What’s happening at PBS? Jim Kutzner / PBS February 16, 2011.
PBS Targeted Level Targeted Coordinator Orientation Presented by: Vermont BEST/PBS Team February,...
Transcript of PBS Targeted Level Targeted Coordinator Orientation Presented by: Vermont BEST/PBS Team February,...
PBS Targeted LevelTargeted Coordinator Orientation
Presented by:
Vermont BEST/PBS Team
February, 2010
Agenda
• Sustaining Universal efforts• Overview of PBS Targeted Level • Role of Coordinator• Role of Targeted Team• Preview Inventory/Self-Assessment• Preview Check-In/Check-Out• Preview of FBA• Plan for SWIS CICO (optional)
Summary of PBS “BIG IDEAS”
Systems (How things are done) Team based planning and problem solving Data-based decision making Long term sustainability
Data (How decisions are made) Ongoing data collection & use ODR’s (# per day per month, location, behavior, student) Suspension/expulsion, attendance, tardies
Practices (How staff interact with students) Direct teaching of behavioral expectations On-going reinforcement of expected behaviors Functional behavioral assessment Other proven strategies
Emphasis on PreventionSchool-wide/Primary
– Reduce new problem behaviors
Secondary/Targeted– Reduce current problem behaviors
Intensive/Tertiary– Reduce complications, intensity, severity of
current behaviors
~80% of Students
~15%
~5%
Establishing Continuum for SWPBS
SECONDARY PREVENTION• Check in/out• Targeted social skills instruction• Peer-based supports• Social skills club•
TERTIARY PREVENTION• Function-based support• Wraparound• Person-centered planning• •
PRIMARY PREVENTION• Teach SW expectations• Proactive SW discipline• Positive reinforcement• Effective instruction• Parent engagement•
SECONDARY PREVENTION• • • • •
TERTIARY PREVENTION• • • • •
PRIMARY PREVENTION•
• • • • •
When to Consider Targeted Interventions
• When universal systems are not sufficient to impact behavior
• When students display chronic patterns of disruptive behavior
• When concerns arise regarding students’ academic or social behavior
Universal Systems Check• Is your leadership team meeting at least monthly? Why not?• Do you have a purpose statement and do all staff know where it can be found?
Why not?• Are behavior expectations posted throughout the school in every hallway and
learning environment? Why not?• Is teaching matrix posted just under/next to or part of behavior expectations in all
environments? Why not?• Are all students regularly receiving instruction on behavior expectations? Why
not?• Is there an acknowledgement system that all staff participate in actively? Why
not?• Is there clear agreement and understanding of staff responsibilities for minor and
major behavior problems? Why not?• Is data being used as the basis for full staff meetings to review progress and refine
strategies? Why not?
First, you must plan to sustain your PBS Universal Level
• Do you still have 80% buy-in? How do you know?
• Who will plan your regular Universal Level roll-out activities? How?
• How will you use data to help in your planning?
Planning to sustain Universal PBSActivity # 1
• Answer the questions discussed above.
• Share your strategies to sustain your PBS Universal Level with a neighbor.
• What barriers exist? Brainstorm solutions.
Which students might need more than Universal Level supports?
Possible Categories of Risk:• Major office disciplinary referrals• Attendance/late to school• Frequent nurse visits• Homework not completed• Behavior concerns not addressed through
discipline system (e.g. social withdrawal, internalizing)
• Other
What is a Targeted Intervention?
• An intervention (or set of interventions) known by all staff and available on an ongoing basis for eligible students throughout the school day.
• Interventions provide additional student support in academic, organizational, and/ or social support areas.
Targeted interventions are…
– Best for low level problem behavior (e.g. talk-outs, minor disruption, task completion);
– Efficient because they use a similar set of strategies across a group of students who need similar support;
– Effective because they focus on decreasing problem behavior in the classroom thereby increasing academic engagement and decrease office referrals.
