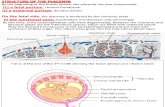
Placenta & Amnion (General Embryology)
-
Upload
dr-sherif-fahmy -
Category
Education
-
view
422 -
download
0
Transcript of Placenta & Amnion (General Embryology)

13th day
Endodermal cells
Secondary yolk sac
Exocoelomic cyst
Somatic mesoderm
Connecting stalk
Somatic mesoderem
Splanchnic mesoderm
1ry chorionic villi
Extra-embryonic coelom Chorionic cavity)
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

13th day
Somatic mesoderm
Connecting stalk
1ry chorionic villi
Cyto-trophoblast
Intervillous space
Syncytio-trophoblast
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Tertiary Chorionic Velli
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Syncytio-trophoblastCyto-
trophoblast
Somatic extraembryonic mesoderm
Fetal blood vessels
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Types of Tertiary Chorionic Velli

Decidua basalis (Decidual plate)
Chorion frondosum
Chorionic plate
Chorion leave
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Fetal Membranes
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Fetal membranes:1- Chorion and placenta.2- Amnion.3- Umbilical cord.4- Yolk sac.
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Chorion
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

It is the wall of chorionic vesicle.Time: Chorionic vesicle is formed at the 12th day by the formation of extra-embryonic mesoderm.Structure of chorion:1- Syncytiotrophoblast.2- Cytotrophoblast.3- Somatic extra-embryonic mesoderm.Chorionic velli:1- Primary.2- Secondary.3- Tertiary.
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Somatic mesoderm
Connecting stalk
Secondary yolk sac
Somatic mesoderm
Extra-embryonic coelom
Amniotic cavity
Splanchnic mesoderm
Syncytio-trophoblast
Cyto-trophoblast
Chorion
Exocoelomic cyst
Embryonic disc
Chorionic Vesicle
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Endodermal cells
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Primary chorionic villus
Cyto-trophoblast
Syncytio-trophoblast
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Syncytio-trophoblast
Cyto-trophoblast
Somatic mesoderm
Secondary chorionic villus
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Syncytio-trophoblast
Cyto-trophoblast
Mesoderm
Fetal blood vessels
Tertiary chorioniv villus

Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

1- Primary chorionic velli (start of 3rd week): cyncytiotropholblasts and cytotrophoblast.
2- Secondary chorionic velli (middle of 3rd week):
Cyncytiotrophoblast, cytotrophoblast and mesoderm (in the central core).
3- Tertiary chorionic velli (end of 3rd week): formation of fetal blood vessels in the mesoderm.
-Tertiary velli, opposite decidua basalis form side branches and called chorion frondosum while under decidua capsularis it will degenerates to form chorion leave.
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

PLACENTA
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Morphology of Placenta• It is the organ of exchange of materials between fetal
and maternal blood.• Shape: Disc like.• Surfaces:• -Fetal surface: It is covered with amnion and fetal blood
vessels. Umbilical cord is attached near the center of this surface.
• -Maternal surface: Shows 15 – 20 rounded elevations (cotyledons) with septa inbetween).
• Diameter: 15 -25 cm.• Thickness: About 3 cm.• Weight: About 500 – 600 gm• Site: At original implantation site which is upper part of
posterior wall of uterus.Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Cotyledon
Groove between cotyledons
Umbilical cord
Maternal surface
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Fetal surface covered with amnion
Umbilical cord
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Formation of Placenta

Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Structure of Placenta

Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Decidua basalis
Arteriol
Venule
Decidual septum
Cytotrophoblastic shell
Decidual plate
Stem villous
Floating velli
Intervillous space
Chorionic plate
Umbilical veinUmbilical arteryAmnion
MesodermSyncytiotrophoblast
Cytotrophoblast
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Structure of Placenta• The placenta is developed from 2 parts:
Chorion frondosum (tertiary velli) and Decidua basalis. The internal structure of placenta is described as follow:
• 1- Chorionic velli: They are stem and absorbing (floating). They are composed of syncytiotrophoblast, cytotrophoblast, mesoderm and fetal blood vessels.
• 2- Intervillous spaces: They are spaces between stem villi that are filled with maternal blood.
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

3- Cytotrophoblastic shell; complete sheet of cytotrophoblastic cells that is present between decidua basalis and intervillous spaces.4- Decidual septa: They descend from roof of intervillous spaces. Each septum is composed of decidua basalis, cytotrophoblast and cyncytiotrophoblasts. There is a groove opposite each septum which are separated from each other by cotyledones.5- Chorionic plate: composed of amnion, extraembryonic mesoderm,cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast.
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

6- Decidual plate: composed of:- Syncytiotrophoblast.- Cytotrophoblast.- Decidua basalis.
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Placental barrier:It is the separation between fetal and maternal blood.Structure:1- Syncytiotrophoblast.2- Cytotrophoblast.3- Extraembryonic mesoderm.4- Endothelium of fetal blood vessels.Functions of the barrier:1- Separates between fetal and maternal blood.2- Permites gaseous and nutritive exchange.3- Prevents passage of bacteria, most viruses and damaging factors.
Disappear in 2nd ½ of pregnancy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Placental circulation:1- Maternal part: Maternal blood flow from endometrial arterioles to the intervillous spaces where floating velli are bathed in maternal blood. Exchange of gases and nutritive materials occurs. Then blood flows back from chorionic plate to endometrial veins.2- Fetal part: umbilical arteries carry venous blood of the fetus to placenta while umbilical veins carry blood loaded with nutritive material and oxygen. Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Functions of placenta1- Exchange of gases and metabolites.2- Transmission of maternal antibodies
starting from 14th week.3- Production of hormones as progesterone,
estrogen, HCG and somatomammotropin 3- Barrier against bacteria and most of viruses.4- Excretory function as it excretes urea and
creatinine.Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Anomalies of Placenta1- Abnormalities in position:
A- Placenta previa parietalis.B- Placenta brevia marginalis.C- Placenta brevia centralis.
2- Abnormality in shape:A- biloped placenta.B- Triloped placenta.
3- Abnormality in number:A- Twin placenta.B- Accessory placenta.
4- Abnormality in attachement of umbilical cord:A- Velamentous.B- Battle door.
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Placenta previa Marginalis & parietalis
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Placenta previa centralis
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Velamentous placenta
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Battle door placenta
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Accessory placenta
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Placenta acretaPlacenta percreta
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

