Presentation 06 - Human Digestion
description
Transcript of Presentation 06 - Human Digestion

Human digestion

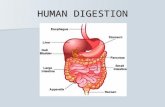
Human digestive system (General plan)
Accessory digestive organs

Organ/s Mechanical digestion
Carbohydrate digestion Protein digestion
Nucleic Acid digestion
Lipid digestion
Oral cavityEsophagusPharynx
ChewingPeristalsis
Stomach ChurningMixingPeristalsis
Small intestineLumen
PeristalsisMixing
Small intestineEpithelium
Polysaccharides(starch, glycogen)
Disaccharides(sucrose, lactose)
Salivary amylaseSmaller polysaccharides,
maltose
Polysaccharides
Pancreatic amylase
Maltose and other disaccharides
Disaccharidases
Monosaccharides
Proteins
Pepsin
Small polypeptides
Pancreatic trypsin and chymotrypsin Smaller polypeptides
Small peptidesDipeptidases,
carboxypeptidase,
aminopeptidase
Amino acids
DNA, RNA
Pancreaticnucleases
Nucleotides
NucleotidasesNucleosides
Nucleosidases, phosphatasesNitrogenous
bases,sugars,
phosphates
Fat globules
Bile saltsFat droplets
Pancreatic lipase
Glycerol, fattyacids, glycerides
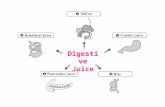
Sites of digestion


• Salivary glands– Water– Some enzymes• Salivary amylase• Lysozyme
– Mucus or mucin• Teeth
Digestion in the Mouth

Swallowing: from mouth to stomach

Muscular sac◦ Churns & mixes
foodGastric glands
◦ Parietal cells HCl, intrinsic factor
◦ Goblet cells mucus
◦ Chief cells pepsinogen, weak gastric lipase
◦ Gastrin Hormone Controls gastric juices
Comes out as chyme (2-6 hours)
Digestion in the Stomach

LiverSecretes bile (stored in gall bladder)Emulsifies fats
GallbladderStores, concentrates, and
releases bile into duodenum
Stimulated by the hormone cholecystokinin (CCK)

• Exocrine function• Acinar cells secrete
pancreatic juice– Amylase– Lipase– Trypsin– Chymotrypsin– Carboxypeptidase– Nuclease– NaHCO3
• Secretin and cholecystokinin (CCK) fr intestinal wall stimulates PJ production
Pancreas


Absorption in the small intestine

Reabsorption and elimination in the large intestine
• Areas of the colon• cecum • rectum • anus
• Absorption of water and electrolytes
• Concentration & elimination of solids
• Home for bacteria• folic acid• vitamin K• several B-vitamins• gases

• Liver
• Gall-• bladder
• CCK
• Entero-• gastrone
• Gastrin
• Stomach
• Pancreas
• Secretin
• CCK
• Duodenum
• Key
• Stimulation
• Inhibition



















![Human digestion _ch[1]._35](https://static.fdocuments.us/doc/165x107/5551b892b4c905ca7f8b4c0a/human-digestion-ch135.jpg)

