Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over · PDF fileCS PS CoreNetwork PDN G i...
Transcript of Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over · PDF fileCS PS CoreNetwork PDN G i...

TELECOM ITALIA GROUPICC 2007Glasgow, June, 24th-28th 2007
| ANDREA BARBARESI | TELECOM ITALIA | TELECOM ITALIA LAB
Andrea Barbaresi, Andrea Mantovani
Performance Evaluation of Quality ofVoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
Contacts:[email protected] G. Reiss Romoli, 274 - 10148 Torino (TO), Italy

1
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
Outline
Introduction
VoIP within 3GPP systems
VoIP bi-directional traffic model
Characterization of VoIP QoS in terms of MOS
Simulation results
Conclusions

2
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
Introduction: motivations
In the last few years IP based networks and broadband access have been widely deployed and are offered now at very low prices
For well known reasons (e.g. higher flexibility, capex&opex reduction, fixed-mobile convergence) also the evolutionary trend of mobile systems is focusing toward all IP packet switched only transmission for any kind of service.
The voice traffic, generally offered through the circuit-switched domain (PSTN) is also expected to move over the evolved all IP mobile network architectures (e.g. LTE/SAE, mobile WiMax, …)
While VoIP service on the fixed network can be considered a consolidated reality with a well known behaviour, this is not true for the wireless scenario, especially in case of mobility.

3
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
Introduction: investigation carried out
We have evaluated by means of system level dynamic simulations the impacts of the UMTS radio access network on the end-to-end QoS of VoIP
The proprietary event-driven simulator RAMSET™ was used; it simulates all the most relevant elements involved in the provisioning of VoIP service (bi-directional traffic model, signalling protocols, UTRAN behaviour in complex network layout)
UTRAN Dedicated transport CHannels (DCHs) were considered
An analytical model (ref. “E-model”, ITU-T G.107) devoted to predict the Mean Opinion Score (MOS, ref. ITU-T P.800) was taken into account for VoIP QoS characterization
This work has been partially developed within the framework of the IST-AROMA project (www.aroma-ist.upc.edu), which is partially founded by the European Community.

4
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
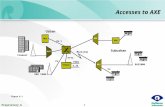
Introduction: VoIP within the heterogeneous multi-RAT network considered by the IST-AROMA project
AROMA project aims to devise and assess a set of specific strategies and algorithms for both the access and the core network parts that can guarantee the end-to-end QoS in the context of an all-IP heterogeneous network
Advanced CRRM/RRM mechanisms leading to an optimized usage of the different RAT technologies (WLAN, GERAN, UMTS, HSDPA, HSUPA, MBMS) were proposed and analyzed
AROMA AROMA -- AAdvanced dvanced RResesoource urce MaManagement Solutions for Future All IP Heterogeneous Mobile Radio nagement Solutions for Future All IP Heterogeneous Mobile Radio EnvironmentsEnvironments
GANC
IP connectivityNetwork(e.g.WLAN )
GANC
IP connectivityNetwork(e.g.WLAN )
GERAN
RNS
RNCNode-B
BSCBTS MSCA or Iu-CS
SGSN
Gb
GGSN
CommonElements(e.g. HSS)
CS
PS
Core Network
PDN(IP networks)Gi
IMS
Gp
OtherGPRSnetworks
PSTN
Mb
PSTN
PDFGo
GqCRF
Gx
Rx
Iur-g
RNC
Iur
BSCIur-g
BTS
Node-B
Iub
Iub
Abis
Abis
BSS
UTRAN
GERAN
RNS
RNCNode-B
BSCBTS MSCor Iu-CS
Iu-CSIu-
SGSN
Gb
Iu-PSIu-PSGGSN
CommonElements(e.g. HSS)
CS
PS
Core Network
PDN(IP networks)Gi
IMS
Gp
OtherGPRSnetworks
PSTN
Mb
PSTN
PDFGo
GqCRF
Gx
Rx
Iur-g
RNC
Iur
BSCIur-g
BTS
Node-B
Iub
Iub
Abis
Abis
BSS
UTRAN
oror Iu-PSIu-PS
Gb
A
GAN
APGANC
IP connectivityNetwork(e.g.WLAN )
GANC
IP connectivityNetwork(e.g.WLAN )
GERAN
RNS
RNCNode-B
BSCBTS MSCA or Iu-CS
SGSN
Gb
GGSN
CommonElements(e.g. HSS)
CS
PS
Core Network
PDN(IP networks)Gi
IMS
Gp
OtherGPRSnetworks
PSTN
Mb
PSTN
PDFGo
GqCRF
Gx
Rx
Iur-g
RNC
Iur
BSCIur-g
BTS
Node-B
Iub
Iub
Abis
Abis
BSS
UTRAN
GERAN
RNS
RNCNode-B
BSCBTS MSCor Iu-CS
Iu-CSIu-Iu-CSIu-
SGSN
Gb
Iu-PSIu-PSIu-PSIu-PSGGSN
CommonElements(e.g. HSS)
CS
PS
Core Network
PDN(IP networks)Gi
IMS
Gp
OtherGPRSnetworks
PSTN
Mb
PSTN
PDFGo
GqCRF
Gx
Rx
Iur-g
RNC
Iur
BSCIur-g
BTS
Node-B
Iub
Iub
Abis
Abis
BSS
UTRAN
oror Iu-PSIu-PSIu-PSIu-PS
Gb
A
GAN
AP
Results of the investigations carried out on VoIP over UTRAN R99, HSPA, WiFi reported in project’s deliverables.
Heterogeneous multi-RAT network architecture

