Paper of Mri
-
Upload
allen-renaldo -
Category
Documents
-
view
221 -
download
0
description
Transcript of Paper of Mri
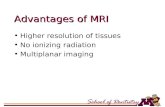
CHAPTER IINTRODUCTIONA. BACKGROUNDMRI has a wide range of applications in medical diagnosis and over 25,000 scanners are estimated to be in use worldwide.MRI has an impact on diagnosis and treatment in many specialties although the effect on improved health outcomes is uncertain. Since MRI does not use any ionizing radiation, its use is generally favored in preference to CT when either modality could yield the same information. MRI is in general a safe technique but the number of incidents causing patient harm has risen. Contraindications to MRI include most cochlear implants and cardiac pacemakers, shrapnel and metallic foreign bodies in the orbits. The safety of MRI during the first trimester of pregnancy is uncertain, but it may be preferable to alternative options.The sustained increase in demand for MRI within the healthcare industry has led to concerns about cost effectiveness and over diagnosis.B. GOALS1. To know what is the definition of MRI2. To know what is the purpose of using MRI3. To know what is the description of MRI4. To know how is the MRI works5. To know how is the precautions for MRI6. To know how is the preparation for MRI7. To know what is the benefit of MRI scan8. To know what is the disadvantages of MRI scan9. To know how is the aftercare treatment of MRI10. To know what is the risk of MRI11. To know how is the parental concern of MRI12. To know how is the pregnancy risk about using MRICHAPTER IICONTAINSA. DEFINITIONMagnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses radio waves, a magnetic field, and a computer to generate images of the anatomy.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), ( ornuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMRI), or magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) ) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to investigate the anatomy and physiology of the body in both health and disease. MRI scanners use magnetic fields and radio waves to form images of the body. The technique is widely used in hospitals for medical diagnosis, staging of disease and for follow-up without exposure to ionizing radiation.B. FUNCTIONMRI is used to visualize the body to assist doctors in their efforts to diagnose certain diseases or conditions and to evaluate injuries. For pediatric imaging, MRI is used for a variety of purposes, including the following: diagnosing diseases of the central nervous system, including the brain and spine detecting musculoskeletal disorders and injuries identifying complications of infectious diseases, such as those associated with Lyme disease or acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) imaging the cardiovascular system detecting congenital heart defects in neonates determining the stage of certain types of cancer valuating bone marrow disease assessing blood vessels in the brain for stroke and other abnormalities assisting in the planning of surgery and cancer treatment evaluating the urinary tractMRI provides images with excellent contrast that allow clinicians to clearly see details of soft tissue, bone, joints, and ligaments. MRI angiography is an imaging technique used to evaluate the blood vessels, for example, to detect aneurysms or cardiovascular problems. Because MRI does not use ionizing radiation to produce images, like x ray and CT, it is often the examination of choice for pediatric imaging and for imaging the male and female reproductive systems, pelvis and hips, and urinary tract and bladder.MRI can also be used to evaluate brain function for assessing language, senses, neurologic disorders, and pain . This technique, called functional MRI, involves rapid imaging to display changes in the brain's blood flow in response to tasks or visual and auditory stimuli. Functional MRI is being researched to image neurologic disorders, such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), delayed cognitive development, and epilepsy.MRI spectroscopy is another emerging imaging technique for evaluating pediatric brain disorders. In MRI spectroscopy, chemicals in the brain are measured and brain tissue is imaged. This technique is being investigated to evaluate traumatic brain injury, speech delay, creatine deficiency syndromes, and mood disorders in young children.Interventional and intraoperative MRI is another developing field that involves performing interventional procedures, primarily brain surgeries, using a specially designed MRI unit in an operating room.C. DESCRIPTIONMRI is performed using a specialized scanner, a patient table, systems that generate radio waves and magnetic fields, and a computer workstation. The scanner, which is usually shaped like a large rectangle with a hole in the center, contains the systems that generate the magnetic field. A motorized and computer-controlled patient table moves into the scanner's center hole during the scan. A technologist operates the MRI scanner from an adjacent control room that contains a computer system and an intercom system for communicating with the patient during the scan.In most MRI scanners, the patient opening is like a long tube, and some patients may become claustrophobic. To be more patient-friendly, different types of MRI scanners have been developed. Newer MRI scanners have shorter patient openings that allow the patient's head to remain outside the machine during body scans. Open MRI scanners are available with columns and open sides to alleviate claustrophobia.Depending on the body area being scanned, special body coils may be used to enhance the images. These coils are foam and plastic braces or wraparound pads that are placed on the body part being imaged. For head imaging, the coil may be shaped like a head or neck rest.Children undergoing an MRI scan are appropriately positioned on the