Organs of the Endocrine System and Their Products
description
Transcript of Organs of the Endocrine System and Their Products

Organs of the Endocrine System and Their Products
• The following major glands will be covered one at a time with their products:
1.Pituitary gland / Hypothalamus
2.Thyroid gland3.Parathyroid gland4.Adrenal gland5.Pancreas (also has exocrine
function)6. Gonadal hormones
(ovaries and testes)7.Thymus

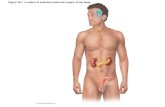
1 .Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)• located in sella turcica of sphenoid bone (in cranial
cavity), inferior to hypothalamus• consists of two lobes:
A. neurohypophysis (~ posterior pituitary)• attached to hypothalamus by infundibulum• contains axons and axon terminals of
neurosecretory cells whose cell bodies are in hypothalamic nuclei
B. adenohypophysis (~ anterior pituitary)• consists of glandular epithelium
http://www.usc.edu/hsc/dental/ghisto/end/c_1.html

A. Neurohypophysis (Posterior Pituitary)
• consists of nerve fibers (axons of neurosecretory cells with cell bodies in hypothalamus) and pituicytes (glial cells that support nerve fibers)
• acts primarily as a storage and releasing area for hormones actually made in hypothalamic nuclei
• hormones released in response to impulses from hypothalamus (neural control)
• hormones are short amino acid chains (peptides)– oxytocin– antidiuretic hormone (ADH or “vasopressin”)

A. Neurohypophysis:Oxytocin (OT)
• action, in pregnant or nursing women:
– stimulates contraction of smooth muscle of uterine wall during labor and delivery
– stimulates ejection of milk in lactating mothers
• action, in men and non-pregnant women, may be involved in sexual arousal and orgasm

A. Neurohypophysis:Oxytocin (OT)
• control:
– during labor/delivery, positive feedback: stretching of uterus/cervix --> sensory impulses to hypothalamus --> increased secretion of OT --> increased contraction
– suckling: sucking of infant on breast --> sensory to hypothalamus --> oxytocin release --> release of milk

A. Neurohypophysis: Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
• action: antidiuretic hormone (ADH) directly affects blood
pressure - acts as powerful vasoconstrictor --> increases
blood pressure (hence name “vasopressin”)
* action: affects water balance (indirect affect on blood
pressure) - acts on tubules of kidney to increase
reabsorption of water less water lost in urine

A. Neurohypophysis: ADH
• disorders:
– hyposecretion due to damage of hypothalamic nucleus or neurohypophysis--> diabetes insipidus - excessive urine production (polyuria) and thirst
– hypersecretion --> SIADH (syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion) - water retention, headache, cerebral edema, weight gain, hypoosmolarity

Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH): Control
• neural control: increased electrolyte (NaCl) concentration --> affects (supraoptic) nucleus in hypothalamus --> impulse to neurohypophysis --> release of ADH --> increased water reabsorption --> decrease in electrolyte concentration
• other stimuli: pain, low BP, morphine, barbiturates, nicotine, aldosterone (hormone from adrenal cortex - hormonal control)
• inhibition: alcohol (results in more urine production and, potentially, dehydration)
• diuretic drugs - some act to supress ADH secretion; used to treat hypertension and congestive heart failure

B. Adenohypophysis (Anterior Pituitary)
• linked to hypothalamus via hypophyseal portal system (capillary networks and small veins)
– carries regulatory hormones from hypothalamus to pituitary
• releasing hormones stimulate secretion of pituitary hormones
• inhibitory hormones inhibit secretion
• consists of epithelial cells
• all hormones produced are proteins
* tropic hormones - affect some endocrine glands or provide maintenance oversight for other organs

B. Adenohypophysis:Growth Hormone (GH)
• highest levels during evening and sleep• action: stimulates increased rate of protein synthesis leading
to cell growth and division– bones and skeletal muscle respond more than other body
cells• action: stimulates use of fat as energy source and decreases
rate of glucose uptake and glucose metabolism (diabetogenic effect – “spares” glucose)
• control:– release stimulated by GHRH (growth hormone releasing
hormone) from hypothalamus– inhibited by GHIH (from hypothalamus) and
somatomedins (produced by liver under GH stimulation)

Growth Hormone (GH): DisordersDisorders:
• hypersecretion
– gigantism (in children)
• up to 8’ tall, normal body proportions
– acromegaly (after epiphyseal plates close)
• enlargement of extremities and face, thickening of soft tissue
• hyposecretion
– pituitary dwarfism - in children, up to 4’ tall
– progeria - premature aging, atrophy of body tissues


Growth Hormone Excess
in childhood leads to GIGANTISM

Growth Hormone Excess
in adulthood leads to ACROMEGALY


B. Adenohypophysis: Prolactin (PRL)
• action:
* stimulates milk production in mammary glands;
– helps stimulate development of mammary glands (along with other hormones);
– in males, may help regulate testosterone production
• control:
– stimulation: PRH (prolactin-releasing hormone from hypothalamus), high estrogens, breast-feeding
– inhibition: PIH (hypothalamus), stimulated by rising PRL levels, low estrogen

B. Adenohypophysis:Prolactin (PRL)
Disorders
• hyperprolactinemia = hypersecretion due to adenohypophyseal tumors; results in galactorrhea, lack of menses and infertility in women, impotence in men

B. Adenohypophysis: Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)• TSH = thyrotropin
– action:
• stimulates secretion of hormones from thyroid gland (T4 and T3); also stimulates development of thyroid in youth
– control:
• release stimulated by TRH (thyroid releasing hormone from hypothalamus)
• inhibited by rising levels of thyroid hormones and by GHIH

B. Adenohypophysis: Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
• ACTH=corticotropin
• action: stimulates release of hormones from adrenal cortex
• control:
– release stimulated by CRH (corticotropin-releasing hormone from hypothalamus)
– release inhibited by rising levels of glucocorticoids from adrenal cortex

B. Adenohypophysis:Gonadotropins
• regulate activity and secretion by gonads (testes in males; ovaries in females)
• control:
– stimulated by GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone from hypothalamus)
– release of GnRH is inhibited by rising levels of estrogens, progestins and androgens (testosterone)
• two important hormones
– FSH
– LH

Gonadotropins:Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
• action:
– females (ovaries) - stimulates development of ovarian follicles and estrogen production
– males (testes) - stimulates sperm production and development
• inhibited by inhibin and testosterone from testes (feedback to hypothalamus and anterior pituitary) and estrogen, progesterone and inhibin from ovaries (feedback to anterior pituitary)

Gonadotropins:Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
• LH=lutropin
– action:
• females (ovaries) - induces ovulation; stimulates secretion of estrogens and progestins (e.g., progesterone)
• males (testes) - stimulates production of androgens (e.g., testosterone )
– inhibited by estrogen, progesterone and inhibin form ovaries (feedback to anterior pituitary) and by inhibin and testosterone from testes (feedback to hypothalamus and anterior pituitary)