5
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
VoIP within 3GPP systems: VoIP protocol stack
IP
UDP
RTP
Voice codec(AMR 12.2kbit/s
@ 20ms.)
RTCP
TCP
IP
UDP
SIP
Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) chosen by 3GPP as standard codec for voice signals in 3G mobile communication systems
RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) is the transport protocol
RTCP (RTP Control Protocol) is an optional control protocol in User Plane
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) is the signalling protocol
User Plane Control Plane
UP protocol stack imposes a total increase of 40 bytes!! (RTP header length is 8 bytes, UDP 12, IP 20 bytes) to the dimension of the AMR frame (mean length ≤ 40 bytes)

6
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
VoIP within 3GPP systems: service accommodation within UTRAN
MAC
PHY
RLC UM
PDCP RRC
PHY
MAC
RLC AM
For data and signaling traffic, assumed RABswere respectively (ref. 3GPP TR25.993):
16.8/16.8 kbit/s UL/DL PS Conversational RAB specifically optimized for AMR VoIP traffic
8/8 kbit/s UL/DL PS Interactive RAB for SIP traffic
In the User Plane:
PDCP performs header compression of RTP/UDP/IP headers by means of ROHC algorithm
RLC works in UM mode (no radio rtx)
Transport channel’s TTI is 20 msec.
MAC payload sizes range from 80 to 336 bits to fit different codec generated frames
User Plane Control Plane
Physical layer Power Control was set up to operate with BLER target values of 2%, 5%, 10%

7
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
VoIP within 3GPP systems: client architectureDe-jittering buffer within VoIP client applications
AMR frames can be lostdue to errors on radio blocks
AMR frames available for decoding
input stream output streamde-jitter buffer
XXX
For better QoS, decoding of AMR frame during talk spurts requires decoder to have frames always available
Playout interruptions (i.e. buffer underflow occurrences) may deal with a degrade on the perceived quality since they produce “silence spikes” (voice clips) during the conversation
Investigations made with static de-jittering buffer lengths of 0, 20, 60, 180 ms.

8
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
Interactive bi-directional Traffic Model
The conversation between two users(A and B) can be modeled as a four state Markov chain (ref. ITU-T P.59)
State A: A talking, B silent
State B: A silent, B talking
State D: Double talking
State M: Mutual silence
The sojourn time in A, B, D, and M states is modeled by a random variable with exponential distribution
The transition probabilities and the exponential distribution parameters are defined in ITU-T P.59

