a tray support ring shall bethe elevation specified on the outline drawing Itshall be a level plane parallel to the MRL
3 The distance from the MRL to the working elevationof any tray support ring shall be within +- 14 in(6mm) of the nominal distance
4 The distance between the working elevations ofany two adjacent tray support rings shall be within+- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance and theaccumulated tolerances between tray support ringsshall not exceed the tolerances in Note 3
5 The highest and lowest points of a tray support ringmeasured adjacent to the vessel shell shall notexceed the following deviations from the workingelevations
6 Tray support rings shall not have a wavinessexceeding 116 in (15mm) for any 1 foot(300mm) of circumferential length
7 Tilt of a tray support ring over its width shall notexceed 116 in (15mm)
8 Orientation of the downcomer centerline shall bewithin 18 in (3mm) of its nominal distance fromthe Vessel Reference Centerline VRC for vesselsup to 72 in (1800mm) dia and within frac14rdquo (6mm)for vessels over 72 in (1800mm) dia
9 Distance from downcomer support bar toVRC shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) of thenominal distance On a multipass tray the distance
between downcomer support bars shall also bewithin +- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance
10 Deviation from nominal distance between down-comer support bars shall be subject to vessel out-of-roundness tolerance Facility for adjustmentmust be provided in the downcomer and weirplates
11 Tilt of downcomer support bars over its width shallnot exceed 116 in (15mm)
12 Distance between top of downcomer (weir) supportbar and top of tray support ring shall be within+- 116 in (15mm) of the nominal distance
13 Tray decks shall have a flat surface within 116 in(15mm) measured across a 1 ft (300mm) squaresurface
14 The difference in height between the highest andlowest points of the weir measured to a levelplane shall not exceed
15 Clearance between bottom of downcomer and topof tray or seal pan below shall not deviate from thenominal clearance by more than
16 The bowing of a downcomer in a horizontal planeshall not deviate from the straight by more than+- 18 in (3mm)
17 Downcomer horizontal clearances measured fromthe bottom edge of downcomer to recessed seal panor inlet weir shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) ofnominal
Vessel Dia Tolerance
48rdquo (1200 mm) and smaller 116rdquo (15 mm)
48rdquo to 84rdquo (1200 e 2100 mm) 332rdquo (25 mm)
Over 84rdquo 18rdquo (3 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo 14rdquo (6 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller +- 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) +- 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo +- 14rdquo (6 mm)
790 Appendices
Figure N-1 Maximum permissible deviation from a circular form e for vessels under external pressure SourceReprinted by permission of ASME
Figure N-2 Example of differences between maximum and minimum inside diameters in cylindrical conical andspherical shells Source Reprinted by permission of ASME
Appendices 791
Tolerances for Shape of Heads
792 Appendices
Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Appendix M Minor Defect Evaluation Procedure
780 Appendices
Appendix N Tolerances
Appendices 781
Tolerance for Vertical Vessels
Notes
1 Minimum thickness as specified2 Out of roundness is defined by ASME VIII-1 Para
UG 80 and is +- 1 of the diameter The followingtolerances are recommended to provide strictercontrol of diametral difference
3 Distance from reference tangent line and top flangeFace 0015 in Ft (1mm 1m) lt 05 in (12mm)
4 Shell amp skirt tolerance Max slope from straightline is 0125 in 10 feet (3mm 3050mm) The totalmaximum deviation allowed is as follows (also seetable for maximum permissible bow)
5 Out of levelness over a horizontal plane
SHELL DIA lt48 (1200) 48 - 84 (1200 - 2100) 84- 180 (2100- 4800) gt180 (4800)
TOLERANCE 125 (3mm) 188 (45mm) 25 (6mm) 313(75mm)
Tan-Tan Length Total Max Deviation
lt50rsquo (15240 mm) 5 (13 mm)
50rsquo - 100rsquo
(15240 mm - 30480 mm)
75 (19 mm)
gt100rsquo (30480 mm) 1 (25 mm)
VESSEL DIAMETER lt48 (1200 mm) 48 -84 (1200-2100) 84 - 120 (2100-3000) gt120 ( 3000 mm)
TOLERANCE 06 (15 mm) 125 (3 mm) 188 (5 mm) 25 (6 mm)
inches mm
6 Height of Skirt or Support
Legs
+ 0 (-) 125 + 0 (-) 3
7 Levelness of Support
Lugs
0125 3
8 Bolt Circle Diameter for
Anchor Bolts
0125 3
9 Height of Anchor Chairs 0125 3
782 Appendices
10 Nozzle projection 0125 3
11 Projection of Manhole 025 6
12 Location of Nozzle 0125 3
13 Location of Manhole 025 6
14 Distance beween
matched instrument
connections
004 1
15 Tilt of Nozzle +- 5 Degree
16 Tilt of Manhole +- 1 Degree
17 Permissible deviation of
bolt holes from CL
006 15
18 Orientation of Nozzle 0125 3
19 Orientation of Manhole 025 6
20 Orientation of Clips amp
Gussets
0125 3
21 Location of Stiffening
rings
025 6
22 C-C location of bolt holes
in clips
0125 3
23 Elevation of Tray
Supports from Ref Tan
Line
025 6
24 Location of Downcomer
Support bars from CL
+ 375 (-) 125 + 9 (-) 3
25 Out of level of Tray
Support Rings
See Tolerances for Trays
26 Distance beween trays or
DC Clearance
0125 3
27 Weir height 006 15
28 Levelness of Downcomer
Supports
0125 3
Appendices 783
784 Appendices
Tolerance for Horizontal Vessels
Notes
1 Minimum thickness as specified2 Out of roundness is defined by ASME VIII-1 Para
UG 80 and is +- 1 of the diameter The followingtolerances are recommended to provide strictercontrol of diametral difference
3 Distance between Reference Line and far end ofshell
4 Deviation from horizontal plane
5 Maximum Permissible Bow lt15 of lengthlt15 (40 mm) (See also Table for Maximum Bow)
6 Out of levelness of supports
Shell dia lt48 (1200) 48 - 84 (1200 - 2100) gt84 (2100)
Tolerance 125 (3) 188 (45) 25 (6)
Vessel Diameter lt 48 (1200 mm) 48 -84 (1200-2100) 84 - 120 (2100-3000) gt120 (3000 mm)
Tolerance 06 (15 mm) 125 (3 mm) 188 (5 mm) 25 (6 mm)
Shell Length lt 50rsquo (15000) gt50rsquo (15000)
Tolerance 015Ft (1 mmM) 01Ft (8 mm M)
+- inches +- mm
7 Height of supports 013 3
8 Distance between hole centers for Anchor Bolts 006 15
9 Distance between supports 013 3
10 Distance from CL Support to Reference Tangent Line 013 3
11 Nozzle projection 013 3
12 Projection of Manhole 025 6
13 Location of Nozzle 013 3
14 Location of Manhole 025 6
15 Distance beween matched instrument connections 004 1
16 Tilt of Nozzle +- 5 Degree
17 Tilt of Manhole +- 1 Degree
(Continued)
Appendices 785
Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
18 Permissible deviation of bolt holes from CL 004 1
19 Location of Nozzle from CL 013 3
20 Location of Manhole from CL 025 6
21 Location of bolt holes of clip from CL 013 3
22 Location of clips and stiffening rings from Reference
Tangent Line
025 6
23 Projection of bolt holes in clips from CL 013 3
786 Appendices
Maximum Permissible Bow
Table N-1Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
Note Item DescriptionNotes
Tolerance
INCHES mm
1 Sub-Assy Length
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 6
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 6
gt15 gt4575 +- 5 +- 6
2 Manways From Reference Tangent Line +-0375 +- 10
3 First Tray Elevation +- 25 +- 6
4 Tray Spacing Non-Cumulative +- 125 +- 3
5 Nozzle Above Tray +- 125 +- 3
6 Tray Spacing At Girth Seam Sub-Assembly +- 375 +- 10
7 Nozzle Clips amp
Elevations
LENGTH
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 3
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 10
15-20 4575-6100 +- 5 +- 13
20-40 6100-12200 +- 75 +- 19
40-80 12200-24400 +- 1 +- 25
80-160 24400-48800 +- 15 +- 38
gt160 gt48800 +- 75 +- 75
8 Out of level Slope For Skirt Diameter gt20rsquo (6 M) 1500 1500
9 Anchor Bolt Circle 5 (12 mm) Max Total +- 25 +- 6
10 Bolt Hole Location-
Clips
Non-Cumulative +- 25 +- 6
Appendices 787
Table N-2US units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (Ft)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bow
lt48 48 to 72 72 to 96 gt96
lt10 012 009 006 006
10-20 025 018 015 01
20-30 035 025 023 015
30-40 05 034 03 02
40-50 06 04 035 025
50-60 07 05 04 03
60-70 085 06 045 035
70-80 1 067 053 04
80-90 11 08 06 045
90-100 12 09 067 05
gt100 15 1 075 055
Table N-3Metric units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (mm)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bows
lt1200 1200-1800 1800-2400 gt2400
lt3000 4 24 16 16
3000-6000 8 47 4 24
6000-9000 11 8 55 4
9000-12000 15 10 8 47
12000-15000 19 13 95 6
15000-18000 23 15 11 8
18000-21000 27 17 135 9
21000-24000 30 21 15 10
24000-27000 34 23 17 11
gt27000 38 25 19 13
788 Appendices
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
Appendices 789
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
1 The Master Reference Line (MRL) shall be estab-lished by the vessel manufacturer and clearlymarked inside and outside of the vessel prior toattaching the bottom head It shall be parallel to theroot land of the bottom seam weld and perpendic-ular to the longitudinal axis of the vessel
2 The working elevation of a tray support ring shall bethe elevation specified on the outline drawing Itshall be a level plane parallel to the MRL
3 The distance from the MRL to the working elevationof any tray support ring shall be within +- 14 in(6mm) of the nominal distance
4 The distance between the working elevations ofany two adjacent tray support rings shall be within+- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance and theaccumulated tolerances between tray support ringsshall not exceed the tolerances in Note 3
5 The highest and lowest points of a tray support ringmeasured adjacent to the vessel shell shall notexceed the following deviations from the workingelevations
6 Tray support rings shall not have a wavinessexceeding 116 in (15mm) for any 1 foot(300mm) of circumferential length
7 Tilt of a tray support ring over its width shall notexceed 116 in (15mm)
8 Orientation of the downcomer centerline shall bewithin 18 in (3mm) of its nominal distance fromthe Vessel Reference Centerline VRC for vesselsup to 72 in (1800mm) dia and within frac14rdquo (6mm)for vessels over 72 in (1800mm) dia
9 Distance from downcomer support bar toVRC shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) of thenominal distance On a multipass tray the distance
between downcomer support bars shall also bewithin +- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance
10 Deviation from nominal distance between down-comer support bars shall be subject to vessel out-of-roundness tolerance Facility for adjustmentmust be provided in the downcomer and weirplates
11 Tilt of downcomer support bars over its width shallnot exceed 116 in (15mm)
12 Distance between top of downcomer (weir) supportbar and top of tray support ring shall be within+- 116 in (15mm) of the nominal distance
13 Tray decks shall have a flat surface within 116 in(15mm) measured across a 1 ft (300mm) squaresurface
14 The difference in height between the highest andlowest points of the weir measured to a levelplane shall not exceed
15 Clearance between bottom of downcomer and topof tray or seal pan below shall not deviate from thenominal clearance by more than
16 The bowing of a downcomer in a horizontal planeshall not deviate from the straight by more than+- 18 in (3mm)
17 Downcomer horizontal clearances measured fromthe bottom edge of downcomer to recessed seal panor inlet weir shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) ofnominal
Vessel Dia Tolerance
48rdquo (1200 mm) and smaller 116rdquo (15 mm)
48rdquo to 84rdquo (1200 e 2100 mm) 332rdquo (25 mm)
Over 84rdquo 18rdquo (3 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo 14rdquo (6 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller +- 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) +- 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo +- 14rdquo (6 mm)
790 Appendices
Figure N-1 Maximum permissible deviation from a circular form e for vessels under external pressure SourceReprinted by permission of ASME
Figure N-2 Example of differences between maximum and minimum inside diameters in cylindrical conical andspherical shells Source Reprinted by permission of ASME
Appendices 791
Tolerances for Shape of Heads
792 Appendices
Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Appendix N Tolerances
Appendices 781
Tolerance for Vertical Vessels
Notes
1 Minimum thickness as specified2 Out of roundness is defined by ASME VIII-1 Para
UG 80 and is +- 1 of the diameter The followingtolerances are recommended to provide strictercontrol of diametral difference
3 Distance from reference tangent line and top flangeFace 0015 in Ft (1mm 1m) lt 05 in (12mm)
4 Shell amp skirt tolerance Max slope from straightline is 0125 in 10 feet (3mm 3050mm) The totalmaximum deviation allowed is as follows (also seetable for maximum permissible bow)
5 Out of levelness over a horizontal plane
SHELL DIA lt48 (1200) 48 - 84 (1200 - 2100) 84- 180 (2100- 4800) gt180 (4800)
TOLERANCE 125 (3mm) 188 (45mm) 25 (6mm) 313(75mm)
Tan-Tan Length Total Max Deviation
lt50rsquo (15240 mm) 5 (13 mm)
50rsquo - 100rsquo
(15240 mm - 30480 mm)
75 (19 mm)
gt100rsquo (30480 mm) 1 (25 mm)
VESSEL DIAMETER lt48 (1200 mm) 48 -84 (1200-2100) 84 - 120 (2100-3000) gt120 ( 3000 mm)
TOLERANCE 06 (15 mm) 125 (3 mm) 188 (5 mm) 25 (6 mm)
inches mm
6 Height of Skirt or Support
Legs
+ 0 (-) 125 + 0 (-) 3
7 Levelness of Support
Lugs
0125 3
8 Bolt Circle Diameter for
Anchor Bolts
0125 3
9 Height of Anchor Chairs 0125 3
782 Appendices
10 Nozzle projection 0125 3
11 Projection of Manhole 025 6
12 Location of Nozzle 0125 3
13 Location of Manhole 025 6
14 Distance beween
matched instrument
connections
004 1
15 Tilt of Nozzle +- 5 Degree
16 Tilt of Manhole +- 1 Degree
17 Permissible deviation of
bolt holes from CL
006 15
18 Orientation of Nozzle 0125 3
19 Orientation of Manhole 025 6
20 Orientation of Clips amp
Gussets
0125 3
21 Location of Stiffening
rings
025 6
22 C-C location of bolt holes
in clips
0125 3
23 Elevation of Tray
Supports from Ref Tan
Line
025 6
24 Location of Downcomer
Support bars from CL
+ 375 (-) 125 + 9 (-) 3
25 Out of level of Tray
Support Rings
See Tolerances for Trays
26 Distance beween trays or
DC Clearance
0125 3
27 Weir height 006 15
28 Levelness of Downcomer
Supports
0125 3
Appendices 783
784 Appendices
Tolerance for Horizontal Vessels
Notes
1 Minimum thickness as specified2 Out of roundness is defined by ASME VIII-1 Para
UG 80 and is +- 1 of the diameter The followingtolerances are recommended to provide strictercontrol of diametral difference
3 Distance between Reference Line and far end ofshell
4 Deviation from horizontal plane
5 Maximum Permissible Bow lt15 of lengthlt15 (40 mm) (See also Table for Maximum Bow)
6 Out of levelness of supports
Shell dia lt48 (1200) 48 - 84 (1200 - 2100) gt84 (2100)
Tolerance 125 (3) 188 (45) 25 (6)
Vessel Diameter lt 48 (1200 mm) 48 -84 (1200-2100) 84 - 120 (2100-3000) gt120 (3000 mm)
Tolerance 06 (15 mm) 125 (3 mm) 188 (5 mm) 25 (6 mm)
Shell Length lt 50rsquo (15000) gt50rsquo (15000)
Tolerance 015Ft (1 mmM) 01Ft (8 mm M)
+- inches +- mm
7 Height of supports 013 3
8 Distance between hole centers for Anchor Bolts 006 15
9 Distance between supports 013 3
