Parts of the Cell Membrane: (p. 184) file · Web viewhow these processes impact the homeostasis of...
Click here to load reader
Transcript of Parts of the Cell Membrane: (p. 184) file · Web viewhow these processes impact the homeostasis of...

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
Unit 6 Cell Structure and FunctionObjectives
Topic 1: Cell Membrane
o I can identify the component parts of the fluid mosaic model and describe their function within the cell membrane.
Topic 2: Osmosis and Diffusion
o I can describe the process of osmosis and diffusion and apply how these processes impact the homeostasis of living organisms.
Topic 3: Movement across the Cell Membrane
o I can differentiate between passive and active transport and how each is utilized within the cell membrane.
Topic 4: Important Scientists and Cell Theory
o I can differentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and list the three parts of the cell theory and the scientists who contributed to its development.
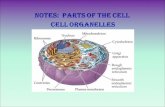
Topic 5: Cell Organelles
o I can identify and describe the function of all membrane bound organelles and structures found in plant and animal cells and how these changes within the cell can lead to specialization.
Important Dates:
Vocabulary Due
Quiz 1 – Vocabulary
Quiz 2 – Topics 1 through 5
LAB – Osmosis and Diffusion
Project –
Unit Test
1

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
VOCABULARYWord Picture Definition
Cell
Cell Theory
Prokaryote
Eukaryote
Organelles
Lipid Bilayer
Concentration
Diffusion
Selective Permeability
Osmosis
Facilitated Diffusion
Active Transport
Endocytosis
2

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
Exocytosis
Phagocytosis
Pinocytosis
Cell Specialization
Fluid Mosaic Model
3

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
7-3 Cell Membrane - Osmosis and TransportParts of the Cell Membrane: (p. 184)
Diffusion vs. Osmosis:
Diffusion –
Osmosis -
Types of Osmosis
Type of Osmosis Description Picture1. Isotonic Solution
2. Hypertonic Solution
3. Hypotonic Solution
4

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
Types of Diffusion
o Simple Diffusion – Example
o Facilitated Diffusion -
Example:
o Active Transport -
Example:
(See pages 188-189)
Diagram:
Forms of Active Transport:
Endocytosis – o
o
5

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
Exocytosis - o
REVIEW: Look over your notes and give a statement with 3 words or less!Fluid Mosaic =
Osmosis =
Isotonic =
Hypertonic =
Hypotonic =
Diffusion =
Simple diffusion=
Facilitated diffusion =
Active diffusion or transport =
Endocytosis =
Pino =
Phago =
Exocytosis =
6

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
Moves:
Osmosis Egg LabBackground InformationCells have an outer covering called the cell membrane. This membrane is
selectively permeable; it has tiny pores or holes that allow objects to move
across it. The cell membrane controls what moves in and out of the cell. Food
and oxygen move into cells across the cell membrane through the process of
diffusion. Diffusion is movement of a substance from an area of high
concentration to an area of low concentration. Osmosis is a special type of
diffusion; it is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable
membrane. Osmosis occurs when water moves from an area where it is more
concentrated to an area where it is less concentrated.
In this lab you will be using an egg with the shell removed. The shell-less egg will
represent a cell and its selectively permeable membrane. The shell of the egg
was removed by soaking the egg in vinegar. The egg shell is made up of the
mineral calcium carbonate. Calcium carbonate dissolves in acids such as
vinegar. During this process it releases the gas carbon dioxide. After the shell
has been dissolved, only the membrane will remain around the egg.
7

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
Name___________________________Block____________________Date____
Beaker 1 – Syrup Solution 1. Is the syrup a hypotonic, hypertonic or isotonic solution for the egg to be
placed in? Explain your answer using the definition. What is the solute in
this solution?
2. Draw what you expect your egg to look like next class? Explain why you
think it will look like your drawing by describing what will occur to the cell,
the syrup and the fluid in the cell?
Drawing Explanation for your prediction
3. Draw what the egg actually looked like. Was your prediction correct? If
not, explain what happened since we put the egg in the syrup.
Drawing Was your prediction correct? If not, explain what happened.
Beaker 2 – Distilled Water Solution4. Is the water a hypotonic, hypertonic or isotonic solution for the egg to be
placed in? Explain your answer using the definition. What is the solute in
this solution?
8

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
5. Draw what you predict will happen to the egg in this solution. Explain your
answer by describing what will occur to the cell, the water and the fluid in
the cell.
Drawing Explanation for your prediction
6. Draw what the egg actually looked like. Was your prediction correct? If
not, explain what happened since we put the egg in the water after being
in the syrup.
Drawing Was your prediction correct? If not, explain what happened.
Review: Use your NOTES and VOCABULARY to answer the questions in
COMPLETE sentences.
7. What was the solute in this experiment?
8. What were the solvents?
9. When did the egg shrink? Why?
10.When did the egg swell? Why?
9

