Ozone Depletion Chandu
-
Upload
chandra-shekhar -
Category
Documents
-
view
238 -
download
0
Transcript of Ozone Depletion Chandu
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
1/25
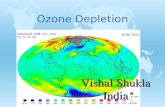
OZONE LAYERDEPLETION1. Why the hole in the atmospheric ozonelayer above us?2. What has been done about this?3. Why should I worry ourselves about theOzone Layer Depletion?
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
2/25
What is Ozone? Ozone Layer? Ozone (O3) is a highly-reactive from of oxygen. Unlike oxygen (O2), ozone has a strong scent
and is blue in color.
Ozone exists within both the tropospheric andstratospheric zones of the Earths atmosphere In the troposphere, ground level ozone is a major
air pollutant and primary constituent ofphotochemical smog
In the stratosphere, the ozone layer is anessential protector of life on earth as it absorbsharmful UV radiation before it reaches the earth.
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
3/25
CFCs and ozone depletion Chlorofluorocarbons arecreated and used inrefrigerators and airconditioners. Thesechlorofluorocarbons are notharmful to humans and havebeen a benefit to us. Oncereleased into the atmosphere,
chlorofluorocarbons arebombarded and destroyed byultraviolet rays. In the processchlorine is released to destroythe ozone molecules
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
4/25
Destruction of ozone by chlorine
Molecular oxygen is broken down in the stratosphere by solarradiation to yield atomic oxygen, which then combines withmolecular oxygen to produce ozone. The ozone is thendestroyed by chlorine atoms.
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
5/25
Ozone destruction by UV rays UV radiation from the sunreleases the radicals Cl andClO. Ozone is a highly unstable
molecule so it readily donatesits extra oxygen molecule tofree radical species such ashydrogen, bromine, andchlorine.
These compound species actas catalysts in the breakdownof ozone molecules.
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
6/25
The ozone depletion process
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
7/25
Responsibility for ozone damageeach year
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
8/25
Global CFC production
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
9/25
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
10/25
Ozone hole in Southernhemisphere October 1979 & 1998
Monthly means of total ozone in the SouthernHemisphere observed with TOMS Images for October of 1979 (left) and 1998 (right).
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
11/25
Ozone hole: size by month
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
12/25
Ozone hole measurements over theAntarctic region 1980-98
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
13/25
Ozone concentration at the centerof ozone hole
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
14/25
Ozone hole over continents:comparison 1996
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
15/25
Image of the ozone hole over theSouth pole: July 10 2003
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
16/25
Image of the ozone hole over theNorth pole: July 10 2003
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
17/25
Ozone status: full day global image, July9th 2003
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
18/25
Effects of UV rays on AquaticEcosystemsOzone depletion causes increases in UVrayss effects on aquatic ecosystems by:
1.decreasing the abundance of phytoplankton affects the food stock for fishes and theabsorption of CO22. decreasing the diversity of aquatic organisms reduces food stock and also destroys severalfish and amphibians.
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
19/25
Effects of UV rays on TerrestrialEcosystems Damage to plant cell DNA molecules - makes
plants more susceptible to pathogens and
pests
Reductions in photosynthetic capacity in the
plant - results in slower growth andsmaller leaves
Causes mutations in mammalian cellsand destroys membranes
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
20/25
Harmful effects of UV rays onpeople Skin cancer
Premature aging (photoaging) of the
skin (different from normalchronological aging)
Cataracts and eye disorders (corneal
sunburn and blindness) Immune system damage
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
21/25
Correlation between Ozonedepletion and skin diseases
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
22/25
The Ultraviolet ExposureIndexINDEX VALUES EXPOSURE
0 2 = Minimal3 - 4 = Low5 - 6 = Moderate7 - 9 = High10 + = Very High
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
23/25
Factors affecting UV exposure Clouds cover - partly cloudy days do
little to reduce UV exposure but rainy orsubstantially overcast days reduce UV
exposures
The time of day peak exposure time
is 12:00 noon - 1:00 p.m. UV intensityis reduced by about half at three hoursbefore and three hours after the peakexposure time.
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
24/25
Factors affecting UV exposure..2 The time of year- more UV is
received in the late spring and earlysummer and much less is received in
the late fall and early winter.
Life styledetermines a personsrisk to UV exposure. Skiing,
sunbathing, or swimming can lead toextremely high exposures. Use oftanning parlors also increase risk.
-
8/3/2019 Ozone Depletion Chandu
25/25
Policy responses to Ozone depletion
Mario Molina and Sherwood Rowlandshowed in 1974 that CFC gases destroy ozone
Coordinating committee on Ozone Layer(CCOL) established by UNEP in the 1970s
Vienna Convention for the protection of theozone layer held in 1985
Montreal Protocolto ban substances that
deplete the ozone layer held in 1987 Amendments to the Montreal Protocol:
London - 1990, Copenhagen - 1992 andMontreal - 1997.