Photosynthesis
-
Upload
alan-taylor -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
1
description
Transcript of Photosynthesis

PhotosynthesisPhotosynthesis

Yes
photosynthesis really is
this simple!

chlorophyll


Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a method of
utilising light energy to synthesise organic molecules
from inorganic sources; i.e. it is autotrophic nutrition.

In simple terms it is the conversion of light energy into chemical energy in organic molecules.
Summary equation
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + light + chlorophyll C6H12O6 + 6 O2

In simple terms the energy needed to break the bonds within carbon dioxide and water is greater than the energy released when the products – glucose and oxygen – are formed.
Therefore the products are at a higher energy level than the reactants and act as a store of chemical potential energy

Simple summary
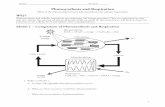
Photosynthesis consists of two separate but interdependent processes which take place in the chloroplasts
P/S Chloroplasts Powerpoint






Light dependent stage
This stage is ‘driven’ by light in the grana. It converts light energy into usable chemical energy in ATP by photophosphorylation and a coenzyme called reduced NADP which is a source of reducing power with a high chemical potential energy.

Light independent stage
This stage is ’driven’ by, and is dependent on, the products of the light dependent stage in the stroma. The ATP and reduced NADP are used to produce sugars which are then stored as starch. The short-term source of chemical energy (ATP) has been converted into a long term store of chemical potential energy (starch).

Summary of the two stages of photosynthesis


Light dependent stage of photosynthesis: summary 11: Chlorophyll in thylakoid membranes in chloroplasts absorbs light energy (especially red & blue wavelengths) and releases ‘excited’ electrons



2: 2: ‘excited electrons pass along a series of electron carriers (in the membranes of the thylakoids of the chloroplast)
energy is released which is used to generate ATP (chemical energy) from ADP + Pi
this is photophosphorylation

3: ‘excited’ electrons combine with the protons from the photolysis of water together with NADP to produce reduced NADP
NADP + 2 H+ + 2 e- reduced NADP

4. electrons lost from chlorophyll are replaced by electrons from the photolysis of water
2H20 4H+ + O2
[catalysed by an enzyme complex associated with chlorophyll]
oxygen is the valuable waste product of
photolysis
All this occurs in the thylakoids of the grana of the chloroplasts


NB. The original light energy is now temporarily stored as chemical energy in ATP and reduced NADP (which has electrons at a higher energy level than they had in the water from which they ultimately come).
NB: light energy has been
converted into chemical energy

Light independent stage of Light independent stage of photosynthesis: summaryphotosynthesis: summary
1. 1. Ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP - contains 5 C atoms and 2 phosphate groups) acts as a carbon dioxide acceptor molecule which leads to the formation of 2 molecules of GP (glycerate-3-phosphate)
2. GP is reduced to TP (triose phosphate) using the energy from ATP and the H atoms from reduced NADP (from the light dependent stage)

3: Some TP is converted into glucose which is stored as starch, as well as being used in the synthesis of amino acids, lipids etc.
4. Some TP is also used to regenerate RuBP in the Calvin cycle so more CO2 can be taken in to produce more sugar etc; this also uses ATP to transfer a phosphate group.
All this occurs in the stroma of the chloroplasts

CO2
GP
TP
RuBP
Nucleic acids

NB. Use of the products of the light dependent stage.
Reduced NADP is used
•to reduce GP to TP (provides the H atoms)
ATP is used
· to provide energy to reduce GP to TP (energy released by hydrolysis)
· to provide a phosphate group to make RuBP (phosphorylation)