10 Distance from CL Support to Reference Tangent Line 013 3
11 Nozzle projection 013 3
12 Projection of Manhole 025 6
13 Location of Nozzle 013 3
14 Location of Manhole 025 6
15 Distance beween matched instrument connections 004 1
16 Tilt of Nozzle +- 5 Degree
17 Tilt of Manhole +- 1 Degree
(Continued)
Appendices 785
Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
18 Permissible deviation of bolt holes from CL 004 1
19 Location of Nozzle from CL 013 3
20 Location of Manhole from CL 025 6
21 Location of bolt holes of clip from CL 013 3
22 Location of clips and stiffening rings from Reference
Tangent Line
025 6
23 Projection of bolt holes in clips from CL 013 3
786 Appendices
Maximum Permissible Bow
Table N-1Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
Note Item DescriptionNotes
Tolerance
INCHES mm
1 Sub-Assy Length
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 6
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 6
gt15 gt4575 +- 5 +- 6
2 Manways From Reference Tangent Line +-0375 +- 10
3 First Tray Elevation +- 25 +- 6
4 Tray Spacing Non-Cumulative +- 125 +- 3
5 Nozzle Above Tray +- 125 +- 3
6 Tray Spacing At Girth Seam Sub-Assembly +- 375 +- 10
7 Nozzle Clips amp
Elevations
LENGTH
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 3
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 10
15-20 4575-6100 +- 5 +- 13
20-40 6100-12200 +- 75 +- 19
40-80 12200-24400 +- 1 +- 25
80-160 24400-48800 +- 15 +- 38
gt160 gt48800 +- 75 +- 75
8 Out of level Slope For Skirt Diameter gt20rsquo (6 M) 1500 1500
9 Anchor Bolt Circle 5 (12 mm) Max Total +- 25 +- 6
10 Bolt Hole Location-
Clips
Non-Cumulative +- 25 +- 6
Appendices 787
Table N-2US units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (Ft)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bow
lt48 48 to 72 72 to 96 gt96
lt10 012 009 006 006
10-20 025 018 015 01
20-30 035 025 023 015
30-40 05 034 03 02
40-50 06 04 035 025
50-60 07 05 04 03
60-70 085 06 045 035
70-80 1 067 053 04
80-90 11 08 06 045
90-100 12 09 067 05
gt100 15 1 075 055
Table N-3Metric units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (mm)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bows
lt1200 1200-1800 1800-2400 gt2400
lt3000 4 24 16 16
3000-6000 8 47 4 24
6000-9000 11 8 55 4
9000-12000 15 10 8 47
12000-15000 19 13 95 6
15000-18000 23 15 11 8
18000-21000 27 17 135 9
21000-24000 30 21 15 10
24000-27000 34 23 17 11
gt27000 38 25 19 13
788 Appendices
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
Appendices 789
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
1 The Master Reference Line (MRL) shall be estab-lished by the vessel manufacturer and clearlymarked inside and outside of the vessel prior toattaching the bottom head It shall be parallel to theroot land of the bottom seam weld and perpendic-ular to the longitudinal axis of the vessel
2 The working elevation of a tray support ring shall bethe elevation specified on the outline drawing Itshall be a level plane parallel to the MRL
3 The distance from the MRL to the working elevationof any tray support ring shall be within +- 14 in(6mm) of the nominal distance
4 The distance between the working elevations ofany two adjacent tray support rings shall be within+- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance and theaccumulated tolerances between tray support ringsshall not exceed the tolerances in Note 3
5 The highest and lowest points of a tray support ringmeasured adjacent to the vessel shell shall notexceed the following deviations from the workingelevations
6 Tray support rings shall not have a wavinessexceeding 116 in (15mm) for any 1 foot(300mm) of circumferential length
7 Tilt of a tray support ring over its width shall notexceed 116 in (15mm)
8 Orientation of the downcomer centerline shall bewithin 18 in (3mm) of its nominal distance fromthe Vessel Reference Centerline VRC for vesselsup to 72 in (1800mm) dia and within frac14rdquo (6mm)for vessels over 72 in (1800mm) dia
9 Distance from downcomer support bar toVRC shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) of thenominal distance On a multipass tray the distance
between downcomer support bars shall also bewithin +- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance
10 Deviation from nominal distance between down-comer support bars shall be subject to vessel out-of-roundness tolerance Facility for adjustmentmust be provided in the downcomer and weirplates
11 Tilt of downcomer support bars over its width shallnot exceed 116 in (15mm)
12 Distance between top of downcomer (weir) supportbar and top of tray support ring shall be within+- 116 in (15mm) of the nominal distance
13 Tray decks shall have a flat surface within 116 in(15mm) measured across a 1 ft (300mm) squaresurface
14 The difference in height between the highest andlowest points of the weir measured to a levelplane shall not exceed
15 Clearance between bottom of downcomer and topof tray or seal pan below shall not deviate from thenominal clearance by more than
16 The bowing of a downcomer in a horizontal planeshall not deviate from the straight by more than+- 18 in (3mm)
17 Downcomer horizontal clearances measured fromthe bottom edge of downcomer to recessed seal panor inlet weir shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) ofnominal
Vessel Dia Tolerance
48rdquo (1200 mm) and smaller 116rdquo (15 mm)
48rdquo to 84rdquo (1200 e 2100 mm) 332rdquo (25 mm)
Over 84rdquo 18rdquo (3 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo 14rdquo (6 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller +- 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) +- 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo +- 14rdquo (6 mm)
790 Appendices
Figure N-1 Maximum permissible deviation from a circular form e for vessels under external pressure SourceReprinted by permission of ASME
Figure N-2 Example of differences between maximum and minimum inside diameters in cylindrical conical andspherical shells Source Reprinted by permission of ASME
Appendices 791
Tolerances for Shape of Heads
792 Appendices
Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Tolerance for Vertical Vessels
Notes
1 Minimum thickness as specified2 Out of roundness is defined by ASME VIII-1 Para
UG 80 and is +- 1 of the diameter The followingtolerances are recommended to provide strictercontrol of diametral difference
3 Distance from reference tangent line and top flangeFace 0015 in Ft (1mm 1m) lt 05 in (12mm)
4 Shell amp skirt tolerance Max slope from straightline is 0125 in 10 feet (3mm 3050mm) The totalmaximum deviation allowed is as follows (also seetable for maximum permissible bow)
5 Out of levelness over a horizontal plane
SHELL DIA lt48 (1200) 48 - 84 (1200 - 2100) 84- 180 (2100- 4800) gt180 (4800)
TOLERANCE 125 (3mm) 188 (45mm) 25 (6mm) 313(75mm)
Tan-Tan Length Total Max Deviation
lt50rsquo (15240 mm) 5 (13 mm)
50rsquo - 100rsquo
(15240 mm - 30480 mm)
75 (19 mm)
gt100rsquo (30480 mm) 1 (25 mm)
VESSEL DIAMETER lt48 (1200 mm) 48 -84 (1200-2100) 84 - 120 (2100-3000) gt120 ( 3000 mm)
TOLERANCE 06 (15 mm) 125 (3 mm) 188 (5 mm) 25 (6 mm)
inches mm
6 Height of Skirt or Support
Legs
+ 0 (-) 125 + 0 (-) 3
7 Levelness of Support
Lugs
0125 3
8 Bolt Circle Diameter for
Anchor Bolts
0125 3
9 Height of Anchor Chairs 0125 3
782 Appendices
10 Nozzle projection 0125 3
11 Projection of Manhole 025 6
12 Location of Nozzle 0125 3
13 Location of Manhole 025 6
14 Distance beween
matched instrument
connections
004 1
15 Tilt of Nozzle +- 5 Degree
16 Tilt of Manhole +- 1 Degree
17 Permissible deviation of
bolt holes from CL
006 15
18 Orientation of Nozzle 0125 3
19 Orientation of Manhole 025 6
20 Orientation of Clips amp
Gussets
0125 3
21 Location of Stiffening
rings
025 6
22 C-C location of bolt holes
in clips
0125 3
23 Elevation of Tray
Supports from Ref Tan
Line
025 6
24 Location of Downcomer
Support bars from CL
+ 375 (-) 125 + 9 (-) 3
25 Out of level of Tray
Support Rings
See Tolerances for Trays
26 Distance beween trays or
DC Clearance
0125 3
27 Weir height 006 15
28 Levelness of Downcomer
Supports
0125 3
Appendices 783
784 Appendices
Tolerance for Horizontal Vessels
Notes
1 Minimum thickness as specified2 Out of roundness is defined by ASME VIII-1 Para
UG 80 and is +- 1 of the diameter The followingtolerances are recommended to provide strictercontrol of diametral difference
3 Distance between Reference Line and far end ofshell
4 Deviation from horizontal plane
5 Maximum Permissible Bow lt15 of lengthlt15 (40 mm) (See also Table for Maximum Bow)
6 Out of levelness of supports
Shell dia lt48 (1200) 48 - 84 (1200 - 2100) gt84 (2100)
Tolerance 125 (3) 188 (45) 25 (6)
Vessel Diameter lt 48 (1200 mm) 48 -84 (1200-2100) 84 - 120 (2100-3000) gt120 (3000 mm)
Tolerance 06 (15 mm) 125 (3 mm) 188 (5 mm) 25 (6 mm)
Shell Length lt 50rsquo (15000) gt50rsquo (15000)
Tolerance 015Ft (1 mmM) 01Ft (8 mm M)
+- inches +- mm
7 Height of supports 013 3
8 Distance between hole centers for Anchor Bolts 006 15
9 Distance between supports 013 3
10 Distance from CL Support to Reference Tangent Line 013 3
11 Nozzle projection 013 3
12 Projection of Manhole 025 6
13 Location of Nozzle 013 3
14 Location of Manhole 025 6
15 Distance beween matched instrument connections 004 1
16 Tilt of Nozzle +- 5 Degree
17 Tilt of Manhole +- 1 Degree
(Continued)
Appendices 785
Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
18 Permissible deviation of bolt holes from CL 004 1
19 Location of Nozzle from CL 013 3
20 Location of Manhole from CL 025 6
21 Location of bolt holes of clip from CL 013 3
22 Location of clips and stiffening rings from Reference
Tangent Line
025 6
23 Projection of bolt holes in clips from CL 013 3
786 Appendices
Maximum Permissible Bow
Table N-1Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
Note Item DescriptionNotes
Tolerance
INCHES mm
1 Sub-Assy Length
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 6
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 6
gt15 gt4575 +- 5 +- 6
2 Manways From Reference Tangent Line +-0375 +- 10
3 First Tray Elevation +- 25 +- 6
4 Tray Spacing Non-Cumulative +- 125 +- 3
5 Nozzle Above Tray +- 125 +- 3
6 Tray Spacing At Girth Seam Sub-Assembly +- 375 +- 10
7 Nozzle Clips amp
Elevations
LENGTH
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 3
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 10
15-20 4575-6100 +- 5 +- 13
20-40 6100-12200 +- 75 +- 19
40-80 12200-24400 +- 1 +- 25
80-160 24400-48800 +- 15 +- 38
gt160 gt48800 +- 75 +- 75
8 Out of level Slope For Skirt Diameter gt20rsquo (6 M) 1500 1500
9 Anchor Bolt Circle 5 (12 mm) Max Total +- 25 +- 6
10 Bolt Hole Location-
Clips
Non-Cumulative +- 25 +- 6
Appendices 787
Table N-2US units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (Ft)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bow
lt48 48 to 72 72 to 96 gt96
lt10 012 009 006 006
10-20 025 018 015 01
20-30 035 025 023 015
30-40 05 034 03 02
40-50 06 04 035 025
50-60 07 05 04 03
60-70 085 06 045 035
70-80 1 067 053 04
80-90 11 08 06 045
90-100 12 09 067 05
gt100 15 1 075 055
Table N-3Metric units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (mm)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bows
lt1200 1200-1800 1800-2400 gt2400
lt3000 4 24 16 16
3000-6000 8 47 4 24
6000-9000 11 8 55 4
9000-12000 15 10 8 47
12000-15000 19 13 95 6
15000-18000 23 15 11 8
18000-21000 27 17 135 9
21000-24000 30 21 15 10
24000-27000 34 23 17 11
gt27000 38 25 19 13
788 Appendices
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
Appendices 789
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
1 The Master Reference Line (MRL) shall be estab-lished by the vessel manufacturer and clearlymarked inside and outside of the vessel prior toattaching the bottom head It shall be parallel to theroot land of the bottom seam weld and perpendic-ular to the longitudinal axis of the vessel
2 The working elevation of a tray support ring shall bethe elevation specified on the outline drawing Itshall be a level plane parallel to the MRL
3 The distance from the MRL to the working elevationof any tray support ring shall be within +- 14 in(6mm) of the nominal distance
4 The distance between the working elevations ofany two adjacent tray support rings shall be within+- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance and theaccumulated tolerances between tray support ringsshall not exceed the tolerances in Note 3
5 The highest and lowest points of a tray support ringmeasured adjacent to the vessel shell shall notexceed the following deviations from the workingelevations
6 Tray support rings shall not have a wavinessexceeding 116 in (15mm) for any 1 foot(300mm) of circumferential length
7 Tilt of a tray support ring over its width shall notexceed 116 in (15mm)
8 Orientation of the downcomer centerline shall bewithin 18 in (3mm) of its nominal distance fromthe Vessel Reference Centerline VRC for vesselsup to 72 in (1800mm) dia and within frac14rdquo (6mm)for vessels over 72 in (1800mm) dia
9 Distance from downcomer support bar toVRC shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) of thenominal distance On a multipass tray the distance
between downcomer support bars shall also bewithin +- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance
10 Deviation from nominal distance between down-comer support bars shall be subject to vessel out-of-roundness tolerance Facility for adjustmentmust be provided in the downcomer and weirplates
11 Tilt of downcomer support bars over its width shallnot exceed 116 in (15mm)
12 Distance between top of downcomer (weir) supportbar and top of tray support ring shall be within+- 116 in (15mm) of the nominal distance
13 Tray decks shall have a flat surface within 116 in(15mm) measured across a 1 ft (300mm) squaresurface
14 The difference in height between the highest andlowest points of the weir measured to a levelplane shall not exceed
15 Clearance between bottom of downcomer and topof tray or seal pan below shall not deviate from thenominal clearance by more than
16 The bowing of a downcomer in a horizontal planeshall not deviate from the straight by more than+- 18 in (3mm)
17 Downcomer horizontal clearances measured fromthe bottom edge of downcomer to recessed seal panor inlet weir shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) ofnominal
Vessel Dia Tolerance
48rdquo (1200 mm) and smaller 116rdquo (15 mm)
48rdquo to 84rdquo (1200 e 2100 mm) 332rdquo (25 mm)
Over 84rdquo 18rdquo (3 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo 14rdquo (6 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller +- 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) +- 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo +- 14rdquo (6 mm)
790 Appendices
Figure N-1 Maximum permissible deviation from a circular form e for vessels under external pressure SourceReprinted by permission of ASME
Figure N-2 Example of differences between maximum and minimum inside diameters in cylindrical conical andspherical shells Source Reprinted by permission of ASME
Appendices 791
Tolerances for Shape of Heads
792 Appendices
Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

10 Nozzle projection 0125 3
11 Projection of Manhole 025 6
12 Location of Nozzle 0125 3
13 Location of Manhole 025 6
14 Distance beween
matched instrument
connections
004 1