9
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
QoS Evaluation: MOS and E-model
MOS (Mean Opinion Score) is a subjective rating method (ITU-T P.800)
a group of listeners rates voice samples from 1 (“bad”) to 5 (“excellent”)
E-Model is an analytical model that reflects the effects of different types of impairments on the end-to-end speech transmission performance (ITU-T G.107)
each impairment factor (i.e. end-to-end delay, packet loss, etc.) can be computed separately
the result of the model is the R-factor that ranges from 100 (best case) to 0 (worst case)
The R factor uniquely determines the MOS

10
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
Simulation assumptions: UTRAN network layout
NW layout consists in 36 macro cells arranged in 12 three-sectorial sites: it can be considered representatives of a general urban environment
Each VoIP call is established between a generic 3G mobile user and the host inside the IP fixed network (i.e. effects of only one radio interface link was considered)
Only delays within UTRAN were considered (no CN and external IP fixed network delays)
The length of simulations was set up to 3000 seconds, enough to collect results with confidence intervals of 95%, which are statistically significant

11
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
Simulation results: delay, FER and MOS
131.770.340.220BLER =10%
131.971.341.220BLER = 5%
132.271.341.320BLER = 2%
Buffer 180msBuffer 60msBuffer 20msBuffer 0msTransmission Delay [ms]
Transmission delay vs. buffer length and BLER
2.432.512.552.57BLER =10%
3.213.283.323.35BLER = 5%
3.913.994.034.04BLER = 2%
Buffer 180msBuffer 60msBuffer 20msBuffer 0msMOS
Frame error rate coincides with BLER since every AMR frame is carried out by a single RLC SDU and UTRAN retransmission are not used.
MOS vs BLER
0
0,5
1
1,5
2
2,5
3
3,5
4
4,5
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
BLER (%)
MO
S
MOS vs. buffer length and BLER
Fixing BLER, MOS decreases when buffer length increases should de-jittering buffer not be used ?

12
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
Simulation results: mean number of playout interruptions
Playout interruptions vs. buffer and BLER
83.5301.3>3000>3000BLER =10%
44.4167.62920>3000BLER = 5%
19.273.52688>3000BLER = 2%
Buffer 180msBuffer 60msBuffer 20msBuffer 0msPlayout interruptions
Playout blocks vs buffer length(% with respect to maximum value)
100,00%
50,83%
0,31%1,18%
0,00%
20,00%
40,00%
60,00%
80,00%
100,00%
120,00%
0 60 120 180
buffer length (ms)
Playout interruptions vs buffer (values expressed relatively to the maximum).
Client’s buffer is used to have AMR frames following the ones that are lost available for decoding
silence spikes strongly decrease when 20–60 ms. de-jittering buffer is considered
~ -50%
~ -99%

13
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
Simulation results: VoIP QoS in terms of MOS & playout interruptions
MOS & playout interruptions vs buffer length (BLER=2%).
MOS, playout blocks vs buffer length
3,5
3,6
3,7
3,8
3,9
4
4,1
4,2
4,3
4,4
4,5
0 60 120 180
buffer length (ms)
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
MOSPlayout blocks
0
0,1
0,2
0,3
0,4
0,5
0,6
0,7
0,8
0,9
1
3,8 3,85 3,9 3,95 4 4,05 4,1 4,15 4,2
MOS
CDF
CDF MOS values (buffer=60ms BLER=2%).
VoIP QoS can be characterized by considering trade-off between MOS (that depends on delay and packet loss) and playout interruptions

14
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
Simulation results: call setup delay analysis (SIP over TCP)
CDF for session setup delay
Session Setup Delay
0
0,1
0,2
0,3
0,4
0,5
0,6
0,7
0,8
0,9
1
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
Time [sec]
CDF
Time required to setup the VoIP call may impact the QoS level
Observed mean call setup delay for VoIP session was about 6.2 s. when 8 kbit/s RAB is used.
Performance when varying BLER are quite constant thanks to fast radio retransmissions
User Host
INVITE
100 TRYING
183 PROGRESS
PRACK
200 OK
UPDATE
200 OK
ACK
BYE
200 OK
180 RINGING
200 OK
CONVERSATION
Ses
sion
set
-up
proc
edur
eS
essi
on re
leas
epr
oced
ure
User Host
INVITE
100 TRYING
183 PROGRESS
PRACK
200 OK
UPDATE
200 OK
ACK
BYE
200 OK
180 RINGING
200 OK
CONVERSATION
Ses
sion
set
-up
proc
edur
eS
essi
on re
leas
epr
oced
ure

