Physiology of Swallowing. Motility of the GIT 1. Motility in the mouth 2 types; a)Chewing or...
-
Upload
vivian-jenkins -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Physiology of Swallowing. Motility of the GIT 1. Motility in the mouth 2 types; a)Chewing or...
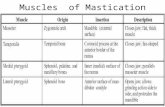
Motility of the GIT 1. Motility in the mouth
2 types; a)Chewing or Mastication:• It is reflex in natureSignificance:1.Breaks the food into small pieces to be easily
swallowed2.Expose food to salivary amylase enzyme, which
begins digestion of starch3.Help digestion of all types of food especially
cellulose containing food e.g. vegetables
Motility of the GIT
b) Swallowing:Def. •Swallowing is the transport of food from mouth to stomachSteps:• It consists of 3 phases or steps;1) Buccal Phase: food is pushed back into pharynx from mouth
Motility of the GIT
b) Swallowing:3) Oesophageal Phase: food pass through esophagus to stomach by peristaltic movements
2. Motility of Esophagus
• The esophagus is nearly 25 cm ms tube
• It is guarded by 2 sphincters;1.Upper esophageal
sphincter prevents air from entering the GIT
2.Lower esophageal sphincter prevents gastric contents from re-entering the esophagus from the stomach
• Esophageal peristalsis sweeps down the esophagus
Motility of GIT
• A minimal amount of carbohydrate digestion occurs in the mouth, chemical digestion really gets underway in the stomach.
• The empty stomach is only about the size of your fist.
• Can stretch to hold as much as 4 liters of food and fluid, or more than 75 times its empty volume, and then return to its resting size when empty.
Physiology of Stomach
3. Motility of Stomach
• The stomach consists of Cardiac, fundus, body and pylorus
• Proximal area (fundus and body) has a thin wall and contracts weakly and infrequently → holds large volumes of food (to store food) .
• Distal area (pylorus) has thick wall with strong and frequent peristaltic contractions that mix and propel food into the duodenum.
• Also, distal area is responsible for gastric emptying into duodenum
Physiology of Stomach
In the epithelium, gastric pits lead to gastric glands that secrete gastric juice. The gastric glands, contain different types of cells that secrete a variety of enzymes
Physiology of Stomach
Parietal cells Located primarily in the middle region of the gastric glands.
produce both hydrochloric acid (HCl) and intrinsic factor.
HCl is responsible for the high acidity (pH 1.5 to 3.5) of the stomach contents and is needed to activate the protein-digesting enzyme, pepsin and also kills much of the bacteria helps to denature proteins, making them more available for enzymatic digestion.
Intrinsic factor is a glycoprotein necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12 in the small intestine.
Physiology of Stomach
Chief cells, which secrete pepsinogen, the inactive proenzyme form of pepsin. HCl is necessary for the conversion of pepsinogen to pepsin.
Enteroendocrine cells, •gastrin - cause gastric glands to increase secretory activity (hydrochloric acid) •histamine - activates parietal cells to release hydrochloric acid •serotonin - causes contraction of stomach •cholecystokinin - potentiates secretin's action on liver/pancreas (increase bile and pancreas "juice")•somatostatin - inhibits gastric secretion of all products and inhibits gastric motility and emptying release gastrin.
Physiology of Stomach
Cephalic phase•This phase begins when you see, smell, taste, or think of food.•This phase which is directed by the CNC, prepared the stomach to receive food.•The neural output proceeds by the way of the parasympathetic division on the autonomic nervous system.•The vagus nerves innervate the submucosal plexus of the stomach.•Next, parasympathetic innervate stomach cells. In respond to stimulation, the production of gastric juice accelerates, reaching rates of about 500 mL/h.
Phases of gastric secretion
Gastric Phase•This phase begins with the arrival of food in the stomach.•This phase continued for three to four hours while the acid and enzymes process the ingested materials.•After the first hour, the material in the stomach is churning like clothing in a wash machine. •As mixing continues a large volume of gastric juice secreted.
Phases of gastric secretion
Intestinal phase•Begins when chyme first enters the small intestine.•The function of intestinal phase is controlling the rate of gastric emptying to ensure that the secretory, digestive and absorption functions of the small intestine can proceed with reasonable efficiency. •The arrival of chyme in the small intestine triggers other neural and hormonal events that coordinate the activities of the intestinal tract and the pancreas, liver and gallbladder.