patient table by the technologist. For some scans, an injected contrast material may be used and is administered using an intravenous catheter. Once the patient is positioned, the technologist goes to an adjacent control room to operate the scanner. The technologist uses an intercom system to instruct the child to hold their breath or remain still at certain times during the scan. Scans range from 30 minutes to 90 minutes, depending on the type of scan. When the MRI machine is scanning, the child hears loud clanging and whirring noises. To alleviate fear or stress related to hearing this noise and being in the small scanning tube, the child may be offered earplugs or specially designed head phones for listening to music. Centers that specialize in pediatric imaging often also have special video goggles so that the child can watch a cartoon or movie during the scan. For infants, neonatal noise guardsare available.MRI scans are performed in a hospital radiology department for inpatients and emergency cases. For scans requested by a physician, the MRI examination can be performed in the hospital radiology department on an outpatient basis or in an imaging center. Hospitals that do not have their own MRI systems may schedule MRI scans by contracting with a company that brings an MRI scanner in a specially designed mobile trailer. Mobile MRI services are frequently used in rural areas. For some conditions, such as orthopedic disorders or injuries, an MRI may be performed in a physician's office using a small MRI unit called an extremity MRI scanner. These scanners are designed to image only the joints or the head. During this type of scan, only the body part to be scanned is placed in the smaller scanner while the patient lies on a couch or sits in a chair.The images from an MRI examination are called slices, because they are acquired in very small (millimeter-size) sections of the body. The image slices are displayed on a computer monitor for viewing or printed as a film. A specialist called a radiologist interprets the images produced during the MRI examination. For emergency scans, images are interpreted immediately so that the child can be treated quickly. For non-urgent outpatient MRI scans, the radiologist interprets the images and sends a report to the referring physician within a few days.D. HOW MRI WORKSThe patient is positioned within an MRI scanner which forms a strong magnetic field around the area to be imaged. In most medical applications, protons (hydrogenatoms) in tissues containing water molecules are used to create a signal that is processed to form an image of the body. First, energy from an oscillatingmagnetic field is temporarily applied to the patient at the appropriate resonance frequency. The excitedhydrogenatoms emit a radio frequency signal which is measured by a receiving coil. The radio signal can be made to encode position information by varying the main magnetic field using gradient coils. As these coils are rapidly switched on and off they create the characteristic repetitive noise of an MRI scan. The contrast between different tissues is determined by the rate at which excited atoms return to the equilibrium state. Exogenous contrast agents may be given intravenously, orally or intra-articularly.E. PRECAUTIONSMRI is a safe procedure that does not involve radiation. However, the magnetic field generated during an MRI examination is so strong that metal objects or objects with metal in them, such as jewelry, eyeglasses, oxygen canisters, and even wheelchairs, will be pulled toward the machine. Therefore, MRI staff must take special precautions to ensure that no metallic objects enter the MRI suite. MRI technologists inspect patient clothing and accessories to make sure there are no metals on them during the scan.F. PREPARATIONPrior to any MRI scan, patients are required to remove all metal objects and remove any clothing with metal on them (zippers, snaps). In most cases, parents have to complete a survey regarding their child's past surgical procedures and medical history to indicate whether the child has any metallic implants. Metallic implants include artificial joints, pacemakers, aneurysm clips, metal plates, pins or screws, and surgical staples. Children with metallic implants are likely to undergo a computed tomography (CT) examination instead of an MRI.Unlike CT, no fasting or laxatives are required prior to an MRI scan. Only one type of MRI scan, called a magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), which scans the bile ducts, requires that the child not eat or drink anything for two to three hours prior to the scan.During the examination, the child must lie still. The MRI scanner does make loud noises throughout the examination, which can be frightening for some children. Before the examination, the procedure should be explained to the child, and it should be emphasized that the examination is painless. Most facilities have specially designed music systems so that patients can wear headsets and listen to music during the scan; some facilities even have special video goggles so children can watch a cartoon or movie during the scan for the diagnosis and treatment of disease.G. BENEFITS OF MRI SCANMRI scans are an important tool that doctors use to investigate the cause of your symptoms. They can help confirm the presence or absence of a disease or injury. However, the diagnosis of a condition usually requires more than a single examination or test. An MRI scan should always be used to supplement your doctors history-taking and examination.
MRI scans: provide very detailed diagnostic pictures of most of the important organs and tissues in your body are sometimes able to show unique information that other tests are unable to show are generally painless do not use radiation and are therefore suitable for use in children and pregnant women. Safety studies have found no long-term negative effects from MRI scans.