15
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
Concluding remarks
This analysis of VoIP QoS level offered by means of UTRAN dedicated transport channel shows that it is possible to have similar QoS levels than PSTN (i.e. MOS > 3.5)
Characterization of VoIP QoS service and performance evaluation versus the main parameters both at application and UTRAN level permits to derive useful information to accommodate VoIP service in UMTS in the best way:
BLER = 2% ( impacts on maximum cell capacity)
De-jittering buffer = 60 ms. (i.e. 3 AMR frames)
UTRAN DCHs soft handover fully supports mobility of VoIP users but maximum cell capacity slightly decrease with respect to CS voice (12. 2 kbit/s CS RAB )

16
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
BACK UP

17
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
Simulation assumptions: main parameters & performance metrics
Main parameters of VoIP service :
Mean call duration = 120 s.
Mean traffic per user = 250 mErlang
12.2 kbit/s AMR codec with Voice Activity Detection (VAD) technique
SIP protocol used above the TCP stack protocols
IPv4 ROHC within PDCP
Performance metrics (versus BLER and buffer length)
MOS
Transmission delay, Frame Error Rate
Number of playout interruptions (i.e. number of times per session in which the de-jittering buffer becomes empty)
Call setup time, call release time

18
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
VoIP within 3GPP systems: the AMR codec
The Adaptive Multi-Rate codec chosen by 3GPP as standard codec for voice signals in 3G mobile communication systems has been considered
AMR uses Algebraic Code Excited Linear Prediction (ACELP) algorithm to reduce the overall bit rate, together with other well known techniques to further improve the quality/bandwidth ratio (e.g. VAD-Voice Activity Detection, DTX-Discontinuous Transmission)
AMR may operate with eight source rates: 12.2 (GSM-EFR), 10.2, 7.95, 7.40 (IS-641), 6.70 (PDC-EFR), 5.90, 5.15 and 4.75 kbit/s
12.2 kbit/s AMR frames of about 40 bytes (or less) are generated every 20 msec.

19
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
The E-model and the R-factor
A-I-IRR effed += ,0
R0 (signal to noise ratio) represents the perceived quality in absence of impairment factors (value of 93.2 was considered for AMR codec)
Id represents all impairments due to the end-to end delayId =0.024•d+0.11•(d-177.3)•u(d-177.3)
where d: e2e delay, u(): Heaviside function
Ie,eff represents all the impairments caused by low bit rate codecs and by packet losses
Ie,eff = Ie +(95- Ie)•p/(p+Bpl)
Where p:packet loss rate and Ie , Bpl are codec-dependent parameters (=5, =10 for AMR 12.2kbit/s)
A is the Advantage Factor considered for mobile environment (=10, ref. ITU-T G.107)

20
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
Traffic model (parameters)
⎪⎩
⎪⎨
⎧
===
5.035.024.01
ppp
⎪⎪⎩
⎪⎪⎨
⎧
====
msmsmsms
M
D
B
A
456/1226/1854/1854/1
λλλλ
Typical values taken by the traffic model (ref. “Elements of interactivity in telephone conversation”, Hammer, Reichl, Raake)

21
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
SIP proceduresUser Host
INVITE
100 TRYING
183 PROGRESS
PRACK
200 OK
UPDATE
200 OK
ACK
BYE
200 OK
180 RINGING
200 OK
CONVERSATION
Ses
sion
set
-up
proc
edur
eS
essi
on re
leas
epr
oced
ure
User Host
INVITE
100 TRYING
183 PROGRESS
PRACK
200 OK
UPDATE
200 OK
ACK
BYE
200 OK
180 RINGING
200 OK
CONVERSATION
Ses
sion
set
-up
proc
edur
eS
essi
on re
leas
epr
oced
ure