15 Tilt of Nozzle +- 5 Degree
16 Tilt of Manhole +- 1 Degree
17 Permissible deviation of
bolt holes from CL
006 15
18 Orientation of Nozzle 0125 3
19 Orientation of Manhole 025 6
20 Orientation of Clips amp
Gussets
0125 3
21 Location of Stiffening
rings
025 6
22 C-C location of bolt holes
in clips
0125 3
23 Elevation of Tray
Supports from Ref Tan
Line
025 6
24 Location of Downcomer
Support bars from CL
+ 375 (-) 125 + 9 (-) 3
25 Out of level of Tray
Support Rings
See Tolerances for Trays
26 Distance beween trays or
DC Clearance
0125 3
27 Weir height 006 15
28 Levelness of Downcomer
Supports
0125 3
Appendices 783
784 Appendices
Tolerance for Horizontal Vessels
Notes
1 Minimum thickness as specified2 Out of roundness is defined by ASME VIII-1 Para
UG 80 and is +- 1 of the diameter The followingtolerances are recommended to provide strictercontrol of diametral difference
3 Distance between Reference Line and far end ofshell
4 Deviation from horizontal plane
5 Maximum Permissible Bow lt15 of lengthlt15 (40 mm) (See also Table for Maximum Bow)
6 Out of levelness of supports
Shell dia lt48 (1200) 48 - 84 (1200 - 2100) gt84 (2100)
Tolerance 125 (3) 188 (45) 25 (6)
Vessel Diameter lt 48 (1200 mm) 48 -84 (1200-2100) 84 - 120 (2100-3000) gt120 (3000 mm)
Tolerance 06 (15 mm) 125 (3 mm) 188 (5 mm) 25 (6 mm)
Shell Length lt 50rsquo (15000) gt50rsquo (15000)
Tolerance 015Ft (1 mmM) 01Ft (8 mm M)
+- inches +- mm
7 Height of supports 013 3
8 Distance between hole centers for Anchor Bolts 006 15
9 Distance between supports 013 3
10 Distance from CL Support to Reference Tangent Line 013 3
11 Nozzle projection 013 3
12 Projection of Manhole 025 6
13 Location of Nozzle 013 3
14 Location of Manhole 025 6
15 Distance beween matched instrument connections 004 1
16 Tilt of Nozzle +- 5 Degree
17 Tilt of Manhole +- 1 Degree
(Continued)
Appendices 785
Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
18 Permissible deviation of bolt holes from CL 004 1
19 Location of Nozzle from CL 013 3
20 Location of Manhole from CL 025 6
21 Location of bolt holes of clip from CL 013 3
22 Location of clips and stiffening rings from Reference
Tangent Line
025 6
23 Projection of bolt holes in clips from CL 013 3
786 Appendices
Maximum Permissible Bow
Table N-1Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
Note Item DescriptionNotes
Tolerance
INCHES mm
1 Sub-Assy Length
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 6
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 6
gt15 gt4575 +- 5 +- 6
2 Manways From Reference Tangent Line +-0375 +- 10
3 First Tray Elevation +- 25 +- 6
4 Tray Spacing Non-Cumulative +- 125 +- 3
5 Nozzle Above Tray +- 125 +- 3
6 Tray Spacing At Girth Seam Sub-Assembly +- 375 +- 10
7 Nozzle Clips amp
Elevations
LENGTH
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 3
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 10
15-20 4575-6100 +- 5 +- 13
20-40 6100-12200 +- 75 +- 19
40-80 12200-24400 +- 1 +- 25
80-160 24400-48800 +- 15 +- 38
gt160 gt48800 +- 75 +- 75
8 Out of level Slope For Skirt Diameter gt20rsquo (6 M) 1500 1500
9 Anchor Bolt Circle 5 (12 mm) Max Total +- 25 +- 6
10 Bolt Hole Location-
Clips
Non-Cumulative +- 25 +- 6
Appendices 787
Table N-2US units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (Ft)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bow
lt48 48 to 72 72 to 96 gt96
lt10 012 009 006 006
10-20 025 018 015 01
20-30 035 025 023 015
30-40 05 034 03 02
40-50 06 04 035 025
50-60 07 05 04 03
60-70 085 06 045 035
70-80 1 067 053 04
80-90 11 08 06 045
90-100 12 09 067 05
gt100 15 1 075 055
Table N-3Metric units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (mm)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bows
lt1200 1200-1800 1800-2400 gt2400
lt3000 4 24 16 16
3000-6000 8 47 4 24
6000-9000 11 8 55 4
9000-12000 15 10 8 47
12000-15000 19 13 95 6
15000-18000 23 15 11 8
18000-21000 27 17 135 9
21000-24000 30 21 15 10
24000-27000 34 23 17 11
gt27000 38 25 19 13
788 Appendices
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
Appendices 789
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
1 The Master Reference Line (MRL) shall be estab-lished by the vessel manufacturer and clearlymarked inside and outside of the vessel prior toattaching the bottom head It shall be parallel to theroot land of the bottom seam weld and perpendic-ular to the longitudinal axis of the vessel
2 The working elevation of a tray support ring shall bethe elevation specified on the outline drawing Itshall be a level plane parallel to the MRL
3 The distance from the MRL to the working elevationof any tray support ring shall be within +- 14 in(6mm) of the nominal distance
4 The distance between the working elevations ofany two adjacent tray support rings shall be within+- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance and theaccumulated tolerances between tray support ringsshall not exceed the tolerances in Note 3
5 The highest and lowest points of a tray support ringmeasured adjacent to the vessel shell shall notexceed the following deviations from the workingelevations
6 Tray support rings shall not have a wavinessexceeding 116 in (15mm) for any 1 foot(300mm) of circumferential length
7 Tilt of a tray support ring over its width shall notexceed 116 in (15mm)
8 Orientation of the downcomer centerline shall bewithin 18 in (3mm) of its nominal distance fromthe Vessel Reference Centerline VRC for vesselsup to 72 in (1800mm) dia and within frac14rdquo (6mm)for vessels over 72 in (1800mm) dia
9 Distance from downcomer support bar toVRC shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) of thenominal distance On a multipass tray the distance
between downcomer support bars shall also bewithin +- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance
10 Deviation from nominal distance between down-comer support bars shall be subject to vessel out-of-roundness tolerance Facility for adjustmentmust be provided in the downcomer and weirplates
11 Tilt of downcomer support bars over its width shallnot exceed 116 in (15mm)
12 Distance between top of downcomer (weir) supportbar and top of tray support ring shall be within+- 116 in (15mm) of the nominal distance
13 Tray decks shall have a flat surface within 116 in(15mm) measured across a 1 ft (300mm) squaresurface
14 The difference in height between the highest andlowest points of the weir measured to a levelplane shall not exceed
15 Clearance between bottom of downcomer and topof tray or seal pan below shall not deviate from thenominal clearance by more than
16 The bowing of a downcomer in a horizontal planeshall not deviate from the straight by more than+- 18 in (3mm)
17 Downcomer horizontal clearances measured fromthe bottom edge of downcomer to recessed seal panor inlet weir shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) ofnominal
Vessel Dia Tolerance
48rdquo (1200 mm) and smaller 116rdquo (15 mm)
48rdquo to 84rdquo (1200 e 2100 mm) 332rdquo (25 mm)
Over 84rdquo 18rdquo (3 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo 14rdquo (6 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller +- 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) +- 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo +- 14rdquo (6 mm)
790 Appendices
Figure N-1 Maximum permissible deviation from a circular form e for vessels under external pressure SourceReprinted by permission of ASME
Figure N-2 Example of differences between maximum and minimum inside diameters in cylindrical conical andspherical shells Source Reprinted by permission of ASME
Appendices 791
Tolerances for Shape of Heads
792 Appendices
Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

784 Appendices
Tolerance for Horizontal Vessels
Notes
1 Minimum thickness as specified2 Out of roundness is defined by ASME VIII-1 Para
UG 80 and is +- 1 of the diameter The followingtolerances are recommended to provide strictercontrol of diametral difference
3 Distance between Reference Line and far end ofshell
4 Deviation from horizontal plane
5 Maximum Permissible Bow lt15 of lengthlt15 (40 mm) (See also Table for Maximum Bow)
6 Out of levelness of supports
Shell dia lt48 (1200) 48 - 84 (1200 - 2100) gt84 (2100)
Tolerance 125 (3) 188 (45) 25 (6)
Vessel Diameter lt 48 (1200 mm) 48 -84 (1200-2100) 84 - 120 (2100-3000) gt120 (3000 mm)
Tolerance 06 (15 mm) 125 (3 mm) 188 (5 mm) 25 (6 mm)
Shell Length lt 50rsquo (15000) gt50rsquo (15000)
Tolerance 015Ft (1 mmM) 01Ft (8 mm M)
+- inches +- mm
7 Height of supports 013 3
8 Distance between hole centers for Anchor Bolts 006 15
9 Distance between supports 013 3
10 Distance from CL Support to Reference Tangent Line 013 3
11 Nozzle projection 013 3
12 Projection of Manhole 025 6
13 Location of Nozzle 013 3
14 Location of Manhole 025 6
15 Distance beween matched instrument connections 004 1
16 Tilt of Nozzle +- 5 Degree
17 Tilt of Manhole +- 1 Degree
(Continued)
Appendices 785
Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
18 Permissible deviation of bolt holes from CL 004 1
19 Location of Nozzle from CL 013 3
20 Location of Manhole from CL 025 6
21 Location of bolt holes of clip from CL 013 3
22 Location of clips and stiffening rings from Reference
Tangent Line
025 6
23 Projection of bolt holes in clips from CL 013 3
786 Appendices
Maximum Permissible Bow
Table N-1Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
Note Item DescriptionNotes
Tolerance
INCHES mm
1 Sub-Assy Length
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 6
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 6
gt15 gt4575 +- 5 +- 6
2 Manways From Reference Tangent Line +-0375 +- 10
3 First Tray Elevation +- 25 +- 6
4 Tray Spacing Non-Cumulative +- 125 +- 3
5 Nozzle Above Tray +- 125 +- 3
6 Tray Spacing At Girth Seam Sub-Assembly +- 375 +- 10
7 Nozzle Clips amp
Elevations
LENGTH
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 3
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 10
15-20 4575-6100 +- 5 +- 13
20-40 6100-12200 +- 75 +- 19
40-80 12200-24400 +- 1 +- 25
80-160 24400-48800 +- 15 +- 38
gt160 gt48800 +- 75 +- 75
8 Out of level Slope For Skirt Diameter gt20rsquo (6 M) 1500 1500
9 Anchor Bolt Circle 5 (12 mm) Max Total +- 25 +- 6
10 Bolt Hole Location-
Clips
Non-Cumulative +- 25 +- 6
Appendices 787
Table N-2US units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (Ft)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bow
lt48 48 to 72 72 to 96 gt96
lt10 012 009 006 006
10-20 025 018 015 01
20-30 035 025 023 015
30-40 05 034 03 02
40-50 06 04 035 025
50-60 07 05 04 03
60-70 085 06 045 035
70-80 1 067 053 04
80-90 11 08 06 045
90-100 12 09 067 05
gt100 15 1 075 055
Table N-3Metric units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (mm)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bows
lt1200 1200-1800 1800-2400 gt2400
lt3000 4 24 16 16
3000-6000 8 47 4 24
6000-9000 11 8 55 4
9000-12000 15 10 8 47
12000-15000 19 13 95 6
15000-18000 23 15 11 8
18000-21000 27 17 135 9
21000-24000 30 21 15 10
24000-27000 34 23 17 11
gt27000 38 25 19 13
788 Appendices
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
Appendices 789
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
1 The Master Reference Line (MRL) shall be estab-lished by the vessel manufacturer and clearlymarked inside and outside of the vessel prior toattaching the bottom head It shall be parallel to theroot land of the bottom seam weld and perpendic-ular to the longitudinal axis of the vessel
2 The working elevation of a tray support ring shall bethe elevation specified on the outline drawing Itshall be a level plane parallel to the MRL
3 The distance from the MRL to the working elevationof any tray support ring shall be within +- 14 in(6mm) of the nominal distance
4 The distance between the working elevations ofany two adjacent tray support rings shall be within+- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance and theaccumulated tolerances between tray support ringsshall not exceed the tolerances in Note 3
5 The highest and lowest points of a tray support ringmeasured adjacent to the vessel shell shall notexceed the following deviations from the workingelevations
6 Tray support rings shall not have a wavinessexceeding 116 in (15mm) for any 1 foot(300mm) of circumferential length
7 Tilt of a tray support ring over its width shall notexceed 116 in (15mm)
8 Orientation of the downcomer centerline shall bewithin 18 in (3mm) of its nominal distance fromthe Vessel Reference Centerline VRC for vesselsup to 72 in (1800mm) dia and within frac14rdquo (6mm)for vessels over 72 in (1800mm) dia
9 Distance from downcomer support bar toVRC shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) of thenominal distance On a multipass tray the distance
between downcomer support bars shall also bewithin +- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance
10 Deviation from nominal distance between down-comer support bars shall be subject to vessel out-of-roundness tolerance Facility for adjustmentmust be provided in the downcomer and weirplates
11 Tilt of downcomer support bars over its width shallnot exceed 116 in (15mm)
12 Distance between top of downcomer (weir) supportbar and top of tray support ring shall be within+- 116 in (15mm) of the nominal distance
13 Tray decks shall have a flat surface within 116 in(15mm) measured across a 1 ft (300mm) squaresurface
14 The difference in height between the highest andlowest points of the weir measured to a levelplane shall not exceed
15 Clearance between bottom of downcomer and topof tray or seal pan below shall not deviate from thenominal clearance by more than
16 The bowing of a downcomer in a horizontal planeshall not deviate from the straight by more than+- 18 in (3mm)
17 Downcomer horizontal clearances measured fromthe bottom edge of downcomer to recessed seal panor inlet weir shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) ofnominal
Vessel Dia Tolerance
48rdquo (1200 mm) and smaller 116rdquo (15 mm)
48rdquo to 84rdquo (1200 e 2100 mm) 332rdquo (25 mm)
Over 84rdquo 18rdquo (3 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo 14rdquo (6 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller +- 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) +- 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo +- 14rdquo (6 mm)
790 Appendices
Figure N-1 Maximum permissible deviation from a circular form e for vessels under external pressure SourceReprinted by permission of ASME
Figure N-2 Example of differences between maximum and minimum inside diameters in cylindrical conical andspherical shells Source Reprinted by permission of ASME
Appendices 791
Tolerances for Shape of Heads
792 Appendices
Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Tolerance for Horizontal Vessels
Notes
1 Minimum thickness as specified2 Out of roundness is defined by ASME VIII-1 Para
UG 80 and is +- 1 of the diameter The followingtolerances are recommended to provide strictercontrol of diametral difference
3 Distance between Reference Line and far end ofshell
4 Deviation from horizontal plane
5 Maximum Permissible Bow lt15 of lengthlt15 (40 mm) (See also Table for Maximum Bow)
6 Out of levelness of supports
Shell dia lt48 (1200) 48 - 84 (1200 - 2100) gt84 (2100)
Tolerance 125 (3) 188 (45) 25 (6)
Vessel Diameter lt 48 (1200 mm) 48 -84 (1200-2100) 84 - 120 (2100-3000) gt120 (3000 mm)