Phases of gastric secretion
The duodenum is a short structure (about 20–25 cm long) continuous with the stomach and shaped like a "C"
Small Intestine
• The Duodenum • The segment of small intestine closest to stomach
• 25 cm long
• “Mixing bowl” that receives chyme from stomach and digestive secretions from pancreas and liver
• Functions of the duodenum • To receive chyme from stomach
• To neutralize acids before they can damage the absorptive surfaces of the small intestine
Small Intestine• The Jejunum • Is the middle segment of small intestine• 2.5 meters long• Is the location of most
• Chemical digestion• Nutrient absorption
• Has few plicae circulares• Small villi
Small Intestine
• The Ileum• The final segment of small intestine• 3.5 meters long • Ends at the ileocecal valve, a sphincter
that controls flow of material from the ileum into the large intestine
Small Intestine
• Intestinal Movements• Chyme arrives in
duodenum
• Weak peristaltic contractions move it slowly toward jejunum
• Myenteric reflexes
• Not under CNS control
• Parasympathetic stimulation accelerates local peristalsis and segmentation
Pancreas
• Lies posterior to stomach• From duodenum toward
spleen• Is bound to posterior wall of
abdominal cavity• Is wrapped in thin,
connective tissue capsuleFunctions of the Pancreas1. Endocrine cells of the
pancreatic islets:• Secrete insulin and
glucagon into bloodstream2. Exocrine cells:
• Acinar cells and epithelial cells of duct system secrete pancreatic juice
Pancreas
• Pancreatic Enzymes • Pancreatic alpha-amylase
• A carbohydrase• Breaks down starches• Similar to salivary amylase
• Pancreatic lipase• Breaks down complex lipids• Releases products (e.g., fatty
acids) that are easily absorbed
• Pancreatic Enzymes • Nucleases
• Break down nucleic acids
• Proteolytic enzymes• Break certain proteins apart• Proteases break large
protein complexes• Peptidases break small
peptides into amino acids• 70% of all pancreatic enzyme
production• Secreted as inactive
proenzymes• Activated after reaching small
intestine
Starch Maltose + Maltotriose pancreatic amylase
pH 7.0
Fat ( Triglyceride ) Monoglyceride + Fatty acids
Lipase + colipase
pH 8.0
Trypsinogen Trypsin
Enterokinase
Chymotrypsinogen Chymotrypsin
protein
polypeptideCarboxypeptidase
amino acid
Functions of pancreatic juice enzymes
Liver• Hepatocytes• Are liver cells• Adjust circulating levels of nutrients
• Through selective absorption and secretion • In a liver lobule form a series of irregular plates
arranged like wheel spokes• Many Kupffer cells (stellate reticuloendothelial cells)
are located in sinusoidal lining• As blood flows through sinusoids
• Hepatocytes absorb solutes from plasma• And secrete materials such as plasma proteins
Liver Function
The Physiology of the Liver1. Metabolic regulation2. Hematological regulation3. Bile production
Liver Function
• Metabolic Regulation• The liver regulates:
1. Composition of circulating blood2. Nutrient metabolism (carbohydrate, lipid &
amino acid)3. Waste product removal4. Vitamin Storage (A, D, E & K)5. Nutrient storage (iron) 6. Drug inactivation
Liver Function
• Composition of Circulating Blood • All blood leaving absorptive surfaces of digestive tract
• Enters hepatic portal system
• Flows into the liver
• Liver cells extract nutrients or toxins from blood• Before they reach systemic circulation through hepatic veins
• Liver removes and stores excess nutrients• Corrects nutrient deficiencies by mobilizing stored reserves or
performing synthetic activities
Liver Function
• Hematological Regulation• Largest blood reservoir in the body
• Receives 25% of cardiac output• Functions of Hematological Regulation
1. Phagocytosis and antigen presentation2. Synthesis of plasma proteins3. Removal of circulating hormones4. Removal of antibodies5. Removal or storage of toxins6. Synthesis and secretion of bile
Liver Function• The Functions of Bile• Dietary lipids are not water soluble• Mechanical processing in stomach creates large
drops containing lipids • Pancreatic lipase is not lipid soluble
• Interacts only at surface of lipid droplet
• Bile salts break droplets apart (emulsification)• Increases surface area exposed to enzymatic attack • Creates tiny emulsion droplets coated with bile salts
Gallbladder
• Is a pear-shaped, muscular sac• Stores and concentrates bile prior to
excretion into small intestine• Is located in the fossa on the posterior
surface of the liver’s right lobe• The Cystic Duct• Extends from gallbladder• Union with common hepatic duct forms
common bile duct
Gallbladder
• Functions of the Gallbladder• Stores bile
• Releases bile into duodenum, but only under stimulation of hormone cholecystokinin (CCK)
• CCK• Hepatopancreatic sphincter remains closed
• Bile exiting liver in common hepatic duct cannot flow through common bile duct into duodenum
• Bile enters cystic duct and is stored in gallbladder