H. DISADVANTAGES OF MRI SCAN Risks from metal objectsMRI scans are considered to be a safe procedure providing you do not have any implants or objects on you that must not go in the scanner.The powerful magnetic fields generated by the MRI scanner will attract metal objects, often with great force. For this reason, youll be instructed to remove all metallic belongings, such as watches, keys and jeweler.The magnetic field of the MRI scanner can also pull on any metal-containing object in your body, such as medicine pumps and aneurysm clips. In other cases, (older-style) medical implants may heat up during the scan as a result of the technology (radiofrequency energy) that is used for the procedure. MRI scans can cause heart pacemakers, defibrillation devices and cochlear implants to malfunction. Every MRI facility will have a comprehensive screening procedure that, when carefully followed, will ensure that MRI is only used on people for whom it is safe. Many newer medical implants are now manufactured to be MRI-compatible, so once the doctors know the exact nature of your implant theyll be able to tell you if its safe for you to have an MRI. If you do have an implant that could make an MRI unsafe, the radiologist may recommend you have a different type of scan.I. AFTERCARENo special aftercare is required following MRI scans, unless sedation or general anesthesia was used during the scan. Then children are required to remain in a supervised recovery area for an hour or more following the procedure to monitor for reactions to anesthesia. If injected contrast material is used, some minor first aid (small bandage, pain relief) for the injection site may be necessary.J. RISKSMRIs present no radiation exposure. Magnetic fields used in MRI have no side effects for the patient. The contrast material used in MRI contains a material called gadolinium that is much less likely to cause severe anaphylactic (allergic) reactions than the iodinated material used for CT scans.Because the MRI examination is long and the patient opening in the machine is small, some children and adolescents may feel claustrophobic. Light sedation or relaxants may be administered, or an MRI scanner with a more open design may be used. For younger infants and children that require sedation or anesthesia to complete the examination, reactions to the anesthesia are possible, including headaches and vomiting. Risks associated with contrast mediaUnlike contrast agents used in X-rays, the contrast dye used in MRI scans (gadolinium chelate) does not contain iodine and rarely causes allergic reactions (such as rashes, hives, nausea, flushing, and dizziness). Severe reactions, such as difficulty breathing and swelling of the lips and mouth, are even rarer, occurring in only about 1 in 10,000 people given gadolinium. Nevertheless, its essential you tell the doctor and radiology practice about any previous allergic reactions youve had, especially if youve had a previous reaction to contrast media. You should also tell the radiology practice before the procedure about all medicines you are taking. In very rare cases (in people with poor kidney function), gadolinium chelate injections can cause a serious condition called nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, which involves the build-up of fibrous tissue in the skin, joints, muscles and internal organs. If there is any chance you may have kidney problems, your doctor may organize a blood test before the scan to assess whether the gadolinium contrast dye is safe to use. Risks associated with general anesthesia or sedationMost young children (under 6 years of age) and babies will need to be given a light general anesthetic before the MRI. This is because young children find it difficult to stay still long enough for the radiographer to get good-quality pictures from the scan. If your child needs an anesthetic before their MRI, a doctor at the radiology practice will discuss the procedure and the risks and benefits of anesthesia prior to the scan. Read about ways to help your child during imaging. Occasionally adults for example a person who is highly agitated or in pain so severe that it makes it hard for them to lie quietly may require general anesthesia for an MRI scan. You can request a sedative, especially if you suffer from claustrophobia or are very anxious. A sedative will help to calm you and make you drowsy, but not put you completely to sleep like a general anesthetic does. While sedatives are generally safe, if you are given a sedative during the scan you may feel drowsy for the rest of the day and will not be able to drive or operate machinery afterwards. You will need to arrange for a relative or friend to take you home after the procedure and stay with you for a period of time as recommended by the radiology practice. Risks associated with incidental findingsSometimes the sensitivity of MRI scans can create problems by picking up incidental findings that is, apparent abnormalities on the scan that have no actual relationship to the illness or injury being investigated. These incidental findings can cause anxiety and sometimes lead people to pursue unnecessary treatment, which may have their own risks and costs.K. PARENTAL CONCERNSYounger children may be frightened of the MRI scanner, and a parent or other family member may be required to be present in the scanning room. To help alleviate fear, taking the child into the MRI room to see the equipment prior to the procedure may be helpful. Anyone remaining in the scanning room during the MRI examination must remove any metal objects, including jewelry and eyeglasses.L. PREGNANCY RISKSMRI is safer for the unborn child (fetus) than imaging with X-rays or CT scans. However, MRI scans can cause slight warming of the body, so as a precaution most clinics avoid MRI scanning during the first 3 months of pregnancy, unless the scan is considered essential. Beyond that, MRI scans are usually considered safe in pregnancy and are occasionally used to check on the babys development, although non-urgent scans are generally delayed until after the baby is delivered. In some situations other scans, such as an ultrasound, may be used instead of MRI.
CHAPTER IIICONCLUSIONA. CONCLUSIONMagnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses radio waves, a magnetic field, and a computer to generate images of the anatomy. MRI is used to visualize the body to assist doctors in their efforts to diagnose certain diseases or conditions and to evaluate injuries.MRI is performed using a specialized scanner, a patient table, systems that generate radio waves and magnetic fields, and a computer workstation. The scanner, which is usually shaped like a large rectangle with a hole in the center, contains the systems that generate the magnetic field.Prior to any MRI scan, patients are required to remove all metal objects and remove any clothing with metal on them (zippers, snaps). In most cases, parents have to complete a survey regarding their child's past surgical procedures and medical history to indicate whether the child has any metallic implants. Metallic implants include artificial joints, pacemakers, aneurysm clips, metal plates, pins or screws, and surgical staples.
REFERENCES1. http://www.healthofchildren.com/M/Magnetic-Resonance-Imaging.html#ixzz3ZG6YTSWW2. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnetic_resonance_imaging
Group 10 --- Magnetic Resonance Imaging 7