Tolerance 06 (15 mm) 125 (3 mm) 188 (5 mm) 25 (6 mm)
Shell Length lt 50rsquo (15000) gt50rsquo (15000)
Tolerance 015Ft (1 mmM) 01Ft (8 mm M)
+- inches +- mm
7 Height of supports 013 3
8 Distance between hole centers for Anchor Bolts 006 15
9 Distance between supports 013 3
10 Distance from CL Support to Reference Tangent Line 013 3
11 Nozzle projection 013 3
12 Projection of Manhole 025 6
13 Location of Nozzle 013 3
14 Location of Manhole 025 6
15 Distance beween matched instrument connections 004 1
16 Tilt of Nozzle +- 5 Degree
17 Tilt of Manhole +- 1 Degree
(Continued)
Appendices 785
Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
18 Permissible deviation of bolt holes from CL 004 1
19 Location of Nozzle from CL 013 3
20 Location of Manhole from CL 025 6
21 Location of bolt holes of clip from CL 013 3
22 Location of clips and stiffening rings from Reference
Tangent Line
025 6
23 Projection of bolt holes in clips from CL 013 3
786 Appendices
Maximum Permissible Bow
Table N-1Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
Note Item DescriptionNotes
Tolerance
INCHES mm
1 Sub-Assy Length
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 6
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 6
gt15 gt4575 +- 5 +- 6
2 Manways From Reference Tangent Line +-0375 +- 10
3 First Tray Elevation +- 25 +- 6
4 Tray Spacing Non-Cumulative +- 125 +- 3
5 Nozzle Above Tray +- 125 +- 3
6 Tray Spacing At Girth Seam Sub-Assembly +- 375 +- 10
7 Nozzle Clips amp
Elevations
LENGTH
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 3
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 10
15-20 4575-6100 +- 5 +- 13
20-40 6100-12200 +- 75 +- 19
40-80 12200-24400 +- 1 +- 25
80-160 24400-48800 +- 15 +- 38
gt160 gt48800 +- 75 +- 75
8 Out of level Slope For Skirt Diameter gt20rsquo (6 M) 1500 1500
9 Anchor Bolt Circle 5 (12 mm) Max Total +- 25 +- 6
10 Bolt Hole Location-
Clips
Non-Cumulative +- 25 +- 6
Appendices 787
Table N-2US units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (Ft)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bow
lt48 48 to 72 72 to 96 gt96
lt10 012 009 006 006
10-20 025 018 015 01
20-30 035 025 023 015
30-40 05 034 03 02
40-50 06 04 035 025
50-60 07 05 04 03
60-70 085 06 045 035
70-80 1 067 053 04
80-90 11 08 06 045
90-100 12 09 067 05
gt100 15 1 075 055
Table N-3Metric units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (mm)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bows
lt1200 1200-1800 1800-2400 gt2400
lt3000 4 24 16 16
3000-6000 8 47 4 24
6000-9000 11 8 55 4
9000-12000 15 10 8 47
12000-15000 19 13 95 6
15000-18000 23 15 11 8
18000-21000 27 17 135 9
21000-24000 30 21 15 10
24000-27000 34 23 17 11
gt27000 38 25 19 13
788 Appendices
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
Appendices 789
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
1 The Master Reference Line (MRL) shall be estab-lished by the vessel manufacturer and clearlymarked inside and outside of the vessel prior toattaching the bottom head It shall be parallel to theroot land of the bottom seam weld and perpendic-ular to the longitudinal axis of the vessel
2 The working elevation of a tray support ring shall bethe elevation specified on the outline drawing Itshall be a level plane parallel to the MRL
3 The distance from the MRL to the working elevationof any tray support ring shall be within +- 14 in(6mm) of the nominal distance
4 The distance between the working elevations ofany two adjacent tray support rings shall be within+- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance and theaccumulated tolerances between tray support ringsshall not exceed the tolerances in Note 3
5 The highest and lowest points of a tray support ringmeasured adjacent to the vessel shell shall notexceed the following deviations from the workingelevations
6 Tray support rings shall not have a wavinessexceeding 116 in (15mm) for any 1 foot(300mm) of circumferential length
7 Tilt of a tray support ring over its width shall notexceed 116 in (15mm)
8 Orientation of the downcomer centerline shall bewithin 18 in (3mm) of its nominal distance fromthe Vessel Reference Centerline VRC for vesselsup to 72 in (1800mm) dia and within frac14rdquo (6mm)for vessels over 72 in (1800mm) dia
9 Distance from downcomer support bar toVRC shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) of thenominal distance On a multipass tray the distance
between downcomer support bars shall also bewithin +- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance
10 Deviation from nominal distance between down-comer support bars shall be subject to vessel out-of-roundness tolerance Facility for adjustmentmust be provided in the downcomer and weirplates
11 Tilt of downcomer support bars over its width shallnot exceed 116 in (15mm)
12 Distance between top of downcomer (weir) supportbar and top of tray support ring shall be within+- 116 in (15mm) of the nominal distance
13 Tray decks shall have a flat surface within 116 in(15mm) measured across a 1 ft (300mm) squaresurface
14 The difference in height between the highest andlowest points of the weir measured to a levelplane shall not exceed
15 Clearance between bottom of downcomer and topof tray or seal pan below shall not deviate from thenominal clearance by more than
16 The bowing of a downcomer in a horizontal planeshall not deviate from the straight by more than+- 18 in (3mm)
17 Downcomer horizontal clearances measured fromthe bottom edge of downcomer to recessed seal panor inlet weir shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) ofnominal
Vessel Dia Tolerance
48rdquo (1200 mm) and smaller 116rdquo (15 mm)
48rdquo to 84rdquo (1200 e 2100 mm) 332rdquo (25 mm)
Over 84rdquo 18rdquo (3 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo 14rdquo (6 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller +- 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) +- 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo +- 14rdquo (6 mm)
790 Appendices
Figure N-1 Maximum permissible deviation from a circular form e for vessels under external pressure SourceReprinted by permission of ASME
Figure N-2 Example of differences between maximum and minimum inside diameters in cylindrical conical andspherical shells Source Reprinted by permission of ASME
Appendices 791
Tolerances for Shape of Heads
792 Appendices
Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
18 Permissible deviation of bolt holes from CL 004 1
19 Location of Nozzle from CL 013 3
20 Location of Manhole from CL 025 6
21 Location of bolt holes of clip from CL 013 3
22 Location of clips and stiffening rings from Reference
Tangent Line
025 6
23 Projection of bolt holes in clips from CL 013 3
786 Appendices
Maximum Permissible Bow
Table N-1Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
Note Item DescriptionNotes
Tolerance
INCHES mm
1 Sub-Assy Length
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 6
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 6
gt15 gt4575 +- 5 +- 6
2 Manways From Reference Tangent Line +-0375 +- 10
3 First Tray Elevation +- 25 +- 6
4 Tray Spacing Non-Cumulative +- 125 +- 3
5 Nozzle Above Tray +- 125 +- 3
6 Tray Spacing At Girth Seam Sub-Assembly +- 375 +- 10
7 Nozzle Clips amp
Elevations
LENGTH
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 3
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 10
15-20 4575-6100 +- 5 +- 13
20-40 6100-12200 +- 75 +- 19
40-80 12200-24400 +- 1 +- 25
80-160 24400-48800 +- 15 +- 38
gt160 gt48800 +- 75 +- 75
8 Out of level Slope For Skirt Diameter gt20rsquo (6 M) 1500 1500
9 Anchor Bolt Circle 5 (12 mm) Max Total +- 25 +- 6
10 Bolt Hole Location-
Clips
Non-Cumulative +- 25 +- 6
Appendices 787
Table N-2US units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (Ft)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bow
lt48 48 to 72 72 to 96 gt96
lt10 012 009 006 006
10-20 025 018 015 01
20-30 035 025 023 015
30-40 05 034 03 02
40-50 06 04 035 025
50-60 07 05 04 03
60-70 085 06 045 035
70-80 1 067 053 04
80-90 11 08 06 045
90-100 12 09 067 05
gt100 15 1 075 055
Table N-3Metric units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (mm)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bows
lt1200 1200-1800 1800-2400 gt2400
lt3000 4 24 16 16
3000-6000 8 47 4 24
6000-9000 11 8 55 4
9000-12000 15 10 8 47
12000-15000 19 13 95 6
15000-18000 23 15 11 8
18000-21000 27 17 135 9
21000-24000 30 21 15 10
24000-27000 34 23 17 11
gt27000 38 25 19 13
788 Appendices
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
Appendices 789
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
1 The Master Reference Line (MRL) shall be estab-lished by the vessel manufacturer and clearlymarked inside and outside of the vessel prior toattaching the bottom head It shall be parallel to theroot land of the bottom seam weld and perpendic-ular to the longitudinal axis of the vessel
2 The working elevation of a tray support ring shall bethe elevation specified on the outline drawing Itshall be a level plane parallel to the MRL
3 The distance from the MRL to the working elevationof any tray support ring shall be within +- 14 in(6mm) of the nominal distance
4 The distance between the working elevations ofany two adjacent tray support rings shall be within+- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance and theaccumulated tolerances between tray support ringsshall not exceed the tolerances in Note 3
5 The highest and lowest points of a tray support ringmeasured adjacent to the vessel shell shall notexceed the following deviations from the workingelevations
6 Tray support rings shall not have a wavinessexceeding 116 in (15mm) for any 1 foot(300mm) of circumferential length
7 Tilt of a tray support ring over its width shall notexceed 116 in (15mm)
8 Orientation of the downcomer centerline shall bewithin 18 in (3mm) of its nominal distance fromthe Vessel Reference Centerline VRC for vesselsup to 72 in (1800mm) dia and within frac14rdquo (6mm)for vessels over 72 in (1800mm) dia
9 Distance from downcomer support bar toVRC shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) of thenominal distance On a multipass tray the distance
between downcomer support bars shall also bewithin +- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance
10 Deviation from nominal distance between down-comer support bars shall be subject to vessel out-of-roundness tolerance Facility for adjustmentmust be provided in the downcomer and weirplates
11 Tilt of downcomer support bars over its width shallnot exceed 116 in (15mm)
12 Distance between top of downcomer (weir) supportbar and top of tray support ring shall be within+- 116 in (15mm) of the nominal distance
13 Tray decks shall have a flat surface within 116 in(15mm) measured across a 1 ft (300mm) squaresurface
14 The difference in height between the highest andlowest points of the weir measured to a levelplane shall not exceed
15 Clearance between bottom of downcomer and topof tray or seal pan below shall not deviate from thenominal clearance by more than
16 The bowing of a downcomer in a horizontal planeshall not deviate from the straight by more than+- 18 in (3mm)
17 Downcomer horizontal clearances measured fromthe bottom edge of downcomer to recessed seal panor inlet weir shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) ofnominal
Vessel Dia Tolerance
48rdquo (1200 mm) and smaller 116rdquo (15 mm)
48rdquo to 84rdquo (1200 e 2100 mm) 332rdquo (25 mm)
Over 84rdquo 18rdquo (3 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo 14rdquo (6 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller +- 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) +- 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo +- 14rdquo (6 mm)
790 Appendices
Figure N-1 Maximum permissible deviation from a circular form e for vessels under external pressure SourceReprinted by permission of ASME
Figure N-2 Example of differences between maximum and minimum inside diameters in cylindrical conical andspherical shells Source Reprinted by permission of ASME
Appendices 791
Tolerances for Shape of Heads
792 Appendices
Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Maximum Permissible Bow
Table N-1Tolerances for trayed columns fabricated in multiple sub-assemblies
Note Item DescriptionNotes
Tolerance
INCHES mm
1 Sub-Assy Length
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 6
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 6
gt15 gt4575 +- 5 +- 6
2 Manways From Reference Tangent Line +-0375 +- 10
3 First Tray Elevation +- 25 +- 6
4 Tray Spacing Non-Cumulative +- 125 +- 3
5 Nozzle Above Tray +- 125 +- 3
6 Tray Spacing At Girth Seam Sub-Assembly +- 375 +- 10
7 Nozzle Clips amp
Elevations
LENGTH
Ft mm
lt5 lt1525 +- 125 +- 3
5-10 1525-3045 +- 25 +- 6
10-15 3045-4575 +- 375 +- 10
15-20 4575-6100 +- 5 +- 13
20-40 6100-12200 +- 75 +- 19
40-80 12200-24400 +- 1 +- 25
80-160 24400-48800 +- 15 +- 38
gt160 gt48800 +- 75 +- 75
8 Out of level Slope For Skirt Diameter gt20rsquo (6 M) 1500 1500
9 Anchor Bolt Circle 5 (12 mm) Max Total +- 25 +- 6
10 Bolt Hole Location-
Clips
Non-Cumulative +- 25 +- 6
Appendices 787
Table N-2US units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (Ft)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bow
lt48 48 to 72 72 to 96 gt96
lt10 012 009 006 006
10-20 025 018 015 01
20-30 035 025 023 015
30-40 05 034 03 02
40-50 06 04 035 025
50-60 07 05 04 03
60-70 085 06 045 035
70-80 1 067 053 04
80-90 11 08 06 045
90-100 12 09 067 05
gt100 15 1 075 055
Table N-3Metric units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (mm)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bows
lt1200 1200-1800 1800-2400 gt2400
lt3000 4 24 16 16
3000-6000 8 47 4 24
6000-9000 11 8 55 4
9000-12000 15 10 8 47
12000-15000 19 13 95 6
15000-18000 23 15 11 8
18000-21000 27 17 135 9
21000-24000 30 21 15 10
24000-27000 34 23 17 11
gt27000 38 25 19 13
788 Appendices
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
Appendices 789
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
1 The Master Reference Line (MRL) shall be estab-lished by the vessel manufacturer and clearlymarked inside and outside of the vessel prior toattaching the bottom head It shall be parallel to theroot land of the bottom seam weld and perpendic-ular to the longitudinal axis of the vessel
2 The working elevation of a tray support ring shall bethe elevation specified on the outline drawing Itshall be a level plane parallel to the MRL
3 The distance from the MRL to the working elevationof any tray support ring shall be within +- 14 in(6mm) of the nominal distance
4 The distance between the working elevations ofany two adjacent tray support rings shall be within+- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance and theaccumulated tolerances between tray support ringsshall not exceed the tolerances in Note 3
5 The highest and lowest points of a tray support ringmeasured adjacent to the vessel shell shall notexceed the following deviations from the workingelevations
6 Tray support rings shall not have a wavinessexceeding 116 in (15mm) for any 1 foot(300mm) of circumferential length
7 Tilt of a tray support ring over its width shall notexceed 116 in (15mm)
