Polyhedron A polyhedron is simply a three-dimensional solid which consists of a collection of...
-
Upload
darcy-beasley -
Category
Documents
-
view
227 -
download
3
Transcript of Polyhedron A polyhedron is simply a three-dimensional solid which consists of a collection of...
PolyhedronPolyhedron
A polyhedron is simply a three-dimensional solid which consists of a collection of polygons, joined at their edges.
A polyhedron is said to be regular if its faces and vertex figures are regular polygons.
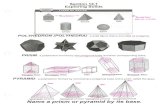
Name that figure. . .Name that figure. . .
Heptagonal Prism
Triangular Prism
Hexagonal Prism
Rectangular Prism
Name that figure. . .Name that figure. . .
Hexagonal Pyramid
Triangular Pyramid
Pentagonal Pyramid
Rectangular Pyramid
Prisms vs. PyramidsPrisms vs. Pyramids
Two congruent, Two congruent, parallel faces are the parallel faces are the basesbases
Sides are Sides are parallelogramsparallelograms
Named by its baseNamed by its base
One baseOne base
Sides are trianglesSides are triangles
Named by its baseNamed by its base
http://www.math.com/school/subject3/lessons/S3U4L1GL.html
PolyhedraPolyhedra Faces: Polygonals regions Faces: Polygonals regions
that make up the surface of a that make up the surface of a solidsolid
Edges: The line segments Edges: The line segments created by the intersection of created by the intersection of two faces of a solidtwo faces of a solid
Vertices: The points of Vertices: The points of intersection of two or more intersection of two or more edgesedges
FigureFigure Number of Number of FacesFaces
Number of Number of VerticesVertices
Number of Number of EdgesEdges
Rectangular Rectangular Prism (Cube)Prism (Cube)
Pentagonal Pentagonal PrismPrism
Rectangular Rectangular PyramidPyramid
Pentagonal Pentagonal PyramidPyramid
Counting Parts of Solids, Navigations (Geometry), Grades 3-5
FigureFigure Number of Number of FacesFaces
Number of Number of VerticesVertices
Number of Number of EdgesEdges
Rectangular Rectangular Prism (Cube)Prism (Cube)
66 88 1212
Pentagonal Pentagonal PrismPrism
Rectangular Rectangular PyramidPyramid
Pentagonal Pentagonal PyramidPyramid
Counting Parts of Solids, Navigations (Geometry), Grades 3-5
FigureFigure Number of Number of FacesFaces
Number of Number of VerticesVertices
Number of Number of EdgesEdges
Rectangular Rectangular Prism (Cube)Prism (Cube)
66 88 1212
Pentagonal Pentagonal PrismPrism
77 1010 1515
Rectangular Rectangular PyramidPyramid
Pentagonal Pentagonal PyramidPyramid
Counting Parts of Solids, Navigations (Geometry), Grades 3-5
FigureFigure Number of Number of FacesFaces
Number of Number of VerticesVertices
Number of Number of EdgesEdges
Rectangular Rectangular Prism (Cube)Prism (Cube)
66 88 1212
Pentagonal Pentagonal PrismPrism
77 1010 1515
Rectangular Rectangular PyramidPyramid
55 55 88
Pentagonal Pentagonal PyramidPyramid
Counting Parts of Solids, Navigations (Geometry), Grades 3-5
FigureFigure Number of Number of FacesFaces
Number of Number of VerticesVertices
Number of Number of EdgesEdges
Rectangular Rectangular Prism (Cube)Prism (Cube)
66 88 1212
Pentagonal Pentagonal PrismPrism
77 1010 1515
Rectangular Rectangular PyramidPyramid
55 55 88
Pentagonal Pentagonal PyramidPyramid
66 66 1010
Counting Parts of Solids, Navigations (Geometry), Grades 3-5
6 12 8
6 12 8
5 9 6
7 15 10
8 18 12
5 8 5
4 6 6
6 10 6
7 12 7
Explain the relationship that exists among the number of faces, edges, and vertices of each solid in the chart.
Faces + vertices = edges + 2
F + v = e + 2
F + v = e + 2
A polyhedron has 7 faces and 15 edges. A polyhedron has 7 faces and 15 edges. How many vertices does it have?How many vertices does it have?