Critical Features• Rapid access to intervention (less than a week)• Positive system of support• Students agree to participate• Implemented by all staff/faculty – very low effort• Flexible intervention based on simple assessment of
function of behavior• Adequate resources allocated (admin, team)• Continuous monitoring and decision-making• Administrative support
Examples: Targeted Group Interventions Based on Functions of
Behavior Access Adult Attention/Support:
Check-In/Check-Out Adult Mentoring Programs
Access Peer Attention/Support: Social Skills Instruction Peer Mentoring Self-Monitoring with Peer Support (function:
academic task escape) Academic Skills Support
Organization/Homework planning support Homework completion club Tutoring
Remember
Common misperception is that these strategies will “fix” the student and the classroom teacher does not need to be an active participant since “specialists” or outside staff are often involved in the intervention – Important to stress that these interventions will require high level of involvement among ALL staff within the school building
Targeted Team has two purposes:
1. Systems level design and accountability
2. Individual student intervention planning and monitoring
Targeted Team membership (focus on Systems):
• The Universal Team or a subset of the
Universal Team can serve this function
• Administrator
• Others
Functions of the PBS Targeted Team (focus on Systems):
• Develops and reviews targeted system development:– Creates referral process, system for student
screening, process for parent contact, measurement of overall targeted intervention effectiveness
– Reviews data for decision making– Link between targeted interventions and Universal
system
Targeted Team membership (focus on individual students):
• Targeted Team Coordinator• 1-3 individuals skilled or developing skills in
function-based assessment, behavior support planning & implementation
• Prepared to meet on a weekly basis• Includes someone skilled in data-based decision
making for individual student progress• Check-In/Check Out Coordinator• Others
Functions of the PBS Targeted Team (focus on individual students):
• Receive referrals• Begin student in Check-in/Check-out intervention
within 72 hours (unless otherwise specified)• Communicate with staff and parents about
intervention• Evaluate student progress-exit student from
intervention/tweak plan/conduct FBA to plan alternative or Intensive interventions
Targeted Team and EST
• Targeted Team negates need for EST for behavioral referrals
• Appropriate members of EST should be considered for targeted team membership
PBS Targeted Coordinator Pre-requisites
• Active knowledge of school’s PBS efforts• Skilled in function-based assessment, behavior support
planning & implementation• Member of the school’s PBS Universal Team and EST
(targeted team may negate need for EST for behavior referrals)
• Role formally endorsed by school principal• Flexibility to complete tasks during the day• Positive rapport with other school staff
PBS Targeted Team Coordinator Responsibilities
• Attend PBS Team Meetings (Universal and/or Targeted system level)
• Meet with (student-focused; 2-3 people) Targeted Team weekly to address student referrals, interventions and to monitor progress
• Attend regional coordinator meetings• Attend all training events• Help team complete tasks on time• Help with team organization• Data organization and reporting
Activity # 2Targeted Coordinator Self-Assessment
Complete the Vermont PBS Targeted School Coordinator Self-Assessment.
This self-assessment is designed to
assist coordinators in identifying current strengths and professional
development goals.
Inventory of Targeted Practices
• After forming your Targeted Team, complete the Targeted Practices Inventory and bring to Training for further discussion.
Inventory of Formal and Informal Targeted Practices/Supports
Intervention/Practice Staff Involved Evidence of Effectiveness (Does practice achieve anticipated Outcomes? Is there data?)
Insert new cell
Inventory of Formal and Informal Targeted Practices/Supports
Intervention/Practice Staff Involved Evidence of Effectiveness (Does practice achieve anticipated Outcomes? Is there data?)
Teacher Mentor Ollie Young Informal process and review
EST Candi Cane, Tess Sweet, Fore Getful
Referral form, teacher nomination of student review, summary report, informal report back to team
Lunch Bunch John Guidance
Informal referral from teachers, students served as needed. Group ends after 8 weeks. No formal measure of review.
Homework Club Suzie Helper Students self nominate, teacher refers to Suzie, students leave club once at grade level.
© 2005 by The
Check-In/Check Out Implementation Manual
• Crone, Horner, & Hawken (2004). Responding to Problem Behavior in Schools: The Behavior Education Program. New York, NY: Guilford Press (www.guilford.com)
• Also referred to as BEP• We will call it
“Check-In/Check/Out”
Most Promising Targeted Intervention
Check-in/Check-outor
Teacher Check, Connect and Expect
Every school does not need every targeted intervention. All schools need one of the above interventions.
What is Check-In/Check-Out and Teacher Check, Connect and Expect?
