Osgood-Schlatter's - PlaymakersOsgood Schlatter's occurs when the area around the growth plate just...
Transcript of Osgood-Schlatter's - PlaymakersOsgood Schlatter's occurs when the area around the growth plate just...
2299 W. Grand River Ave.Okemos, MI 48864
517-349-3803www.playmakers.com
Osgood-Schlatter's
•
• Improper footwear: If you overpronate, your arch can collapse as you walk or run, causing the shinto rotate and the knee to drift medially. Putting a medial arch support under your foot doesn’t allow thefoot to flatten and the shin to internally rotate. Maintaining proper foot alignment also allows for betteralignment in the knee, hips, and low back to reduce improper tracking and stress on the patellartendon. Being in a shoe that does not match the shape of your foot can either cause your foot to hangoff of the platform or have too much extra room inside the shoe. Both of these can lead to excessivemovement and stress the patellar tendon.
• Overuse: repeated traction of the patella can cause pain, swelling, and tenderness.• Muscular imbalances: You have 4 quad muscles: vastus medialis, vastus intermedius, vastus
lateralis, and the rectus femoris. If there is an imbalance in strength and/or flexibility, it could pullharder on the patellar tendon or pull the patella out of the femoral groove, causing excessive andabnormal stress.
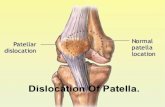
Osgood Schlatter's occurs when the area around the growth plate just below the patellar tendon gets inflamed from repeated traction and high stress from physical activity. This condition occurs in adolescents during rapid growth (typically between ages 8 and 15). Due to the proximity of this growth plate to the connection point of the Patellar tendon, symptoms and treatments are very similar to Patellar Tendinitis. It is important to note that because it is a growth plate issue, this condition cannot be ‘cured’, but the symptoms can be treated. Symptoms typically subside once the growth plate fully ossifies (turns to bone) between the ages of 15 and 18.
Description:
Pain directly below the patella The onset of OSD is usually gradual. If you have a sudden onset of pain with no previous symptoms around the patellar tendon insertion point, please see a doctor as it may be a more serious injury.Symptoms typically worsen with activity as repeated traction over the growth plate causes pain, swelling, and tenderness.
o Activities with frequent jumping or sprinting, such as basketball and soccer, tend to worsen symptoms.A noticeable bump may occur at the location of the growth plate as the bone forms.There are typically no long-term residual effects of the knee after the bone forms and OSD symptoms subside.
Symptoms:
•
••
••
Note: We always recommend seeing a physician or attending our Injury Clinic on Wednesdays from 6-8pm for more information.
Sports Activity During Rapid Growth: The insertion point of the patellar tendon begins as soft tissue. During stages of skeletal development (girls aged 10-12 and boys 12-15), the growth plate on the tibia begins to ossify (form into bone). During this time, repeated traction and stress of the patella causes microavulsions (small separations) of the patella tendon from the tibia, resulting in pain and inflammation. As the body attemps to repair these microavulsions with new bone, a noticeable bump may form at the patellar tendon insertion point. This bumps typically does not cause any long-term symptoms.Poor foot biomechanics: Pronation is a necessary function of the foot. Pronation allows the foot to disperse shock, reduce the impact felt on the body up the chain, and adapt to the surface of the ground. However, overpronation is an excessive amount of pronation, in which the arch can collapse with each step. Overpronation can cause the foot to flatten out and the tibia (shin) to internally rotate, which in turn causes the knee drift medially (inward). This can cause abnormal tracking of the patella and pulling of the patellar tendon.
•
Possible Causes:
Self-treatment options:Support: Make sure that you are wearing the proper amount of support for your foot. This can be determined byhaving a gait analysis done to see how your foot, arch, knee, and hip move as you walk.
Stretching: See below for pictures of suggested exercises.o Standing quad stretch, standing hamstring stretch
Strengthening: See below for pictures of suggested exercises.o Straight leg raise, quad sets (knee press), side-lying straight leg raise, seated knee extensions
Be patient and consistent: Be consistent with the recommendations. These stretches and exercises can helpreduce the symptoms, but the condition has to resolve itself naturally.
Products: Supportive Insoles, Patella Tendon Knee Strap, Insoles, massage ball, a knee bracewith patellar support, leukotape, KT tape
Sitting Knee Extension: Sit in a chair. Dorsiflex your foot (pull your toes toward your shin). Straighten your knee as far as you can without pain. Hold for 5 seconds and then bring it down. Do 10 reps. Repeat with the other leg. Perform the same movement with the foot and leg rotated outward and then rotated inward. Progress by adding ankle weights.
o Basketball shoes and soccer cleats tend to have poor support. Inserts may help in these instances.
Standing Hamstring Stretch: Stand in front of an elevated object or stairs. Extend one leg, resting your heel on the object. Keeping your knee straight and maintaining good posture, hinge forward from the waist until you feel a stretch in the hamstrings. If you feel the stretch in your back, you are arching your back too much. Hold for 30 seconds. Repeat with other leg.
Side Lying Straight Leg Raise: Lie on your side. Dorsiflex your foot (pull your toes toward your shin) Slowly raise the top leg as high as you can without rotating your upper body or pelvis. Bring the leg back down to the starting position. Do 10-20 reps with each leg. Do the same movement with the toes pointed inward and then pointed outward. Progress by adding ankle weights.
STRAIGHT LEG RAISE: Lie flat on your back. Bend one leg with its foot flat on the surface. Dorsiflex your foot (pull your toes toward you). Tighten your thigh and lift your other leg. Keep your leg straight. Only lift to the height of the other knee. Going slowly will increase the effectiveness. Do 10 reps. To strengthen the different quad muscles, perform the same movement with the foot and leg rotated outward and then rotated inward. Repeat with the other leg. Progress by adding ankle weights
Foam Rolling Quadriceps and Hamstrings: Begin with both legs resting on the foam roller as you support yourself with your arms. Begin just above the knee and roll up two inches and down one inch, slowly progressing over the entire quad/hamstring. Progress up to the hip and then back down to just above the knee. To roll the inner/outer quad/hamstring, repeat with one of the legs rotated outward and then inward. You may progress by putting all of the weight on just one leg instead of both.
Standing Quad Stretch: Stand next to a stable surface that you can use to help balance. Maintain good posture, bend your knee and pull your foot upward. Hold for 30 seconds and then bring it down. Repeat with the other leg.
Rest: “Play it by pain” – use pain to dictate your level of activity.Free Clinics: Most people walk and run in a way that puts excessive braking and friction on theirjoints, muscles, and tendons. Take a FREE Good Form Running and/or Good Form Walkingclinic to have your form analyzed! Our Stretch, Strengthen, and Roll class will cover commonmuscle imbalances and how to correct them.