Photosynthesis Slide
-
Upload
missumie86 -
Category
Documents
-
view
218 -
download
0
Transcript of Photosynthesis Slide
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
1/21
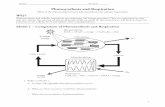
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
http://e/Photosynthesis%20in%20plants%20-%20Lesson%20Animation%20%20for%20Kids.mp4 -
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
2/21
Photosynthesis
The first observation regarding plant nutrition
was probably made by Aristotle
After a series of experiment done by
scientists, a conclusion can be made
light
6CO2 +6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2
chlorophyll
http://e/Photosynthesis%20in%20plants%20-%20Lesson%20Animation%20%20for%20Kids.mp4 -
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
3/21
Photosynthesis
Substances required for photosynthesis
i. Carbon dioxide
ii. Water
iii. Light energy
Substances produced from photosynthesis
i. Glucose
ii. Oxygen
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
4/21
Photosynthesis
Where does photosynthesis happens?????
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
5/21
Leaf structure and function
Leaves are the main photosynthetic organs of
a plant.
Young stems and other green parts may also
carry out photosynthesis.
Arrangement of leaves ????????
Why leaves have this arrangement ???????
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
6/21
Cross section of leaf
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
7/21
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
8/21
Leaf structure and function
Part of a leaf Functions
Lamina Trap sunlight for photosynthesis to
occur
Petiole Holds the leafin the best position to
receive the maximum amount of
light
Vein Main vein leads down the leaf and
branches out into side veins to
support lamina
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
9/21
Leaf structure and function
Part of a leaf Functions
Cuticle Reduces the loss of water by evaporation
through the epidermis
Upper and lowerepidermis
Maintain the shape of the leafProtects the cells of the leaf from
bacterial and fungi infections and from
injuries
Pallisade mesophyll Carry out photosynthesis
Spongy mesophyll Carry out photosynthesis
Involved in the exchange of the gases
between leaf and the atmosphere
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
10/21
Leaf structure and function
Part of a leaf FunctionsXylem Transport of water and minerals salts
Give support to the leaf
Phloem Transport of sugar which is the product of
photosynthesis from leaf to other parts ofthe plants
Guard cells Involved in the control of the size of
stomata
Controls transpiration through thestomata
Stomata Allow exchange of gases between the
internal parts of the leaf and the
atmosphere
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
11/21
Adaptation of leaf
Adaptation ImportanceLeaves are thin and flat This exposes large surface area of
leaves to sunlight and air, carbon
dioxide diffuses in and oxygen diffuses
out efficientlyLeaves are arranged
alternately
This maximizes exposure of surfaces
of leaves to sunlight
Arrangement of cells of
the spongy mesophyll isloose
This makes diffusion of gases occur
efficiently
Layer of cuticle and
epithelial cells are
transparent
This ensures that sunlight can
penetrate to the mesophyll layer
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
12/21
Adaptation of leaf
Adaptation ImportanceNumber of stomata on
lower surface of leaves is
large
Avoid excessive loss of water to
surrounding
To allow exchange of gases to
occurThe cells of pallisade
mesophyll have chloroplast
and arranged close to
upper epidermis
Chloroplast are exposed to sunlight
and absorb energy for
photosynthesis
Network of veins are
widely distributed on the
lamina
Enables transport of water,
minerals salts and product of
photosynthesis to be carried out
efficiently
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
13/21
Leaf structure and function??????
Lamina
Cuticle
Epidermis
Palisade mesophyll
Spongy mesophyll
Guard cell
Stoma
Xylem
Phloem
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
14/21
Thank you
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
15/21
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
16/21
Adaptation of plants from different
habitats
Plants need to have a method for gaseous
exchange and an efficient means of absorbing
light energy
Land plants eg hibiscus
Aquatic plants eg water lilies
Desert plants eg cactus
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
17/21
Adaptation of plants from different
habitats
Land plants
- Large number of stomata on the lower
surfaces of leaves
- To allow maximum absorption of carbon
dioxide
- Most chloroplasts are found in palisade cells
and spongy mesophyll cells.
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
18/21
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
19/21
Adaptation of plants from different
habitats
Aquatic plants
- Have large, round and flat leaves
- Stomata are mostly distributed in the uppersurface of the leaves
- Aquatic plants submerged in the water do not
have stomata
- Chloroplast are found in leaves and stems of
these plants
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
20/21
-
7/29/2019 Photosynthesis Slide
21/21
Adaptation of plants from different
habitats
Desert plants
- Have reduced leaves
- Have sunken stomata