A school-based program for providing systematic and frequent reinforcement and encouragement for positive behaviors so that the student receives high rates of immediate feedback. Most useful with:
– Students who do not respond to school-wide interventions
– Students with repeated referrals– Students seeking adult attention
CICO and TCCE Elements
• Daily positive adult contact• Check-in/Check-out system• Daily Report Card (DPR) – increased attention
to behavioral goals• For all school settings• Home school partnership• Collaborative team-based process
Teacher Check Connect and Expect• Student is greeted each day in a friendly positive way by the
teacher.• Teacher reviews behavior expectations with the student, and
encourages student to do well.• After each time period, teacher checks in with student about
progress during time period and indicates points on daily progress report (dpr).
• At end of day, teacher writes the total amount of points achieved for the day on dpr.
• Completed daily progress reports are sent to the targeted team for input into data information system. system.
• Targeted team reviews progress after four weeks unless otherwise indicated.
Check-In/Check-Out Cycle: How does it work?
• Morning check-in – Students checks in with coordinator within 15 minutes of
arrival time– Coordinator collects and hands out Daily Progress Report
form– daily goal set with students– Students encouraged to make good choices
• Student gives DPR form to each teacher prior to each period (section of time).– (Can also be used in cafeteria or playground… anywhere
there is a supervisor).
Check-In/Check-Out Cycle: How does it work?
• End of day check-out– During last 20 minutes of the day– Goes over daily progress– Reviews progress towards goals– Points tallied– Reward– Graphs student progress
• Daily Progress Report form copy taken home and signed.• Return signed copy next morning.
Check-in/Check-out Coordinator
“Someone the students enjoy and trust”• Enthusiastic• Leads check-in and check-out• Enters data daily• Prioritizes students for review at team meetings• Creates graphs for meetings• Gathers extra info for meetings• Maintains records
Getting Started Activities
1. Determine how CICO or TCCE will be implemented in your school
2.Develop DPR3.Develop reinforcement system for students 4.Develop referral system5.Create system for managing daily data6.Plan for fading students off intervention7.Develop staff training8.Develop student and parent training
First Steps: Determine how CICO or TCCE will be
implemented in your school
• Establish the Targeted Student Focused Team• Determine CICO or TCCE• Establish number of students that can be
served on program at one time• Determine the name of this program for your
school
A Context for Positive Behavior Support
• A redesign of environments, not the redesign of individuals
• Plan describes what we will do differently• Plan is based on identification of the
behavioral function of problem behaviors and the lifestyle goals of an individual
FBA Team Process Steps1. Collect information.2. Develop testable hypothesis or summary statement.3. Collect direct observation data to confirm summary statement.4. Develop “competing pathways” summary statement.5. Develop BIP.6. Develop details & routines for full implementation of BSP.7. Develop strategies for monitoring & evaluating implementation of
BSP.
FunctionsProblemBehavior
Obtain/GetSomething
Escape/Avoid
Something
SocialTangible/Activity
Adult
Stimulation/Sensory
Peer
Pos Reinf Neg Reinf
Identifying who needs an FBA/BIP
• Multiple office disciplinary referrals• Existing targeted interventions not successful
or inappropriate• Academic/behavior data indicates challenge• High intensity or frequency of behavior• Behavior impedes academic performance or is
disruptive to the learning environment• Function of behavior unclear
Source: Crone, D.A. & Horner, R.H., 2003
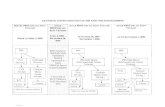
Level 1 – PBS Essential Components•Classroom System
•Non-Classroom System•School-wide System
Tier 1 Implemented with Fidelity?
If Yes, then
Teacher Referral Data Decision Rules Universal Screening Tools
Non-responder as compared to typical peer?Full access to Level 1 Supports?
Is identification process accurate?
Step 1: Try CICO First (most students)
Step 2: Conduct a Simple FBA:1. Define Problem, 2. Develop Hypothesis, 3. Indentify Resources,
4. Select Intervention
Avoid Tasks?
Obtain Attention?
Obtain Attention? Skill
Deficit?
Social Skills Club
Mentoring
CICO –Continu
ed..
Academic
Support
and/or Analysis Full Assessment
CICO-SWIS
Organized around same three areas as SWIS:1. Data Entry2. Reporting3. Tool
Reports organized to be used for two levels of problem-solving1. Overall CICO Implementation2. Individual Student Progress Monitoring