8 Orientation of the downcomer centerline shall bewithin 18 in (3mm) of its nominal distance fromthe Vessel Reference Centerline VRC for vesselsup to 72 in (1800mm) dia and within frac14rdquo (6mm)for vessels over 72 in (1800mm) dia
9 Distance from downcomer support bar toVRC shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) of thenominal distance On a multipass tray the distance
between downcomer support bars shall also bewithin +- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance
10 Deviation from nominal distance between down-comer support bars shall be subject to vessel out-of-roundness tolerance Facility for adjustmentmust be provided in the downcomer and weirplates
11 Tilt of downcomer support bars over its width shallnot exceed 116 in (15mm)
12 Distance between top of downcomer (weir) supportbar and top of tray support ring shall be within+- 116 in (15mm) of the nominal distance
13 Tray decks shall have a flat surface within 116 in(15mm) measured across a 1 ft (300mm) squaresurface
14 The difference in height between the highest andlowest points of the weir measured to a levelplane shall not exceed
15 Clearance between bottom of downcomer and topof tray or seal pan below shall not deviate from thenominal clearance by more than
16 The bowing of a downcomer in a horizontal planeshall not deviate from the straight by more than+- 18 in (3mm)
17 Downcomer horizontal clearances measured fromthe bottom edge of downcomer to recessed seal panor inlet weir shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) ofnominal
Vessel Dia Tolerance
48rdquo (1200 mm) and smaller 116rdquo (15 mm)
48rdquo to 84rdquo (1200 e 2100 mm) 332rdquo (25 mm)
Over 84rdquo 18rdquo (3 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo 14rdquo (6 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller +- 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) +- 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo +- 14rdquo (6 mm)
790 Appendices
Figure N-1 Maximum permissible deviation from a circular form e for vessels under external pressure SourceReprinted by permission of ASME
Figure N-2 Example of differences between maximum and minimum inside diameters in cylindrical conical andspherical shells Source Reprinted by permission of ASME
Appendices 791
Tolerances for Shape of Heads
792 Appendices
Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Table N-2US units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (Ft)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bow
lt48 48 to 72 72 to 96 gt96
lt10 012 009 006 006
10-20 025 018 015 01
20-30 035 025 023 015
30-40 05 034 03 02
40-50 06 04 035 025
50-60 07 05 04 03
60-70 085 06 045 035
70-80 1 067 053 04
80-90 11 08 06 045
90-100 12 09 067 05
gt100 15 1 075 055
Table N-3Metric units
Vessel Length
Tan-Tan (mm)
Vessel Diameter amp Maximum
Permissible Bows
lt1200 1200-1800 1800-2400 gt2400
lt3000 4 24 16 16
3000-6000 8 47 4 24
6000-9000 11 8 55 4
9000-12000 15 10 8 47
12000-15000 19 13 95 6
15000-18000 23 15 11 8
18000-21000 27 17 135 9
21000-24000 30 21 15 10
24000-27000 34 23 17 11
gt27000 38 25 19 13
788 Appendices
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
Appendices 789
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
1 The Master Reference Line (MRL) shall be estab-lished by the vessel manufacturer and clearlymarked inside and outside of the vessel prior toattaching the bottom head It shall be parallel to theroot land of the bottom seam weld and perpendic-ular to the longitudinal axis of the vessel
2 The working elevation of a tray support ring shall bethe elevation specified on the outline drawing Itshall be a level plane parallel to the MRL
3 The distance from the MRL to the working elevationof any tray support ring shall be within +- 14 in(6mm) of the nominal distance
4 The distance between the working elevations ofany two adjacent tray support rings shall be within+- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance and theaccumulated tolerances between tray support ringsshall not exceed the tolerances in Note 3
5 The highest and lowest points of a tray support ringmeasured adjacent to the vessel shell shall notexceed the following deviations from the workingelevations
6 Tray support rings shall not have a wavinessexceeding 116 in (15mm) for any 1 foot(300mm) of circumferential length
7 Tilt of a tray support ring over its width shall notexceed 116 in (15mm)
8 Orientation of the downcomer centerline shall bewithin 18 in (3mm) of its nominal distance fromthe Vessel Reference Centerline VRC for vesselsup to 72 in (1800mm) dia and within frac14rdquo (6mm)for vessels over 72 in (1800mm) dia
9 Distance from downcomer support bar toVRC shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) of thenominal distance On a multipass tray the distance
between downcomer support bars shall also bewithin +- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance
10 Deviation from nominal distance between down-comer support bars shall be subject to vessel out-of-roundness tolerance Facility for adjustmentmust be provided in the downcomer and weirplates
11 Tilt of downcomer support bars over its width shallnot exceed 116 in (15mm)
12 Distance between top of downcomer (weir) supportbar and top of tray support ring shall be within+- 116 in (15mm) of the nominal distance
13 Tray decks shall have a flat surface within 116 in(15mm) measured across a 1 ft (300mm) squaresurface
14 The difference in height between the highest andlowest points of the weir measured to a levelplane shall not exceed
15 Clearance between bottom of downcomer and topof tray or seal pan below shall not deviate from thenominal clearance by more than
16 The bowing of a downcomer in a horizontal planeshall not deviate from the straight by more than+- 18 in (3mm)
17 Downcomer horizontal clearances measured fromthe bottom edge of downcomer to recessed seal panor inlet weir shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) ofnominal
Vessel Dia Tolerance
48rdquo (1200 mm) and smaller 116rdquo (15 mm)
48rdquo to 84rdquo (1200 e 2100 mm) 332rdquo (25 mm)
Over 84rdquo 18rdquo (3 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo 14rdquo (6 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller +- 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) +- 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo +- 14rdquo (6 mm)
790 Appendices
Figure N-1 Maximum permissible deviation from a circular form e for vessels under external pressure SourceReprinted by permission of ASME
Figure N-2 Example of differences between maximum and minimum inside diameters in cylindrical conical andspherical shells Source Reprinted by permission of ASME
Appendices 791
Tolerances for Shape of Heads
792 Appendices
Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
Appendices 789
Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
1 The Master Reference Line (MRL) shall be estab-lished by the vessel manufacturer and clearlymarked inside and outside of the vessel prior toattaching the bottom head It shall be parallel to theroot land of the bottom seam weld and perpendic-ular to the longitudinal axis of the vessel
2 The working elevation of a tray support ring shall bethe elevation specified on the outline drawing Itshall be a level plane parallel to the MRL
3 The distance from the MRL to the working elevationof any tray support ring shall be within +- 14 in(6mm) of the nominal distance
4 The distance between the working elevations ofany two adjacent tray support rings shall be within+- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance and theaccumulated tolerances between tray support ringsshall not exceed the tolerances in Note 3
5 The highest and lowest points of a tray support ringmeasured adjacent to the vessel shell shall notexceed the following deviations from the workingelevations
6 Tray support rings shall not have a wavinessexceeding 116 in (15mm) for any 1 foot(300mm) of circumferential length
7 Tilt of a tray support ring over its width shall notexceed 116 in (15mm)
8 Orientation of the downcomer centerline shall bewithin 18 in (3mm) of its nominal distance fromthe Vessel Reference Centerline VRC for vesselsup to 72 in (1800mm) dia and within frac14rdquo (6mm)for vessels over 72 in (1800mm) dia
9 Distance from downcomer support bar toVRC shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) of thenominal distance On a multipass tray the distance
between downcomer support bars shall also bewithin +- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance
10 Deviation from nominal distance between down-comer support bars shall be subject to vessel out-of-roundness tolerance Facility for adjustmentmust be provided in the downcomer and weirplates
11 Tilt of downcomer support bars over its width shallnot exceed 116 in (15mm)
12 Distance between top of downcomer (weir) supportbar and top of tray support ring shall be within+- 116 in (15mm) of the nominal distance
13 Tray decks shall have a flat surface within 116 in(15mm) measured across a 1 ft (300mm) squaresurface
14 The difference in height between the highest andlowest points of the weir measured to a levelplane shall not exceed
15 Clearance between bottom of downcomer and topof tray or seal pan below shall not deviate from thenominal clearance by more than
16 The bowing of a downcomer in a horizontal planeshall not deviate from the straight by more than+- 18 in (3mm)
17 Downcomer horizontal clearances measured fromthe bottom edge of downcomer to recessed seal panor inlet weir shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) ofnominal
Vessel Dia Tolerance
48rdquo (1200 mm) and smaller 116rdquo (15 mm)
48rdquo to 84rdquo (1200 e 2100 mm) 332rdquo (25 mm)
Over 84rdquo 18rdquo (3 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo 14rdquo (6 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller +- 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) +- 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo +- 14rdquo (6 mm)
790 Appendices
Figure N-1 Maximum permissible deviation from a circular form e for vessels under external pressure SourceReprinted by permission of ASME
Figure N-2 Example of differences between maximum and minimum inside diameters in cylindrical conical andspherical shells Source Reprinted by permission of ASME
Appendices 791
Tolerances for Shape of Heads
792 Appendices
Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Tolerances for Trays Tray Support Rings and Downcomers
1 The Master Reference Line (MRL) shall be estab-lished by the vessel manufacturer and clearlymarked inside and outside of the vessel prior toattaching the bottom head It shall be parallel to theroot land of the bottom seam weld and perpendic-ular to the longitudinal axis of the vessel
2 The working elevation of a tray support ring shall bethe elevation specified on the outline drawing Itshall be a level plane parallel to the MRL
3 The distance from the MRL to the working elevationof any tray support ring shall be within +- 14 in(6mm) of the nominal distance
4 The distance between the working elevations ofany two adjacent tray support rings shall be within+- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance and theaccumulated tolerances between tray support ringsshall not exceed the tolerances in Note 3
5 The highest and lowest points of a tray support ringmeasured adjacent to the vessel shell shall notexceed the following deviations from the workingelevations
6 Tray support rings shall not have a wavinessexceeding 116 in (15mm) for any 1 foot(300mm) of circumferential length
7 Tilt of a tray support ring over its width shall notexceed 116 in (15mm)
8 Orientation of the downcomer centerline shall bewithin 18 in (3mm) of its nominal distance fromthe Vessel Reference Centerline VRC for vesselsup to 72 in (1800mm) dia and within frac14rdquo (6mm)for vessels over 72 in (1800mm) dia
9 Distance from downcomer support bar toVRC shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) of thenominal distance On a multipass tray the distance
between downcomer support bars shall also bewithin +- 18 in (3mm) of the nominal distance
10 Deviation from nominal distance between down-comer support bars shall be subject to vessel out-of-roundness tolerance Facility for adjustmentmust be provided in the downcomer and weirplates
11 Tilt of downcomer support bars over its width shallnot exceed 116 in (15mm)
12 Distance between top of downcomer (weir) supportbar and top of tray support ring shall be within+- 116 in (15mm) of the nominal distance
13 Tray decks shall have a flat surface within 116 in(15mm) measured across a 1 ft (300mm) squaresurface
14 The difference in height between the highest andlowest points of the weir measured to a levelplane shall not exceed
15 Clearance between bottom of downcomer and topof tray or seal pan below shall not deviate from thenominal clearance by more than
16 The bowing of a downcomer in a horizontal planeshall not deviate from the straight by more than+- 18 in (3mm)
17 Downcomer horizontal clearances measured fromthe bottom edge of downcomer to recessed seal panor inlet weir shall be within +- 18 in (3mm) ofnominal
Vessel Dia Tolerance
48rdquo (1200 mm) and smaller 116rdquo (15 mm)
48rdquo to 84rdquo (1200 e 2100 mm) 332rdquo (25 mm)
Over 84rdquo 18rdquo (3 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo 14rdquo (6 mm)
Vessel Dia Tolerance
72rdquo (1800 mm) and smaller +- 18rdquo (3 mm)
72rdquo to 108rdquo (1800 e 2700 mm) +- 316rdquo (5 mm)
Over 108rdquo +- 14rdquo (6 mm)
790 Appendices
Figure N-1 Maximum permissible deviation from a circular form e for vessels under external pressure SourceReprinted by permission of ASME
Figure N-2 Example of differences between maximum and minimum inside diameters in cylindrical conical andspherical shells Source Reprinted by permission of ASME
Appendices 791
Tolerances for Shape of Heads
792 Appendices
Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Figure N-1 Maximum permissible deviation from a circular form e for vessels under external pressure SourceReprinted by permission of ASME
Figure N-2 Example of differences between maximum and minimum inside diameters in cylindrical conical andspherical shells Source Reprinted by permission of ASME
Appendices 791
Tolerances for Shape of Heads
792 Appendices
Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Tolerances for Shape of Heads
792 Appendices
Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Tolerances for Heat Exchangers
Appendices 793
Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Table N-4Tolerances for flanges
Threaded Slip-on Lap Joint and Blind Welding Neck
Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06 Outside
Diameter
OD 24 amp Less +- 06
OD gt 24 +- 125 OD gt 24 +- 125
Inside Diameter Threaded To Standard Gage Limits Inside Diameter 10 amp Smaller +- 03
SLIP-ON amp LAP
JOINT
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 12 thru 18 +- 06
12 amp Larger +06 -0 20 thru 42 +125 - 06
Outside
Diameter of
Hub
12 amp Smaller +09 -06 Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03
14 thru 42 +- 125 25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015
Diameter of
Contact Face
0625 RF +- 03 Diameter of
Hub at Base
When X is 24
or Smaller
+- 06
25 RF TampG
MampF
+- 015 When X is over
24
+- 25
Diameter of
Counterbore
10 amp Smaller +03 -0 Diameter of