22
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
83.5301.3>3000>30002.432.512.552.57131.770.340.22010%44.4167.62920>30003.213.283.323.35131.971.341.2205%19.273.52688>30003.913.994.034.04132.271.341.3202%
Buffer 180ms
Buffer 60ms
Buffer 20ms
Buffer 0ms
Buffer 180ms
Buffer 60ms
Buffer 20ms
Buffer 0ms
Buffer 180ms
Buffer 60ms
Buffer 20ms
Buffer 0ms
Playout interruptionsMOSTransmission delay [ms]BLER

23
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
UE_RLC
UE_MAC
TE_IP
TE_TCP TE_UDP
NodeB_PHY
RNC_RLC
RNC_MAC
RNC_PHY
RNC_GTP_U SGSN _ GTP_U GGSN_GTP_U
HOST_IP
HOST_TCP HOST_UDP
Uu Iub
UE NodeB RNC
Iur
SGSN GGSN HOST
UE_PDCP RNC_PDCP
GGSN_IP
UE_PHY
PS-Domain USER Plane PCG
TE _ APP _ TCP TE _HTTP TE _ APP _ UDP Streaming
ClientRTSP/RTP
PCG
HOST _APP _TCPHOST _HTTP HOST_ APP _ UDP HOST APP
RTS/RT
PSSG
Streamingserver
VoIPG
TE_APP_VOIP_RTP TE_APP_VOIP_SIP
HOST_APP_VOIP_
RTP HOST_APP_VOIP_
SIP
Voip GW
VoIPG
VoIP Client

24
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
UE_RLC
UE_MAC
UE_PHY
UE_RRC
UE_PMM
UE_SM
NodeB_MACb
RNC_RLC
RNC_MAC
RNC_PHY
RNC_RRC RNC_RANAP SGSN_RANAP
SGSN_SM
SGSN_PMM
GGSN_GTP_C
NodeB_RRC
NodeB_RLC
Uu Iub
UE NodeB RNCIur
SGSN GGSN
SGSN_GTP_C
RNC_NBAP
NodeB_PHY
System Information Broadcastspecific protocol termination
PS-Domain CONTROL Plane
NodeB_MACb
RNC_RLC
RNC_MAC
RNC_PHY
RNC_RRC RNC_RANAP
NodeB_NBAP
NodeB_RRC
NodeB_RLC
Iub
NodeB RNC
NodeB_PHY
frame protocol frame protocol
NodeB signaling
GGSN_PDP_Context_Manager

25
Performance Evaluation of Quality of VoIP Service over UMTS-UTRAN R99
| ANDREA BARBARESI| TELECOM ITALIAICC 2007
TELECOM ITALIA GROUP
NOTE: Alternative 1x0 is used to have CRC present in all transport formats.Header compressor should ensure that small_CID is used and that CID 0 is allocated to this RAB
180-220RM attribute
546Uplink: Max number of bits/radio frame before rate matching
1092Max number of bits/TTI after channel coding16CRC, bitTCCoding type20TTI, ms
1x344TF17, bits1x336TF16, bits1x312TF15, bits1x304TF14, bits1x296TF13, bits1x288TF12, bits1x272TF11, bits1x240TF10, bits1x224TF9, bits1x208TF8, bits1x192TF7, bits1x176TF6, bits1x160TF5, bits1x144TF4, bits1x136TF3, bits1x104TF2, bits1x88TF1, bits
0x344 (alt 1x0)TF0, bitsTFS
88, 104, 136, 144, 160, 176, 192, 208, 224, 240, 272, 288, 296, 304, 312, 336, 344 (alt 0, 88, 104, 136, 144, 160, 176, 192, 208,
224, 240, 272, 288, 296, 304, 312, 336, 344)
TB sizes, bitDCHTrCH typeLayer 1N/AMAC multiplexing
0MAC header, bitMAC8UMD PDU header, bit
16800Max data rate, bps
80, 96, 128, 136, 152, 168, 184, 200, 216, 232, 264, 280, 288, 296, 304, 328, 336 (alt 0, 80, 96, 128, 136, 152, 168, 184, 200,
216, 232, 264, 280, 288, 296, 304, 328, 336)
Payload sizes, bitUMRLC mode
DTCHLogical channel typeRLC0PDCP header size, bitPDCP
RABRAB/Signalling RBHigher layerRAB PS Conversational 16.8kbps UL/16.8kbps DL – VoIP