Phylogenetic Comparision of Volume Ratios of Caudate and … · 2015-07-17 · Afrotheria...
Transcript of Phylogenetic Comparision of Volume Ratios of Caudate and … · 2015-07-17 · Afrotheria...

Afrotheria
Phylogenetic Comparision of Volume Ratios of Caudate and Putamen M. L. Whitson, J. A. Baun, *R. C. Switzer III; NeuroScience Associates, Knoxville, TN 37934
Coronal sections through the forebrain of primatebrain display a familiar view of the internal capsuleseparating the caudate and putamen. A cursoryreview of images from diverse species found in thewebsite http://brainmuseum.org/sections/index.html,indicates that most mammals have this characteristicfeature with the exception of animals such as rats andmice. The presence of a caudate separated by theinternal capsule from the putamen does not appear tobe a function of gyrencephaly or lissencephaly nor ofmere size.
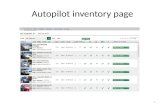
A further comparison of the different speciesleaves the impression that in some animals, such asdog, the caudate is much larger than the putamen,whereas in primate the two are more equitable. Todetermine if this difference was illusory or real, theratio of the volumes of putamen and caudate weredetermined from sections from the brains of dog (bea-gle; Canis familiaris) and of a primate (African Greenmonkey; Cholorocebus sabaceus). The impressionwas confirmed and the study was extended to includeother species for a better phyologenetic representa-tion. Images of brain section images from thebrainmuseum.org website for goat, cat, hyrax andsquirrel monkey were used for volume calculations.Images of the pig brain were derived from NSAʼs slides.
Caudate and putamen are collectively knownas striatum and receive input from most ofcortex, but with regional differences. It isperhaps such differences that govern thedynamics of brain development and determinejust where the components of the internalcapsule will coalesce and divide caudate fromputamen as occurs in most species or doesnot as in rats and mice.Similar ʻforcesʼ may be at play in deciding howcortex is folded and have been discussed byWelker et. al. (Welker W. Why does cerebral cortexfissure and fold? A review of determinants of gyri and sulci.Jones EG, Peters A, eds. (1990) Vol. 8b. New York: PlenumPress. 3–136. Cerebral cortex).Other instances of fiber pathway variationshave been observed that follow phylogeneticgroupings. (Switzer, R.C., Johnson, J.I. and Kirsch,J.A.W.: Phylogeny through brain traits: The relation of thelateral olfactory tract fibers to the accessory olfactoryformation as a palimpsest of mammalian descent. Brain,Behavior and Evolution 17: 339-363, 1980).
Sections stained for nissl substance and myelin wereused to delineate and measure the areas (Image J) ofputamen and caudate in a series of uniformly spacedslides from the rostral to caudal limits of bothstructures. Using Simpson's approximation formulaethe volumes for each structure were determined andratios calculated.
Dog
Carnivora
Eulipotyphla
Chiroptera
Pholidota
Perissodactyla
Lagomorpha
Rodentia
Dermoptera
Scandentia
Xenarthra
Afrosoricida
Macroscelidea
Tubulidentata
Proboscidea
Sirenia
Marsupialia
Monotremata
Cetartiodactyla
Primates
Hyracoidea
Cat
African GreenMonkey
Squirrel Monkey
Pig
Goat
Hyrax
Caudate
Putamen
Rhesus
Silhouettes rostral to caudal of blackenedcaudate extracted from captured imagesthat were used for area and volumecalculation using thresholding methods inImageJ.Sequence from Dog brain.
We would like to dedicate this study to Wally Welker,University of Wisconsin, whose devotion and work has beena cornerstone for comparative neuroanatomy.Without the fruits of his work, studies such as this would notbe possible.
W.I. Welker 1926-2007
Phylogenetic tree redrawn from Figure 1 Springer et.al. Trends inEcology and Evolution, vol.19 August 2004, 430-437.
Laurasiatheria
Euarchontoglires
Xenarthra
The molecular based tree of the 4 clades ofplacental mammals is shown in different colors.The animals examined are representative of 3 ofthe 4 clades.Diminutive proportional size of the putamen to the
caudate in cat and dog seems unique within thissampling even within the same clade,Laurasiatheria. Examination of other carnivores aswell as other species across all clades shouldreveal the extent of this uniqueness. The opposite proportion of putamen greater thancaudate occurs in hyrax and warrants furtherexamination of other members of clade Afrotheria.
c a u d a t e / (caudate + putamen) putamen / (caudate + putamen) Rodentsʼ internal capsule:
to coalesce or not to coalesce to create a Caudate and Putamen
Guinea pig
Capybara Mountain Beaver
Grey Squirrel
InternalCapsule