Hub at Point of
Welding
5 amp Smaller +09 -03
12 thru 42 +06 -0 6 amp Larger +156 -03
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Drilling Bolt Circle 5 thru 24 +-
06
26 thru 42 +-
06
Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03 Bolt Hole
Spacing
+- 03 +- 03
Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max Eccentricity of
Bolt Circle
with Respect
to Bore
03 Max
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Eccentricity of
Facing with
Respect to
Bore
Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0 Thickness 18 amp Smaller +125 -0
20 thru 42 +188 -0 gt18 +188 -0
Length Thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06 Length thru
Hub
10 amp Smaller +- 06
12 thru 42 +- 125 12 thru 42 +- 125
Ring Joint Facing Ring Joint Gasket
Depth Dim L +015 -0 Ring Width Dim A +-0008
Width Dim D +-0008 Ring Depth Dim BampH +-0015
Pitch
Diameter
Dim P +-0005 Width
Octagonal
Flat
Dim C +-0008
Radius at
Bottom
Dim r Max Pitch Diameter Dim P +-0007
Angle 23o Angle +- 5o Radius Dim r +-0015
Angle 23o Angle +-05o
Notes
1 All tolerances per Tube-Turn Catalog
2 See ASME B165 for flange dimensions and tolerances
794 Appendices
Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Table N-5Flange face tolerances
Maximum Tolerances
Flange Rating Nominal Size Waviness TIR (In) Positive Radial Tilt (a)
150 lt24 0016 0009
gt24 0012 0012
300-600 All Sizes 0006 0012
900-2500 All Sizes 0005 0003
75 125 175 250 350 gt26 0006 0018
Notes
1 Negative radial tilt is not allowed
Table N-6Maximum permissible offset in butt welding
Thickness
Joint category UW-33
A B C D
Inches mm Inches mm Inches mm
lt5 lt125 25 T 25 T 25 T 25 T
5 to 75 125 to 19 0125 32 25 T 25 T
75 to 15 19 to 38 0125 32 0188 48
15 to 2 38 to 50 0125 32 0125 T 125 T
gt2 gt50 06 T lt b lt 37 06 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 75 125 T lt b lt 19
Appendices 795
Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Table N-7General tolerances For machined or fabricated parts
10 Machined Parts
11 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Tolerance + or -
mm
015 02 05 08 12 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Distance Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
15751 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
6301 to
787
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 002 003 005 008 012 016 02 024 028 03
12 Radii
Radii mm 5 to 3 3 to 6 6 to 30 30 to 120 120 to
400
400 to
1000
1000 to
2000
2000 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
02 05 1 2 4 6 8 10
Radii Inches 2 to
125
126 to
25
026 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
001 001 004 008 016 024 03 039
13 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to 60 601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
15 20 30 45 90
14 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 0 to 6 61 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
Above
8001
Tolerance + or -
mm
01 025 05 1 15 25 35 5 7
Length Inches 0 to 25 26 to
125
126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
Above
3151
Tolerance + or -
inches
0005 001 002 004 006 01 014 02 028
15 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 0 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 3 4 7 10 14 18 21 24 28 31 35
Distance Inches 0 to 475 476 to
1575
1578 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 012 016 028 04 055 07 08 1 11 12 14
20 Fabricated Parts
21 Linear Dimensions and Diameters
Distance mm 0 to 30 31 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
16001 to
20000
Above
20001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 2 2 3 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
Distance Inches 0 to 125 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
475
4751 to
630
6301 to
790
Above
791
796 Appendices
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 008 012 016 024 031 039 047 055 063
22 Radii
Radii mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
Tolerance + or -
mm
3 6 9 12 15
Radii Inches 126 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
Tolerance + or -
inches
012 025 038 05 06
23 Angular Dimensions
Angle Degrees 0 to 10 101 to 20 201 to 40 401 to
60
601 to 90
Tolerance + or -
minutes
30 45 60 90 120
24 StraightnessPlaneness (Maximum distance between a straight line and actual line or plane surface and actual surface)
Length mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
4000
4001 to
8000
8001 to
12000
12001 to
16000
Above
16001
Tolerance + or -
mm
1 15 3 45 6 8 10 12 14
Length Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
3951 to
7875
7876 to
1575
1576 to
315
3151 to
472
4721 to
630
Above
631
Tolerance + or -
inches
004 008 012 018 024 031 04 047 055
25 Rectangularity (Maximum difference in length between the diagonals)
Distance mm 30 to 120 121 to
400
401 to
1000
1001 to
2000
2001 to
3000
3001 to
4000
4001 to
5000
5001 to
6000
6001 to
7000
7001 to
8000
8001 to
9000
9001 to
10000
Tolerance + or -
mm
2 35 7 14 21 28 35 42 49 56 63 70
Distance Inches 12 to
475
476 to
1575
1576 to
395
396 to
7875
7876 to
118
1181 to
157
1571 to
197
1971 to
236
2361 to
275
2751 to
315
3151 to
355
3551 to
395
Tolerance + or -
inches
008 014 028 055 083 11 138 165 193 22 25 275
Appendices 797
Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Flange Bolt Hole Orientation
798 Appendices
Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Stress Due to Out of Tolerance Condition
Notationd frac14 Peaking or banding measurementd frac14 for peaking
5 ( a1 + a2 ) or
25 ( b1 + b2)d frac14 For banding
5 ( a1 + b1 )e frac14 Amount of offset inE frac14 Modulus of elasticity PSIL frac14 Half the length of gauge inP frac14 Internal pressure PSIG
Rm frac14 Mean vessel radius int frac14 Vessel thickness inb frac14 Factorn frac14 Poissonrsquos ratio
sP frac14 Stress due to peaking PSIsO frac14 Stress due to offset PSIsX frac14 Longitudinal stress PSIsf frac14 Circumferential Stress PSI
Note Peaking and banding are for longitudinal seamsonly Offset can be for longitudinal seams or circumfer-ential seams
Calculations
STRESS DUE TO PEAKING OR BANDING
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Factor b
b frac14h2 L=t
i 31 v2
sf
E131=2
For n frac14 3
b frac14h33 L=t
i sf=E
131=2bull Stress due to peaking or banding sP
sP frac14 6sfd tanh b
t1 v2
b
For n frac14 3
sP frac14 659 sfd tanh b
tb
STRESS DUE TO OFFSET
bull Circumferential stress due pressure sf
sf frac14 P Rm=t
bull Longitudinal stress due pressure sX
sX frac14 P Rm=2 t
bull Stress due to offset sO
sO frac14 3 e s
t1 v2
For n frac14 3
sO frac14 eth33 e sTHORN=twhere s frac14 Applicable case of sX or sf
Appendices 799
Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Figure N-3 Measurement of out of tolerance conditions
800 Appendices
Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Appendix O Guideline for Application of Pressure Relief Values (PRVs)
Appendices 801
References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

References
[1] Roark RJ Formulas for Stress and Strain 5th EditionMcGraw-Hill Book Co 1975
[2] ASME Code Section VIII Division 2[3] ASME Code Section VIII Division 1
802 Appendices
Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Index
Note Page numbers with ldquofrdquo denote figures ldquotrdquo tables
AAgitationdefined 345jacket vessels 126
Agitators helical pipe coils with 332Air hardening 738AISC Steel Construction Manual 186 188Allowable stresses and load combinations
200ndash201Alloys 720ndash721Anchor boltsconical skirt 252saddle supports for large vessels 271ndash272for vertical vessels 293
Anchor bolts base details andcentered neutral axis method 291ndash292equivalent area method 191force 291number of 283t 291shifted neutral axis method 283t 284 288
Anchor strap 430
Anchoring of saddle supports 187ndash188Anchor-type impellers 346Angle a calculating 67Angle joint 762Annealing 738ndash740ASCE wind design per 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190ASME (American Society of Mechanical
Engineers)Section VIII Division 1 2ndash4 6ndash7 10ndash11
13 15ndash16 27 29 55ndash56 83 85ndash86136 186 200ndash201 428 474 481496ndash497 509 594 744ndash745
Section VIII Division 2 2 5ndash8 10ndash11 1315ndash21 27 56ndash57 95ndash96 146 186 188200ndash201 474ndash476 481 496ndash497 499509 594 733
Section VIII Division 3 21 475ndash476481 497 499
specifications 737ndash738STS-1 method 420ndash421 425
Attachments converting 399ndash401Autoclave testing 740Autofrettage 482ndash483history of 483pressure 483
AWWA D-100 588 594Axial compressionbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
95ndash96Axial stress 80Axle loads 573
BBafflesapplications 381ndash390attaching stiffeners dorsquos and dontrsquos for
384configurations 390curved 381dimensions 382helical pipe coils with 332
803
Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Baffles (Continued)for mixersagitators 347ndash348notation 382sample problem 386ndash388stiffened versus unstiffened 381stiffener design 384thermal check 384unstiffened check 384weld sizes 385ndash386widths and wall clearances 345
Bar stiffeners moment of inertia of 49tBarge transportation see Transportation
bargeBase details for vertical vessels design ofanchor bolts equivalent area method286f 287f
anchor bolts force 291ndash292anchor bolts number of 283t 291base plate 288f 292bending moment 284tbolt chair data 283tbolt stress allowable 283tconcrete properties 284tconstants 284tgussets 289ndash290notation 281ndash282 291skirt thickness 290skirt types 282fstresses allowable 291ndash292top plate or ring 289
Base plate designs 681ndash690for legs 275ndash276for lugs 281t 700for saddles 270ndash271weights of 112t
Base plate designsconical skirt 252
Base support damping 419Bauschinger Effect 483Beam on elastic foundation methods 436Beamsbeam seat 298 305fmultiple loads 575support blocks welded to 319ndash320tail 681ndash690see also Support of internal beds
Bending moment 80buckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 96
Bending stressprimary general 11 80secondary 12
Biaxial states of stress 4Bijlaard P P 188analysis 436 448
Binscompression ring design 590ndash591deep granularpowder 589ndash590
deep versus shallow 587dimensional data 587fmaterial properties 593tnotation 586purging techniques effects of 594rankine factors 593t 594roofs 594shallow granularpowder 588ndash589small internal pressures 590solids versus liquids in 586struts 591support arrangements 593surcharge 594weights 586ndash587
Blind flanges with openings 167Bolt(sing) 593application 729tcheck of 701flange 72 147t 148 163t 164f
696t 701loads for rectangular 699materials 728 729tproperties 696tweights of alloy stud 111t
Bolt spacingmaximum 144minimum 144
Bolt torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171calculations 171friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of170
notation 169ndash170notes 171
Bolted connections shear loads in 584ndash585bearing type connection 585cases of 584ndash585friction type connection 585
Bolted flange connections bolt loads in 141Bolted flat covers 508ndash509 510fBottom catalyst dump nozzles dimensions
weights of 115fBraces leg 187see also Legs seismic design for braced
Bracketscantilever-type 580circular platforms and spacing of 570high-temperature 579types of 576
Bridgman closure 504 518ndash537calculation procedure 528ndash537design procedure 523nomenclature 523studding flanges worksheet for 527f 538fthreaded closures with 539ndash545
Brinell testing 735ndash736Brittle fractures 8
Bucklingcreep 29elastic 56general 29lateral of stiffening rings 51ndash52local 29
Buckling of thin-walled cylindrical shells95ndash96
axial compression 95ndash96bending moment 96critical length load and stress 95external pressure 95interaction 96shear stress 96
Buildingsrisk category of for wind and earthquake
loads 207Buried vessels see Underground tanks
and vesselsButt joint 762
CCarbide solution treated 763Carbon steel plate weights of 101Centered neutral axis method 282
291ndash292Center of gravity finding or revising 90Charpy impact testing (CIT) 736ndash737Choker (cinch) lift at base 688Circular platformsbracket spacing 570dead loads 570dimensions 563f 564fformulas 564kneebrace design 565 570live loads 567t 568t 570moment at shell graph 566fnotation 563ndash570
Circular rings stress inallowable stress 438ndash439coefficient graphs 445fcoefficient values 438t 439tmoment diagrams 437fmoments and forces determining 439notation 437radial load determining 437shell stress due to loadings 439t
Circumferential compression stresstorispherical head knuckle region of
72fCircumferentiallatitudinal stress 3formula 38
Clips 575Closures 502ndash547
Bridgman 504 518ndash537delta ring 504 515ndash517double cone 513
804 Index
flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

flanged 503lens ring 511see also High pressure closures
Code Case 2286 54ndash57 56tnomenclature 54ndash57
Coil wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel476
Coils see Helical pipe coilsCollapse use of term 12Columns see Leg supportsComposite stiffenersbaffles and 381moment of inertia of 50t
Compression plate 280ndash281Compression ring design bins and elevated
tanks and 590ndash591Concentric cone 59fConcrete properties of 295Cone lifting lugs 691ndash693Cones formula 39t
Cone-cylinder intersections 64dimensions of 59fworksheet to determining loads at65f 66f
Cones design of 58ndash64for external pressure 61ndash63geometry 59with half apex angle 63for internal pressure 59ndash60nomenclature 58notes 64sample problem 64
Conical skirt seismic design for 248ndash252anchor bolts 252base plate 252calculation 251design of 251longitudinal stress in shell due to shearband 252
nomenclature 248notes 252shear ring 251
Conventional jackets 124Conversion factors 357Corner joint 762Corrosionfatigue 8stress 8
Creep 23ndash31allowable tensile stress in 26ndash27allowable compressible stress in 27buckling 29fatigue 27ndash29stages of 24ndash25
Creep-buckling 29Creep-fatigue 27ndash29Critical length 95
Critical Reynolds number 126ndash127Critical wind velocity 418 420 423fCross bracing 187 218ndash222 615Cryogenic applications 32ndash33
specifications 33Cut threads 763Cycle counting methods 16Cyclic service fatigue analysis for 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Cylinderscalculating proportions 99tsee also Cone-cylinder intersections
Cylindrical shells 38buckling of thin-walled 95ndash96external pressure design for 43formulas 38
Cylindrical shells stress inbending moment 458f 460f 462fcalculating b values for rectangular
attachments 452ndash454calculation steps 452ndash454circumferential moment 454 455tconcentration factors 450fdimensions for clips and attachments
450fgeometric parameters 451flongitudinal moment 453 455tmembrane force 457f 458f 461fnotation 449ndash464radial load 452shear stress 456
DDampingb values 421tcoefficient and topographic factors 422tdata 423ndash424design criteria 419ndash420design modifications 420equations 424factor 419graph of critical wind velocity 423fprecautions 420procedures and examples 424ndash425summary of 421ttypes of 419
Data sheet sample 745Davitsarrangement 562fmoments and forces 558ndash559notation 558ndash563radial load 560ndash561
selection guide 559fstress in 559ndash560 563types of rigging 558f
