Pages 370-379. Flow is unidirectional Vessels that carry blood away from the heart: (from largest...
-
Upload
ira-martin -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
0
Transcript of Pages 370-379. Flow is unidirectional Vessels that carry blood away from the heart: (from largest...
Flow is unidirectional
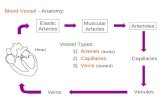
Vessels that carry blood away from the heart: (from largest to smallest)◦ Arteries > arterioles > Capillary beds
exchanges between tissues and blood take place at the capillary beds
Vessels that return blood toward the heart:◦ Venules and veins
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Three tissue layers (tunics) in blood vessels from deep to superficial:
◦ Tunica intima- innermost endothelium◦ Tunica media- middle smooth muscle◦ Tunica externa- outermost fibrous connective
All vessels possess this arrangement except capillaries
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Arteries:◦ thicker tunica media for larger volume and pressure◦ Stronger and more elastic
Capillaries: one cell layer thick for diffusion between blood and tissues
Veins:◦ thinner tunica media than arteries◦ operate under low pressure◦ valves to prevent backflow of blood against gravity◦ Larger lumen (channel)◦ Skeletal muscle helps move blood toward the heart
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
VeinArtery Tunica intima• Endothelium• Loose connective tissue
Tunica media• Smooth muscle
• Collagen fibersTunica externa
LumenArteriole Capillary
network
Venule
Valve
Lumen
Basement membraneEndothelial cells
Capillary(b)
Precapillary sphinctersVascular shunt
Truecapillaries
Terminal arteriole Postcapillaryvenule
(a) Sphincters open; blood flows throughtrue capillaries.
Varicose veins: ◦ structural defect due to incompetent valves◦ Common in people who:
Are obese stand for long periods of time
◦ Predisposing factor for thrombophlebitis: inflammation of a vein resulting from a clot can lead to pulmonary embolism
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
circulation between the heart and tissues
◦ Aorta (oxygenated blood) Largest artery in the body Leaves from the left ventricle of the heart
◦ Superior and inferior venae cavae (deoxygenated) enter the right atrium of the heart Superior drains the head and arms Inferior drains the lower body
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
CEREBRUM:◦ Blood supply branches from
internal carotid arteries Basilar artery
BRAIN STEM AND CEREBELLUM:◦ Blood supply branches from
Basilar artery
This system of arteries branches to form a circle which supplies the major brain structures
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Frontal lobe
Internal carotidartery
Temporal lobe
Pons
Occipital lobe
Anterior
Posterior
Cerebral arterial circle(circle of Willis)
Basilar arteryVertebral artery
Cerebellum
(a)
sends blood from certain organs (digestive, pancreas, spleen) for processing by the liver
The hepatic portal vein is the transport vessel
After nutrients are removed and stored, blood is returned to systemic circulation◦ via the hepatic portal vein to the inferior vena cava
veins are supplying the liver with blood for processing while arteries supply the liver with oxygen
© 2015 Pearson Education, Inc.
Arterialblood
Venousblood
Stomach and intestine Liver
Inferiorvena cava
Liver cells (hepatocytes)
Nutrientsand toxinsleave
Nutrients andtoxins absorbed
Hepaticportal vein
Hepaticvein
First capillary bed Second capillary bed(liver sinusoids)
Hepatic portal system
Liver
Hepaticportal vein
Smallintestine
Inferior vena cava(not part of hepaticportal system)
Gastric veins
SpleenStomach
Splenic vein
Inferiormesenteric vein
Superiormesenteric vein
Large intestine