F + v = e + 2
A polyhedron has 10 edges and 6 vertices. A polyhedron has 10 edges and 6 vertices. How many faces does it have?How many faces does it have?
F + v = e + 2
A polyhedron has 6 faces and 8 vertices. A polyhedron has 6 faces and 8 vertices. How many edges does it have?How many edges does it have?
Connect Math Shapes SetConnect Math Shapes Set
http://phcatalog.pearson.com/component.cfm?http://phcatalog.pearson.com/component.cfm?site_id=6&discipline_id=806&subarea_id=1316&program_id=23245&prsite_id=6&discipline_id=806&subarea_id=1316&program_id=23245&product_id=3502oduct_id=3502
CMP Cuisenaire® Connected Math CMP Cuisenaire® Connected Math Shapes Set (1 set of 206)Shapes Set (1 set of 206)ISBN-10:ISBN-10: 157232368X 157232368XISBN-13:ISBN-13: 9781572323681 9781572323681Price:Price: $29.35 $29.35
PentominosPentominos
How many ways can you arrange five tiles How many ways can you arrange five tiles with at least one edge touching another with at least one edge touching another edge? edge?
Use your tiles to determine arrangements Use your tiles to determine arrangements and cut out each from graph paper. and cut out each from graph paper.
PentominosPentominos
http://www.ericharshbarger.org/pentominoes/http://www.ericharshbarger.org/pentominoes/
Building a BoxBuilding a Box
Illuminations: Illuminations:
How many different nets can you draw that How many different nets can you draw that can be folded into a cube?can be folded into a cube?
http://illuminations.nctm.org/activitydetail.aspx?ID=84http://illuminations.nctm.org/activitydetail.aspx?ID=84
It’s the view that counts! It’s the view that counts! (3-5 Geometry, Navigations)(3-5 Geometry, Navigations)
When you have a 3-D shape, what do you When you have a 3-D shape, what do you see when you look at eye level from the see when you look at eye level from the front, then from above, and then at eye front, then from above, and then at eye level from the side?level from the side?
How could you represent the shape so that How could you represent the shape so that someone else might be able to build it?someone else might be able to build it?
It’s the view that counts! It’s the view that counts! (3-5 Geometry, Navigations)(3-5 Geometry, Navigations)
Using three linking blocks, draw on grid Using three linking blocks, draw on grid paper a two-dimensional representation of paper a two-dimensional representation of the front, side, and top views of your the front, side, and top views of your building. Label the views. building. Label the views.
It’s the view that counts! It’s the view that counts! (3-5 Geometry, Navigations)(3-5 Geometry, Navigations)
FRONT TOPSIDE
It’s the view that counts! It’s the view that counts! (3-5 Geometry, Navigations)(3-5 Geometry, Navigations)
Using four linking blocks, draw on grid paper Using four linking blocks, draw on grid paper a two-dimensional representation of the a two-dimensional representation of the front, side, and top views of your building. front, side, and top views of your building. Label the views. Label the views.
Have your neighbor recreate your building based on your views.
It’s the view that counts! It’s the view that counts! (3-5 Geometry, Navigations)(3-5 Geometry, Navigations)
It’s the view that counts! It’s the view that counts! (3-5 Geometry, Navigations)(3-5 Geometry, Navigations)
Transfer your drawing to a three-Transfer your drawing to a three-dimensional view. dimensional view.
Isometric Explorations Isometric Explorations (6-8 Geometry, Navigations)(6-8 Geometry, Navigations)
Isometric Explorations Isometric Explorations (6-8 Geometry, Navigations)(6-8 Geometry, Navigations)
Isometric Explorations Isometric Explorations (6-8 Geometry, Navigations)(6-8 Geometry, Navigations)
Isometric Explorations Isometric Explorations (6-8 Geometry, Navigations)(6-8 Geometry, Navigations)
VolumeVolume
Cylinder Cylinder vs. vs. Cone Cone
Cube vs. Square pyramidCube vs. Square pyramid
lwhV
BhV
3
13
1
hrV 2 hrV 2
3
1
lwhV
BhV