Dean effect 126 327Defect evaluation minor 780Defects and failures of pressure vessels 733Deflectiondynamic 420static 420tower 399ndash401
Dehydrogenation heat treatment (DHT)740
Delta ring closure 504 515ndash517Demisters 376configuration of 377fflow distribution guidelines for
maintaining 378fnotes 376pads properties of 380t
Density of various materials 112tDesignfailure 7ndash8load combinations 34tpressure 83 762temperature maximum 84
Dimpled jackets 125Discontinuity stress 14Dished heads see Torispherical headsDisplacement method 14Distortion energy theory 5 7Distribution forging 551 552fDouble cone closures 513Double eddy 126 327Downcomer bars weights of 109tDraining vessels time required for
777ndash778Drumscalculating LD ratio 96sizing of 96types of 96
Dynamic analysis 200 420 425Dynamic deflection 420Dynamic instability 418Dynatech test 410
EEccentric cone 58fElastic deformation 8Elastic-plastic method 21Elastic ratcheting analysis 21Elastic stress analysis 21Elasticity modulus of 170 170tElastomeric O-Rings 508Ellipsoidal headsinternal pressure and 70ndash75proportions calculating 99
Elliptical internal manways 181
Index 805
Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Elliptical heads reinforcement for openingsin 85
Elliptical openings reinforcement for 85Empty weight 102End plug 509 518 532 539Energy absorbed by shell 419Equicohesive temperature 24Equivalent lateral force (ELF) 200Erectionbolting 593contractor duties 586ndash587design steps 664flanges top body 672grouting 594guidelines 660leveling 591lifting attachments types of 666ndash674lifting loads and forces 675ndash680local loads in shell due to 710ndash712lugs dimensions and forces of 674flugs shell flange 672notation 665plumbness 591requirement for 586shims 590ndash591soleplates 590straightness 591stresses allowable 664ndash665tailing devices 660tolerances 589ndash590trunnions 672vertical vessels setting of 586weight 102
Euler 29Examination of pressure vessels 732External pressurebuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells 95Code Case 2286 56 95cone for external pressure 44f 61for cylindrical shells 43dimensional data for cones due to 69ffor intermediate heads 74fjacket vessels 125openings and 86for spheres and heads 45f 47ndash48stiffeners combining vacuum with othertypes 42
stiffeners location of 169ndash170stiffeners moment of inertia of bar 49tstiffeners moment of inertia of composite50t
stiffening rings check for externalpressure 75f
stiffening rings moment of inertia of 50toriconical transition 69 70unstiffened shells maximum length of48t
External restraint 13External ring stiffener 52sample problem given 53
FFabricated weight 102Fabrication failure 3ndash7Failures 7ndash8categories of 7ndash8failure modes 8
Fatigueanalysis 15ndash23creep 27ndash29screening criteria for 10t
Fatigue analysis for cyclic service 15ndash23cycle counting methods 16factors influencing design 15ndash16general 21histograms 16protection against ratcheting 21screening procedures 16ndash21
Fiber elongations 134ndash137Fillet weld 782Finite element analysis 436Flange(s)blind flanges with openings 167dimensions for RTJ gasket 145ffaces dimensions of 144flat face 155ffull gasket 155fmaximum allowable pressure for 164freverse 154fring 153fslip-on 152f 155fstandards 140studding 176ndash177 178fweld neck 151f
Flange design 139ndash184notes 144ndash148strategy 140ndash141
Flanged closures 503Flanged heads see Torispherical headsFlangesFlangesblind with openings 167bolt hole orientation 798bolt torque for sealing 169ndash171bolts 147t 163tcoefficients table of 158tndash160terection utilizing top body 672formulas 11gasket facing and selection 141ndash142gasket materials and contact facings34t
gasket widths 34thigh-pressure 140hub stress correction factor 162f
integral factors 25floose hub factors 27f 28flow-pressure 140maximum allowable pressure for 77fnotation 11reverse design 77fRFWN 113fring design 76fslip-on (flat face full gasket) design 77fslip-on (loose) design 75fspecial 140ndash141steps for designing 140ndash141studded 517 549f 550fweights of 106tweld neck (integral) design 74f 104fsee also Lugs flange
Flat face flange 155fFlat heads 76ndash80examples 76ndash80formulas 76large openings in 81ndash83notation 76openings in 85stress in 80
Flat plates 775ndash776Flat ring gaskets 504Follower ring 529Force method 14Forming strains 134ndash137Formulasfor calculating weights 104ffor cylinders 38dimensional 68flanges designing 11flat heads designing 76general vessel 38 764ndash767minimum design metal temperature91ndash92
stress factors 81 150torispherical and ellipsoidal head for
stress 71fFracture appearance transition temperature
(FATT) 763Friction factor 170Full anneal 740Full gasket flange 155f
GGaskets 507ndash508
allowable pressures 509tBridgman 503ndash505 507contact faces types of 143contact surface finishes 143ndash144delta ring 503 504 507 515ndash518 518fdouble cone 503 505 513ndash515 513fndash
515feffective width 157t
806 Index
facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

facing and selection 141ndash142 143tfactor 141flat ring 504lens ring 503 505 511 511f 512fmaterial modulus of elasticity of 170materials and contact facings 156tmetal 507ndash508 507tO-ring 503 505 508ring joint 504RTJ gasket flange dimensions for 145fself energized 505self sealing closures with non-yielding505
self sealing closures with yielding 504self-energized 505 508types of 142twidths 157tyielding 503 504
General buckling 29General loads 9Geometry factors 81Girder 614column design properties of 614ndash615combined section properties of 614compression case 615stiffeners properties of 614tension case 615
Gravity separation 376Gross structural discontinuity 762Grouting 594Gussets 278ndash279 289ndash290
designing 326ndash327
HHandling operations 713fHardness testing 734ndash735requirements for 735Rockwell 736Vickers pyramid 736
Headsexternal pressure design for hemispherical42ndash50
flat 76ndash83formula 39tintermediate 74ndash75internal pressure and ellipsoidal 76internal pressure and torispherical 76properties of 748stresses in due to internal pressure70ndash73
Heads shape tolerances for 792Heat transfer coefficient 126 327 339t
340tHeat treatment 738ndash741defined 740terms and conditions of 738ndash741types of 739f
Helical pipe coils 326ndash344advantages of 326baffles and agitators 332calculations 333ndash335data 336tdesign requirements 326ndash327design tips 326ndash327examples 319ndash327film coefficients 336tgases properties of 336theat loss 339theat transfer coefficient 327 339t
340tlayout for flat-bottom tanks 330fliquids properties of 338tmanufacturing methods 326metal conductivity effect of 344tmetals thermal conductivity of 337tnotation 332notes 327ndash330physical design 326pressure drop 327 335Reynolds number 336 339 352ndash353steam and water properties of 337tsteam and water viscosity of 338tsupports for 331thermal design 326types of 329fwater and liquid petroleum products
viscosity of 343fHemispherical heads external pressure and
45f 47ndash48High pressure closures 503 506tdesign methods 505flanged 503ndash505flat ring gaskets 504materials 504ring joint gaskets 504self energized gaskets 505self sealing closures with non-yielding
gaskets 505self sealing closures with yielding gaskets
504High pressure vessel 473ndash556
ASME VIII Division 3 475ndash476construction types 476 478fdesign options checklist 484texamples 487general 474ndash487multilayer 480ndash482testing amp NDE requirements checklist of
485f 486fsee also Shell design
Hilicoflex O-Rings 508Histograms 16Holding times 779fHomogenization 740
Horizontal vesselserection of 669fpartial volumes of 752f 753tplatform splice 573platforms for 572ftolerances for 784f 785ndash786walkways or continuous platforms for
573see also Saddles horizontal vessels and
design ofHot box design 186Hot wire method 410Hub ringsfor bed supports 321bolted splice connection 323fdefined 321gussets designing 321ndash325load design for 325floads and dimensions of 323fnomenclature 321with radial beams 321 322f 324fring analysis 315splice connection designing 323ndash325support ring 321supports for 325ftorsion in 326
Hydraulic pre-tightening 547Hydrostatic end forces 82Hydrostatic testing of pressure vessels
733ndash734field 734shop 733
IImpact testing avoiding 91Impellersaction of 351types of 346 349
Impingement plates 391calculation 391nomenclature 391
Incremental collapse 8Intercrystalline 24Intermediate headsexternal pressure and head thickness 74internal pressure and head thickness 74methods of attachment 75fshear stress 75
Intermediate stress relieve (ISR)740ndash741
Internal force 80Internal pipe distributors 353ndash357
calculations 356descriptions 360fdimensions for 355fexamples 356ndash357feed options (elevations) 358f 359f
Index 807
Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Internal pipe distributors (Continued)nomenclature 354ndash356notes 354sparger details 361f
Internal pressurebuckling and 96cone for internal pressure 59ndash60for ellipsoidal heads 70ndash73for intermediate heads 74for torispherical heads 70ndash73
Internal restraint 13Internal ring stiffener 53sample problem given 54
Interrupted Quench 740Isochronous curves 29
JJ factor 741Jack bolts 518 529ndash530Jacketed vessels 124ndash127
agitation 126closures types of 131f 132fconventional 124critical Reynolds number 126ndash127design 125dimpled 125equivalent diameter finding 125ndash126external pressure 125heat transfer coefficient 126miscellaneous details 130fmulti-jacketed vessels external pipingconfigurations for 129f
nomenclature 127pressure drop 125ndash133sample problems 127ndash133with spiral baffle 124spiral half pipe coil welded to shell124ndash125
spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124thermal design 127ndash133thickness of 127ndash133types of 128f
KKneebraced designpipe supports 578 581
Knuckle radius thickness required 69ndash70
LLD ratio 96Lamersquo equations 499ndash502Large diameter self-reinforced manways
dimensions and weights for 116fLarge-diameter nozzle openings 394Larson-Miller relation 26Lateral buckling of stiffening rings
51ndash52
Lateral stability 299Lattice beams 310ndash315
configuration of 310fdesign of 313fdiagonals of 314dimensions of 310fend diagonal of 314ndash315load design for 312fnotes 315properties of 314ring analysis 315stability check 315
Leg supports 187base plates for 275ndash276
Legs erection of vessels with 669fLegs seismic design for bracedflow chart for 216flegs and cross-bracing sizes for 223load diagrams 218fnotation 217
Legs seismic design for unbracedcalculations 210dimensional data 209fleg configurations 209fleg sizing chart 214fnotation 208ndash209vertical load 213t
Length critical 95Lens ring closure 511Lifting see ErectionLigaments 86Lightly loaded attachments 762Linear elastic 497Loadscombinations 10t 200ndash201 643lifting 675ndash680on wire rope 714f
Local bucklingdefined 29
Local loads 8ndash9attachments converting 448methods for analyzing 436methods for reducing shell stress436ndash437
ring stiffeners partial 446ndash448in shell due to erection forces 710ndash712stress in circular rings 446stress in cylindrical shells 449ndash464stress in spherical shells 465ndash471
Local primary membrane stress 12Local thin area (LTA) 432ndash433multiple 433nomenclature 432notes 433single 432ndash433
Logarithmic decrement 420 421tLongitudinalmeridional stress 3
Lubricating bolts 171formula 39t
Lugs 188dimensions and forces 674fshell flange 672side 670f 671ftailing 689ndash690top head and cone lifting 691ndash693
Lugs design ofbase plate 275ndash276compression plate 280ndash281dimensions standard 281tgussets 278ndash279notation 278
Lugs flangebase plate design 700bolt loads for rectangular 699bolt properties 696tbolts check of 701design steps 698diagram 695ndash704dimensions 696tfull circular base plate design 699loads 674nozzle flange check 698sample problem for top 702ndash704side 697 711ndash712tension maximum 698top 697 711ndash712
Lugs seismic design for 229ndash239anchor bolts required size of 238b values computing equivalent 233t
453coefficients 453tgeometric parameters computing 233notation 223ndash230radial loads 233f 234t 235fradial thermal expansion 238reinforcing pads use of 233ndash234stress diagrams 254fstresses 234t 455tstresses combining 234fstresses computing 232f
MMagnetic particle inspection 737Main nut 518 539Major attachments 762Manways weights of 108tMaterialfailure 7ndash8properties 59tselection guide 61t
Maximum allowable nozzle loads 462ndash464Maximum allowable pressure (MAP) 762calculating 53defined 83
808 Index
Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Maximum allowable temperature (MAT)762
Maximum allowable working pressure(MAWP) 762
calculating 53defined 83
Maximum permissible bow 787Maximum principal stress theory 4 7Maximum shear stress theory 4ndash5Maximum stress theory 4fMax-min cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Mechanical pre-tightening 547Membrane stressanalysis 3local primary 12primary general 12secondary 12
Mesh pad construction and installation379f
Metal gaskets 507ndash508properties of 507t
Metal O-Rings 508Metric guidelines and conversions
768ndash771Minimum design metal temperature
(MDMT) 763arbitrary 91design temperature and 84determining 91texemption 91flow chart for 94fformulas 91ndash92notation 90ndash91test 91
Minimum pressurization temperature(MPT) 763
Minor attachments 762Minor defect evaluation 12Mist eliminators see DemistersMixersapplications 345 350fbaffles 345 348impellers action of 351impellers types of 346 349mounting 345 348notation 345ndash351
Mixing defined 345Modal response spectrum analysis 200Moment coefficients for base rings
686tMoment of inertiaof bar stiffeners 49tcalculation form 398fof composite stiffeners 50tof stiffening rings 50f
Moments calculating 82
MPC Omega method 26Multi-jacketed vessels external piping
configurations for 129fMultilayer autofiettage thick-walled
pressure vessel 9Multilayer pressure vessels 480ndash482advantages of 481ndash482in ASME Code 481disadvantages of 482features of 481ndash482general 481history of 480
Multilayer thick-walled pressure vessel476
Multiwall thick-walled pressure vessel476
NNational Building Code (NBC) 425Nil ductility transition temperature (NDT)
763Normal loads 9ndash10Normalizing 740Norton-Bailey power law 26Nozzle position 89fNozzle reinforcement 85ndash86for large-diameter openings 394
Nozzles 551bottom catalyst dump 115fquench 114fside catalyst dump 119fthrough 181weights of 108t
OObround openings reinforcement for
85Occasional loads 9ndash10Openingsin elliptical heads 85external pressure and 86in flat heads 81ndash83 85large-diameter nozzle 394multiple 86near seams 86through seams 86in torispherical heads 85
Operating pressure 84Operating temperature 84Operating weight 102 267O-Rings 505 508elastomeric 508hilicoflex 508metal 508
Overstrain ratio 483Over-tightening 547Overweight percentage 102
PPaddle-type impellers 346Panel test 410Partial ring stiffeners 446ndash448Peak stress 12ndash13Perforated spargers see Internal pipe
distributorsPeriod of vibration (POV) 201ndash204 202f
203f 206fPipe coils see Helical pipe coilsPipe distributors 353Pipe supportsalternate-type 581brackets cantilever-type 580brackets high-temperature 579brackets types of 576design of 576ndash583dimensions 576tkneebraced 578 581unbraced 576weight of 577t