AMNION

Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Extraembryonic coelom (Chorionic Cavity)
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

AMNION-It is a membrane that enclose amniotic cavity.-Formation: -It is formed at the 8th day as a small cavity in
epiblast cells with formation of amnioblasts. -So, floor of the cavity is epiblast while the
roof is formed from amnioblasts. -By the 12th day it becomes separated from cytotrophoblasts by primary mesoderm (Extraembryonic).-Amnio-ectodermal junction is at the margin of oval embryonic disc at the 3rd week.Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

8th day of pregnancy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Endometrium
Syncytio-trophoblast
CytotrophoblastBlastocele Amnioblast
Amniotic cavity
Epiblast Hypoblast Trophoblast
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

9th & 10th days
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Cyto-trophoblast
Amnioblast
Amniotic cavity
Epiblast
HypoblastHeuser’s membrane
Primary yolk sacFibrin clot
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

-At 3rd month amnion comes in contact with chorion to form amnio-chorionic membrane with obliteration of chorionic cavity.-By the end of 3rd month, uterine cavity is obliterated due to expansion of amniotic cavity. -Finally, the amniotic cavity surrounds the fetus and forms a tubular sheath around the umbilical cord.
-Expansion of amniotic cavity leads to folding of the embryonic disc and amnio-ectodermal junction will be present at primitive umbilical ring.
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Extraembryonic coelom (Chorionic Cavity)
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Decidua basalis
Decidua parietalis
Decidua capsularis
Chorion frondosum
Uterine cavity
Amniotic cavity
Chorion frondosum
Fused decidua parietalis and capsularis
Amniotic cavity
Decidua basalis
Chorionic cavity
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Amniotic fluid- Normal volume is 1000 – 1500 cc clear
watery fluid.- Source: 1st from amnioblast then from
kidney.- If the volume is less than 500 cc it is
called oligohydramnios.-If the volume is more than 2000 cc is
called polyhydramnios. Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Functions of amniotic fluid:1- At early pregnancy:1- Acts as water cushion that absorbs external shocks. 2- Acts as heat insulator.3- Prevents adhesion of embryo to wall of uterus.4- Prevents adhesion of fetal parts.2- At late pregnancy:1- A space for accumulated urine.2- Allows fetal movements to help body muscles to develop.3- Help suckling training and development of gut muscles. Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

3- During labor:1- Protects against uterine contractions.2- Formation of bag of water that gradually dilate the cervix.3- Sterile amniotic washes vagina before passage of baby.4- Rupture of amniotic sac is a sign of start of delivery.
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Abnormalities of amniotic fluid:1- Polyhydramnios.Causes:1- No cause (35 %).2- Maternal diabetes.3- Congenital malformation e.g. anencephaly and esophageal atresia.2- Oligohydramnios.Cause:-Renal agenesis.
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

YOLK SAC

Fate & development of yolk sac• Primary yolk sac: It replaces cavity of blastocyst
after the formation of Heuser’s membrane which is formed of flat cells that originate from hypoblast cells at 9th & 10th day.
• Secondary yolk sac: additional cells from hypoblast cells will line the Heuser’s membrane, reduction of size of yolk sac and formation of allantois. This occurs in the 13th day.
• Defenitive yolk sac: During 3rd week, hypoblast become replaced by endoderm. After folding, it shares in formation of gut and the part remains outside the embryo is called defenitive yolk sac. It is connected to yolk sac by vitello-intestinal duct.
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

7th day:
Dr. Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

8TH Day of PregnancyEndometrium
Cytotrophoblasts Hypoblasts
Amniotic cavity
Epiblast
Dr.Sherif Fahmy
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

9th & 10th days
Primary yolk sac
Heuser’s membrane
Syncytio-trophoblast
Hypoblast
Amniotic cavity
Epiblast
Cyto-trophoblast Dr. Sherif Fahmy

13th day
Endodermal cells
Secondary yolk sac
Exocoelomic cyst
Connecting stalk
Splanchnic mesoderm
Extra-embryonic coelom Chorionic cavity)
Dr.Sherif Fahmy
Chorionic Vesicle
Dr. Sherif Fahmy


Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Functions of yolk sac:• Gut: foregut, midgut and hindgut.• Allantois: forms part of urinary bladder.• Primordial germ cells: Which are
spermatogonia and oogonia which are formed in its caudal part (hind gut).
• Vitelline vessels: develop from mesoderm around vitelline duct. Intra-embryonic part form portal vein and arteries of intestine.
• Blood cells: develop in the mesoderm around the yolk sac.
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Abnormalities of Yolk Sac• 1- Vitelline cyst and fistula
due to persistence of vitelline duct.
• 2- Urachal cyst and fistula due to persistence of urachus from allantois.
Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Dr. Sherif Fahmy

Dr. Sherif Fahmy