PBS Overview Goal for Today To introduce you to key principles and basic concepts for a continuum...
-
Upload
jason-byrd -
Category
Documents
-
view
217 -
download
1
Transcript of PBS Overview Goal for Today To introduce you to key principles and basic concepts for a continuum...

PBS Overview PBS Overview

Goal for Today
To introduce you to key principles and basic concepts for a continuum of support for students known as Positive Behavior Supports (PBS)

Did you know?
“We live in an era when research tells us that the teacher is probably the single most important factor affecting student achievement- at least the single most important factor that we can do much about. (Marzano, 2003)

Challenges
Poor attendance
Academically deficient
Disruptions by students in classrooms
Discipline


Positive Behavior Supports

Why?

Public school teachers must deal with all of America’s children.
(Marzano, 2003) These students enter the
classroom with a staggering array of serious issues in their lives.

What happens if we do not intervene?
Three years after leaving school, 70% of antisocial youth have been arrested (Walker, Colvin, & Ramsey, 1995).
82% of crimes are committed by people who have dropped out of school (APA Commission on Youth Violence, 1993).
The stability of aggression over a decade is very high; about the same as IQ (Walker et al., 1995).

What happens if we do not intervene?
If antisocial behavior is not changed by the end of grade 3, it should be treated as a chronic condition much like diabetes. That is, it cannot be cured but managed with the appropriate supports and continuing intervention (Walker, Colvin, & Ramsey, 1995).

Contributing Factors:Poverty & Language
Over a year (11-18 mo.)Over a year (11-18 mo.) Children in poverty—hear 250,000
words per year Children in homes of professionals—
hear 4 million words per year

Parent – Child
Affirmative statements Professional—30 per hour Working class—15 per hour Poverty—6 per hour (prohibition twice
as often as affirmative feedback)

Meaningful Differences ““To keep the confidence-building To keep the confidence-building
experiences of welfare children experiences of welfare children equal to those of working class equal to those of working class children, the welfare children children, the welfare children would need to be given 1,100 more would need to be given 1,100 more instances of affirmative feedback instances of affirmative feedback per week…”per week…” (p.201).(p.201).
““It would take 26 hours per week It would take 26 hours per week of substituted experience for the of substituted experience for the average welfare child’s experience average welfare child’s experience with affirmatives to equal that of with affirmatives to equal that of the average working-class child”the average working-class child” (p. (p. 202).202).
-Hart & -Hart & RisleyRisley

What Do Schools
Exclusion and punishment are the most common responses to conduct disorders in schools.
Lane & Murakami, (1987); Rose, (1988); Nieto, (1999); Sprick, Borgmeier, & Nolet, (2002)
Exclusion and punishment are ineffective at producing long-term reduction in problem behavior.
Costenbader & Markson (1998)

A Solution?

Positive Behavior Support (PBS) is a general term that refers to the application of an applied science that uses proactive and effective educational methods, behavioral interventions, environmental redesign and systems change methods to support individuals who exhibit disruptive and/or dangerous behaviors in school, work, social, community and family settings (Carr et al., 2002; Horner et al., 1990).

Based in Behavioral Science
Behavior is learned Behavior is related to the immediate
and social environmental factors Systemic manipulation of the
environmental factors influences behavior
Behavior can change Appropriate and effective feedback
leads to changes in behavior

The Foundation
“Students learn appropriate behavior in the same way they learn to read – through instruction, practice, feedback, and encouragement.”

A Research Based Foundation
Research indicates that one way to effectively support children with problem behavior is to build skills through effective teaching.
(Carr et al., 2002; Horner, Albin, Sprague & Todd, 2000)

Academic Systems Behavioral Systems
1-5% 1-5%
5-15% 5-15%
80-90% 80-90%
Intensive, Individual Interventions•Individual Students•Assessment-based•High Intensity
Intensive, Individual Interventions•Individual Students•Assessment-based•Intense, durable procedures
Targeted Group Interventions•Some students (at-risk)•High efficiency•Rapid response
Targeted Group Interventions•Some students (at-risk)•High efficiency•Rapid response
Universal Interventions•All students•Preventive, proactive
Universal Interventions•All settings, all students•Preventive, proactive
The Triangle

Behavior Support ???

What?

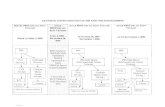
Systems of Support
Nonclass
room
Setting S
ystems
ClassroomSetting Systems
Individual Student
Systems
School-wideSystems

How?

Guiding Principles
Requires long-term commitment to systems change of effective practices
Implemented consistently by staff and administration
Positive behaviors are publicly acknowledged Problem behaviors have clear consequences Student behavior is monitored and staff
receive regular feedback Strategies are implemented at the school-wide,
specific setting, classroom, and individual student levels
Strategies are designed to meet the needs of all students

“Behavior change is like a kaleidoscope: Once the tube is
turned even a fraction of an inch, the entire pattern changes.”
-John Maag