Pipes weights of 110tPlastic deformation excessive 8Plastic instability 8Plate overage 102Pneumatic testing of pressure vessels 734Post connection plate 616Posts see Leg supportsPrecipitation hardening 763Pressure drop 125ndash126
jacket vessels 125ndash133Pressuredesign 83drop and design of helical pipe coils
125ndash126 335operating 84see also External pressure Internal
pressurePressure relief values (PRVrsquos) application
guideline for 801Primary stressbending 80general 11local 12
Process Anneal 740Proof testing of pressure vessels 734Propeller-type impellers 346Pull-up studs 528ndash529PWHTmaximum 741minimum 741requirements for 21ndash31
QQuench amp tempered 763Quench nozzles weights of 114fQuenching 740
Index 809
RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

RRadial beamshub rings with 322f 324fload design for 325fmoment of inertia of 319
Radial stress 3Radial thermal expansionseismic design for lugs 238
Radiographic examination 738Rail transportation see Transportation railRainfall cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Rankine factors 593t 594Ratcheting 21Reactor bottom outlet estimated weights
118fReactor inlet estimated weights 117fRecrystallization 740Rectangular platforms 571ndash575Refractory lined equipment 411Refractory lined vessels 411Refractory lines components skin
temperature of 412Refractory liningsallowable refractory stresses 408calculations 415ndash416creep rate 408failures and hot spots causes of410ndash411
flow chart 413fheat loss and cold face temperaturecalculating 409ndash410
hot versus cold face 408notation 299 397 414notes 411ndash412properties and data 397properties of materials 417tselection 408ndash409shrinkage 408spalling 408specific heat 410stresses allowable 394summary of results 418tthermal conductivity 410
Refractory materials properties of 417tReinforcementnozzle 85ndash86 394for studding outlets 175
Relaxation of joints 171Reservoir cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Resistance 419Retaining ring 530ndash531Reverse flange design 154fReynolds number 126 334 369fRibbon wound 479f 480Rigging terminology 558f
Ring(s)analysis 436ndash446compression 590ndash591joint gaskets 504support of internal beads 306supports 189see also Circular rings stress in
Hub rings Stiffening ringsRing flange design 153fRing girdersbending moments internal 403tdesign check for base 683design steps 404ndash406dimensions and forces 402fformulas 403load diagrams 404notation 402ndash403
Rings seismic design forcalculations 224coefficients 226fmaximum bending moments 228tnotation 223ndash229thickness determining 241f
Roark Technical Note 446Rockwell hardness testing 736Rolled threads 763
SSaddle(s)supports 187ndash188weights of 112tsee also Transportation shipping saddles
Saddles horizontal vessels and design ofcircumferential bending 262circumferential compression 262coefficients 263f 264tdimensional data 254fdimensions for saddles 265flongitudinal bending 261ndash262moment diagram 255fnotation 253ndash254procedure for locating 260stress diagram 223stresses shell 260stresses types and allowable 259ndash260tangential shear 262transverse load 257
Saddles large vessels and design ofanchor bolts 271ndash272base plate designs 270ndash271dimensional data 268fforces and loads 267ndash269notation 267rib design 272ndash273web design 269
Sealing flanges bolt torque for 169ndash171calculations 171
friction factor 170gasket material modulus of elasticity of
170notation 169ndash170notes 171
Seamsopenings near 86openings through 86pads over 86
Secondary stress 12Seismic design general 199ndash204
allowable stresses and load combinations200ndash201
equivalent lateral force 200modal response spectrum analysis 200notes 204period of vibration 201ndash204 206f
Seismic design for vesselson braced legs 217ndash223on conical skirt 248ndash252design response spectrum 208fgeneral 204ndash205on lugs 229ndash239on rings 223ndash229risk category 207tsite classification 207tsite coefficient 207ton skirts 239ndash247on unbraced legs 208vibration periods 206f
Self energized gaskets 505Self sealing closureswith non-yielding gaskets 505with yielding gaskets 504
Self-energized gaskets see O-RingsService considerations 33Service failure 7ndash8Shackles steel 715tShear band 252Shear loads in bolted connections 584ndash585Shear stress intermediate heads and 75
Shear stressbuckling of thin wall cylindrical shells
96at internal or external pressure on ring
section 52ndash53Shellslongitudinal in shell due to shear band
252shipping saddlessee also Transportation shipping saddlesthickness required 40f
Shell design 496ndash502high pressure design safety factors for
496ndash497thick walled cylinders 497ndash502
498fndash502f
810 Index
Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Shell stresses due to loadings at supportbeam locations 316
equations 316nomenclature 316
Shell thickness procedures 616ndash617Shifted neutral axis method 281ndash291Shims 590ndash591Shipping saddle 558calculation 585example 586notes 586ndash594tension band notation 585
Shipping weight 102Shrink ring 482 518 521f 524f 525fSide catalyst dump nozzles dimensions and
weights of 119fSign convention 439ndash440Simplified cycle counting procedure for
fatigue analysis 16Simplified elastic-plastic method 21Skirt supports 186see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofcrippling 684
Skirts design of 684Skirts seismic design forconical skirt 248ndash252 253fdimensional data 240flongitudinal stresses 246ndash247nonuniform vessels 240ndash245notation 239uniform vessels 239
Sleeve nuts 546Slenderness ratio method 29Spheres external pressure design for 45f47ndash48
Slip-on flange design 152f 155fSoleplates 590Solution Annealing 740Spalling 408Sparger details 361fSpheres field-fabricated 594ndash630accessories 595codes of construction 594combined girder-shell section dimensionaldata for 612
conversion factors 596data sheet 604fdimensional data 597 608fabrication methods 595field hydrotests 595formulas 596heat treatment 595leg and brace dimensions 608leg attachment 597liquid levels 597materials of construction 594ndash595
nomenclature 605notation 596notes 595ndash596products stored 594shell section properties of 611sizes thicknesses and capacity range
595supports for 595types of 599weights 601t 602f 603f
Spherical shellsformula 38
Spherical shells stress in 465ndash471calculation steps 465formulas 471notation 465notes 471stress indices loads and geometric
parameters 471Spherically dished covers 165Spheroidization 740Spiral baffle jacket with 124Spiral pipe coil welded to shell 124half 124ndash125
Spiral weld 762Splice connection designing 321ndash325Spray headers 365fSquare platforms 571ndash575Stabilizing treatment 740Stacks vibration 418ndash427Stainless steel sheet weights of 422tStatic deflection 420Steady loads 9Steady state creep 25Steels 720ndash721Step cooling 741Stiffenerscombining vacuum with other types
42ndash43composite 381 388texternal ring 52geometry 51finternal ring 53location of 42ndash43moment of inertia of bar 49tmoment of inertia of composite 50t
Stiffening rings 51ndash54check for external pressure 51tdimensions 51f 52fhorizontal vessels 52ndash53lateral buckling of 51ndash52moment coefficients for base 686tmoment of inertia of 50nomenclature 51partial 446ndash448properties of 51ndash54sample problem given 53ndash54
section shell stresses due to internal orexternal pressure on 52ndash53
shell influence with formula derivationfor 51
size base 685Stiffeners properties of 614Strain hardening 763Strain high 8Strainsfiber elongation forming 134ndash136formed heads blank diameter for 134ndash136nomenclature 134notes 136pipe bends wall thinning of 134
Stressallowable 772ndash774analysis 2ndash3categories of 11ndash13circumferentiallatitudinal 3combined 616corrosion 8due to banding 799ndash800due to offset 799ndash800due to out of tolerance condition 799due to peaking 799ndash800in flat heads 80 82formula factors 81 149ndash150in heads due to internal pressure 70ndash73intensity 6ndash7limits of 13longitudinalmeridional 3radial 3redistribution 9relief 740in shell 539ndash540types of 11
Stress theoriescomparison of 5ndash7maximum 4maximum shear 4ndash5
Struts 591Stud tensioners 171Studding flanges 176ndash177dimensions of 177nomenclature 177worksheet for 177ndash180 178f
Studding outlet 172 175Studs 546pretightening methods 546ndash547
Sub-critical anneal 740Superposition principle of 448Support blocks 319ndash320notes 320welded integral with beam 319ndash320welded to top of beam 320
Support of internal beadsbeams 298ndash299design of 303f
Index 811
Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Support of internal beads (Continued)load design 299 302fnomenclature 299ndash300procedure 299ring 306
Support of internal beds 298ndash306beam seat support 298clip support 298double beam 301fforces and moments summary of 305tgrating 306hub ring 298lattice beam 298ndash299load on circular ring 306methods of 299nomenclature 299ndash300single beam 301f
Supportsbase details for vertical vessels design of291ndash292
base plates for legs 275ndash276for bins and elevated tanks 593coils 331leg 187 278ndash281lugs 188for radial beams 325fring 189 298ndash309saddle 187ndash188saddles design of horizontal vessel on253ndash266
saddles design for large vessels267ndash273
seismic design for vessels 204ndash205seismic design for vessels on braced legs217ndash223
seismic design for vessels on lugs229ndash239
seismic design for vessels on rings223ndash229
seismic design for vessels on shirts239ndash247
seismic design for vessels on unbracedlegs 208ndash217
skirt 186spheres 595wind design per ASCE 189ndash197see also Pipe supports
Surge capacities 779Sway bracing 222 615
TTail beams 684Tailing devices 672Tailing lugs 689ndash690Tanks elevateddimensional data 587fliquid-filled 588
small internal pressures 590support arrangements 592fsee also Bins
Tanksunderground 428ndash432
Temperaturemaximum design 84operating 84see also Minimum design metal
temperatureTempering 740Test pressure 762Test weight 102Testing of pressure vessels 732ndash733
Brinell 735ndash736hardness 734ndash735hydrostatic 733ndash734locations of 735methods of 735pneumatic 734proof 734quantity of 735timing of 735
Thermal conductivity 410Thermal design procedure for jacket
vessels 125Thermal gradients 13Thermal pre-tightening 547Thermal stress ratcheting 13 21Thermal stress 13ndash14Thick walled cylinders 497ndash502Lamersquo equations 499ndash502nomenclature 497ndash502requirements of 498ndash499thickness determination worksheet for498fndash502f
Thinning allowance 102 109t 120t617
Thin-walled cylindrical shells see Bucklingof thin-walled cylindrical shells
Thread load distribution 540Thread root tooth bending stress 540ndash541Threaded closures 539ndash545with Bridgman gasket 544ndash545design procedures 539ndash541nomenclature 539
Through nozzles 181Tie rods 187Toe angle 573Tolerances 781ndash784condition stress due to out of 799flange bolt hole orientation 798for horizontal vessels 784ndash786maximum permissible bow 787ndash788for shape of heads 792for tray support rings and downcomers789ndash791
for trayed columns fabricated in multiplesub-assemblies 786ndash787
for trays 789for vertical vessels 781ndash782
Top head lugs 678Toriconical transitions dimensional data
and formulas 67ndash70due to external pressure 69ndash70for large end 68ndash69for small end 69
Torispherical headsinternal pressure and 46freinforcement for openings in 85
Torque for sealing flanges 169ndash171Towerdeflection 189ndash197dimensions of 366nomenclature of 366vibration 418ndash427
Transcrystalline 24Transformation range 740Transformation temperature 740Transportationaxle loads 573forces 632 648with incorporation of shipping factors
576 578ndash581lashing 633 655fload diagrams for moments and forces
649ndash650methods 634organizations involved in 633site descriptions 717tstresses checking 659fstresses determining 633uniform load case 576 578ndash581vertical vessel on two saddles 576
578ndash581Transportation bargedirections of ship motions 643fforces 641tpitch and roll 642ndash643
Transportation railbolster loads 639f 640fcapacity ratios for loads 638fclearances 637fforces on 643multiple car loading details 637fspecial factors 633ndash634types of cars 636f
Transportation shipping saddlesconstruction methods 653f 654fguidelines for 632ndash633tension bands on 656ndash657
Transportation truckexamples of 647fforces on 644f
812 Index
Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

Transporter stability 573Tray support rings tolerances for 789ndash791Tray supports weights of 109tTrayed columns fabricated in multiple
sub-assemblies tolerances for786ndash787
Tray nomenclature 366ndash367Trays 366ndash374
assembly of 370fnomenclature of 366ndash367plates 371ndash374tolerances for 789tower dimensions of 366ndash368types of 367
Tray types 367Triaxial states of stress 4ndash5Trunnions 664design of 706ndash709loads 710tailing 672
Turbines 346Turnbuckles 18723 rule 257
UUltrasonic examination 737ndash738Unbraced legs seismic design for see Legs
seismic design for unbracedUnderground tanks and vessels 428ndash432
anchor strap 430buried vessels 429ndash430example 431external pressure 430nomenclature 428notes 431ndash432in pit 430ndash431saddle design 430
Unstiffened shells maximum length of 48tUserrsquos design specification 34ndash35
VVacuum chart method 56tValve trays weights of 109tVertical vessels
anchor bolts for 293platforms for 571ftolerances for 781ndash782see also Base details for vertical vessels
design ofVessel proportionscalculating 96ndash99volumes and surface areas 749ndash755
Vesselsclassification of 755parts of 755ndash760in pit 430ndash431types of 755underground 428ndash432vessel definition 87fvessel nomenclature 428
Vibration towers and stacks and 418ndash427Vickers pyramid hardness testing 736Volumes and surface areas 749ndash755Vortex shedding 418design modifications to eliminate 419
WWashers 546Water calorimeter 410Weightsallowance for plate overages 102of bolts alloy stud 111tof carbon steel plate and stainless steel
sheet 105testimating 102of flanges 106t 113fformulas for 103t 104fof nozzles and manways 108tof pipes 110tof saddles and baseplates 112tthinning allowance 109tof tray supports and downcomer bars
109tof valve trays 109tof weld neck flange 104f
Weights types ofempty 102
erection 102fabricated 102operating 102shipping 102test 102
Weirs flow over 375Weld neck (integral) flanges 74f 104fWeld neck flange design 151fWeldingchecking 692ndash693leg supports 187lug 692ndash693pad eye 693re-pad 693saddle supports 188skirt supports 186
Wind design per ASCE 189ndash197ASCESEI 7-10 190design procedure 190exposure categories 193gust factor determining 191notation 189ndash190notes 193ndash197sample problem 191ndash192
Wind velocity critical 418ndash420Wire wound 475Wire wrapped thick-walled pressure vessel
476WRC Bulletin 107 188 436WRC Bulletin 198 448
XX-ray requirements for 732
YYield criteria see Stress theories
ZZick L P 187Zickrsquos analysis 187ndash188 430 633Zickrsquos stresses 187ndash188Zorilla method 424ndash425
Index 813
This page intentionally left blank

This page intentionally left blank