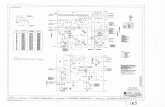
Piping & Instrumentation Diagram
Transcript of Piping & Instrumentation Diagram

Plant Design• The objective of Plant Design is to define the equipment, piping, instrumentation and
all process requirements needed to build and operate a process plant. • Plant design normally starts with a process scheme • Process Requirements (chemical and petrochemical applications ) - Plant Capacity, in
MTPY (metric tons per year) , Product specification in terms of purity or maximum content of certain impurities
• Process Design – 1. A process flow diagram (PFD) is a diagrammatic representation of a process
using symbols to represent the various components (equipment, lines, and control instrumentation) that make up the unit. Only the main components are shown.
2. Piping and instrumentation diagram (P&ID) show how industrial process equipment is interconnected by a system of pipelines. P&ID schematics also show the instruments and valves that monitor and control the flow of materials through the pipelines.This document will be the basis for developing the piping drawings and for specifying the instrumentation and control systems. It is a rather detailed document and for this reason, each P&ID covers only a small part of the process. So, a typical petrochemical unit may have 20 to 30 P&IDs, while larger units may well have 60 to 100.

ApplicationsProcess Plants built as engineering & construction (E&C) projects require complex piping.
These projects include the following:
chemical plantsBiotech plantsBrewery Crude oil refineriesFood processingFertilizer plantsOil & GasNuclear Power plantsPharmaceuticalPulp Paper millsWater Treatment plants

PFD Example

P&ID Example

P&ID Example

Piping & Instrumentation Diagram
Symbolic representation of a plant, with its equipment, piping, and instrumentation clearly identified. It is the basis for all detail engineering work. Also known as Mechanical Flow Diagram (MFD).

Categories• P&ID drawings fall into two categories:
• 1) Dumb, which are basically CAD-centric 2D diagrams • 2) Intelligent data-centric diagrams that range from
simple database connectivity to a full-blown data model that includes engineering rules, automatic design validation, standards compliance, integration with design and calculation packages, and the like.
• The P&ID stage of design is generally considered engineering, and the physical stage is considered design or layout.

Purpose & Scope
• The responsibility for the Process and technical content of the P&ID’s lies with the Process, Mechanical, Piping and Instrument disciplines.
• It is the responsibility of personnel on the project team to ensure that the standards described within this document are maintained, and that any deviations from these standards are documented and reported to the P&ID Coordinator, checked by all Disciplines and approved by the Area Manager
-------------------------------------------------------------------------• Scope - This instruction outlines the Work Process and
Project Settings for P&ID development and the corresponding milestone issues of the document.

Description• Piping is the physical elements that interconnect the equipment and
in which the process streams flow. Piping comes in different sizes and materials. It is the duty of the process engineer to specify the size and materials of the piping and also the thermal insulation, if required. The term piping also includes accessories such as elbows, tees, valves, flanges, etc. The most common material is carbon steel. Other metals, such as various grades of stainless steel, and plastic materials, such as PVC, Teflon, are also used.
• Instrumentation is devices used to measure, control, and monitor the process variables. These variables can be flow, temperature, pressure, liquid level, viscosity, and others. Control valves and relief valves are also an important part of the instrumentation.

Representation• P&ID shows all of piping including the physical sequence of branches, reducers, valves, equipment, instrumentation. The
P&ID are used to operate the process system.
A P&ID should include:
• Instrumentation and designations • Mechanical equipment with names and numbers • All valves and their identifications • Process piping, sizes and identification • Miscellaneous - vents, drains, special fittings, sampling lines, reducers, increasers and swagers • Permanent start-up and flush lines • Flow directions • Interconnections references • Control inputs and outputs• Interfaces for class changes • Vendor and contractor interfaces • Identification of components and subsystems delivered by others • Intended physical sequence of the equipment
• A P&ID should not include:
• manual switches • equipment rating or capacity • pressure temperature and flow data • elbow, tees and similar standard fittings • extensive explanatory notes

Classification• Legends and Symbol Diagrams/Standard Details
• Process P&ID - Process P&ID’s define on-plot process unit design, as well as off-plot tankage and shipping systems
• Utility Plant P&ID - Utility Plant P&ID's define utility units such as cooling towers, air compressors, boilers, unit drain collection systems, fire water systems, and water treatment plants.
• Utility Distribution P&ID - Show the distribution of utilities within a given process. Valving and instrumentation on piping are shown for main headers up to and including branch root valves.
• Interconnecting (Rack) P&ID –They are the connecting link between individual process, utility plant, and utility distribution P&ID's. They are usually prepared for the offsite pipe racks and link the various process and utility plants.
• Vendor P&ID - They are prepared for systems which support major equipment packages.

P&ID Format• P&ID's are to be prepared with the following format and organization:
• All P&ID drafting shall be by Computer Aided Drafting (CAD), using P&ID software• P&ID's shall follow the format of the Legends and Symbols and current project Standard
Drawings.• The P&ID Coordinator for the project will identify and assign numbers and titles to all
P&ID's.
P&ID's include;
o Water Systems, Cooling Water, Utility Water, Raw Water, Fire Watero Steam, Condensate, Boiler Blowdown, and Boiler Feed Watero Air, Nitrogen, Natural Gas, Fuel Gas, etc.o Chemicals and Additiveso Waste Water, Sewer, Effluento Relief System
• Interconnecting P&ID's are prepared to represent the offsite interconnecting piperacks and piping.
They are generally segregated as follows:o Above Ground Process Lineso Above Ground Utility Lineso Underground Process and Utility Lines

Accompanying Deliverables From The P&IDEquipment ListAn Equipment List shall be issued in a timely manner to compliment the P&ID’s and Updatedjudiciously as additional design data or vendor data becomes firm.Line Designation Table (LDT)The Line Designation Table (LDT) shall be issued from Bentley Data Manager each time a P&ID issueis made, starting with the IFA issue.Other ListThe Valve, SP items and Instrumentation Lists shall be issued from Bentley Data Manager each time aP&ID issue is made, starting with the IFA issue.Tie-In Control ListA Tie-in Control List shall be issued indicating the extent of the Vendorpackage battery limits each time a P&ID issue is made starting with IFA.“Holds” ListA "Holds" list must be issued each time a P&ID issue is made starting with IFD. The "Hold" indicateswhere the information used as input to the P&ID is preliminary and the item is used with risk in thedownstream design.Revision listA Revision List defines the changes made in the design so that appropriate action can be taken toaccommodate those changes. A Revision List must accompany any issue of the P&ID after IFH if thechanges are too extensive to be distinguished in the revision box and by clouding.

General Responsibilities • Area Manager - has overall responsibility for all engineering work, including
preparation, approval, stamping and issue of P&ID's • Lead Engineers - Prepare and, OWN all P&ID's.
Coordinate P&ID information between systems and related areas of plants.• Process Engineer - Issue Process Flow Diagrams, issue process data
sheets for equipment, Develop process equipment list .• Piping Engineer - Issues the piping material classification index and the
piping material specifications. Assign line numbers and prepare the Line Designation Tables. Verify the conformance of the P&ID to equipment data sheets and specifications.
• Mechanical Engineers - Prepare and issue an Equipment List showing all equipment on the project. Provide Lead Engineers with equipment requirements that are to be shown on P&ID's. Work jointly with Lead Engineers to develop Material Handling P&ID’s on jobs withsignificant Material Handling equipment.

Sanjay PhadkeNeilsoft
Manikchand Ikon Building 7th Floor CTS 18 & 18/1 Dhole Patil Road
Pune 411001