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
Diffusion ApplicationName___________________________Block____________________Date____
Directions: Name the physical or physiological process involved in each of the following situation. Select carefully as each answer may be used only once! Choose form the following:
1. A person soaks celery in water so the cells swell. This makes it crisp before serving
2. A person pours salt on the grass growing in the cracks in the sidewalk and the grass dies.
3. Roots of broccoli absorb calcium even when their cells contain higher concentrations of Ca than the soil solution around them.
4. When you wake up you can smell the coffee your mom or dad is making in the kitchen.
5. A student studying blood places some cells in distilled water; they swell and burst.
6. A bottle of cologne is left open soon the odor and the other gasses in the room are evenly distributed through all the parts of the room.
7. As they invade your body, bacteria are engulfed by white blood cells as the cell membrane closes behind them.
8. What is meant by a concentration gradient? How does it affect the rate of diffusion? Draw a picture to explain you answer. Think about how an odor moves across a room.
9. What other factors that affect the rate of diffusion?
10.Label the cell membrane diagram.
10
Osmosis Active Transport Turgor PressureDiffusion Equilibrium Hypertonic SolutionHypotonic Solution

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
11.Answer the following: A cell takes in two substances (A and B) which are present in concentrations lower outside the cell than inside the cell. Substance A is a large molecule needed by the cell. Substance B is a liquid droplet. Each substance enters the cell by a different process. Describe how each substance enters the cell using vocabulary from your notes.
11

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
OSMOSIS and DIFFSIONDefine the Following:
1. Diffusion
2. Semi permeable membrane
3. Fluid Mosaic
4. Osmosis
Complete the tableType of Solution ISOTONIC HYPERTONIC HYPOTONICEffect of a cell(choose words or use a diagram)
Freshwater protozoan such as a Paramecium must constantly pump out water to keep from bursting. What does this tell you about the solute concentration INSIDE the Paramecium compared to the solute concentration of its water environment?
What would happen if you made the solute concentration outside the Paramecium the same as that of the inside?
12

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
PASSIVE and ACTIVE TRANSPOTComplete the table by writing YES or NO
ACTIVE TRANSPORT
FACILITATED TRANSPORT
SIMPLE DIFFUSION
Requires energyMoves molecules against the concentration gradientRequires a membrane proteinSodium potassium pump is an example
Answer the following questions: 1. Name substances that can diffusion across the cell membrane.
2. Name a substance that is too large to diffuse across the cell membrane.
3. What prevents charged molecules from diffusion across the cell membrane?
4. How is facilitated transport similar to simple diffusion?
5. How does facilitated transport differ from simple diffusion?
Chapter 7: Cells Structure and Function
13

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
Part A: Cell Theory Read Section 7-1 (169 –172) in your textbook to gather the following information.
1. State the three parts to the traditional CELL THEORY:A
B
C
2. Describe what Anton van Leeuwenhoek and Robert Hooke did to contribute to the cell theory.
Anton van Leeuwenhoek Robert Hooke
3. Describe what these 3 scientists contributed to the cell theory.Matthias Schleiden Theodor Schwann Rudolph Virchow
4. Biologists divide cells into two categories known as Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. Compare with a Venn Diagram.
Part B: Cell Organelles Structure and Function
1. Draw with COLOR and Label a plant and animal cell2. Using information that can be found using your text (chapter 7), give the
function of the following organelles as well as the type of cell they are found in.
3. Place and X in the box if found in Plant, Animal and or Prokaryote
14

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
15

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
Structure Function Quick Picture
Animal Plant Prokaryote
1. Cytoplasm X X X
2. Cell Membrane
3. Nucleus
4. Nucleolus
5. Ribosome
6. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
7. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
8. Mitochondria
9. Golgi apparatus
10. Lysosome
11. Cytoskeleton
12. Vacuole
13. Centrioles
14. Chloroplasts
16

Useful Information: Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
15. Cell Wall
1. What organelles are found in plants cells that are NOT found in animal cells?
__________________________________________________________________
2. Compare and contrast the following 2 organelles:
Mitochondria Chloroplast
Picture
Type of cell found in
Function in the cell
Differences
Similarities
Photosynthesis Equation:CHOLORPLAST = PLANT CELLS
Water + Carbon Dioxide + Light = Oxygen + Glucose
Cellular Respiration Equation:MITOCHONDRIA = ANIMAL & PLANT
Cells
Oxygen + Glucose = Water + Carbon Dioxide + Energy (ATP)
Part C: Levels of Organization Read pages 192 –193 of your book briefly describe and draw the following levels of organization.
17
Cells Tissues Organs Organs Systems