Organic Halides. A structural unit in a molecule responsible for its characteristic behavior under a...
-
Upload
saige-beman -
Category
Documents
-
view
216 -
download
1
Transcript of Organic Halides. A structural unit in a molecule responsible for its characteristic behavior under a...

Organic HalidesOrganic Halides

AA structural unit in a molecule responsible for its structural unit in a molecule responsible for its
characteristic behavior under a particular set ofcharacteristic behavior under a particular set of
reaction conditionsreaction conditions
Functional GroupFunctional Group

AlcoholAlcohol ROHROH
Alkyl halideAlkyl halide RRXX ( (XX = F, Cl, Br, I) = F, Cl, Br, I)
AmineAmine primary amine: Rprimary amine: RNHNH22
secondary amine: Rsecondary amine: R22NHNH
tertiary amine: Rtertiary amine: R33NN
Families of organic compoundsFamilies of organic compoundsand their functional groupsand their functional groups

IUPAC NomenclatureIUPAC Nomenclature
of Alkyl Halidesof Alkyl Halides

The two that are most widely used are:The two that are most widely used are:functional class nomenclaturefunctional class nomenclaturesubstitutive nomenclaturesubstitutive nomenclature
Both types can be applied to alcohols andBoth types can be applied to alcohols andalkyl halides.alkyl halides.
IUPAC NomenclatureIUPAC Nomenclature
There are several kinds of IUPAC nomenclature.There are several kinds of IUPAC nomenclature.

Name the alkyl group and the halogen asName the alkyl group and the halogen asseparate words (separate words (alkylalkyl + + halidehalide))
Functional Class Nomenclature of Alkyl HalidesFunctional Class Nomenclature of Alkyl Halides
CHCH33FF CHCH33CHCH22CHCH22CHCH22CHCH22ClCl
CHCH33CHCH22CHCHCHCH22CHCH22CHCH33
BrBr
HH
II

Name the alkyl group and the halogen asName the alkyl group and the halogen asseparate words (separate words (alkylalkyl + + halidehalide))
Functional Class Nomenclature of Alkyl HalidesFunctional Class Nomenclature of Alkyl Halides
CHCH33FF CHCH33CHCH22CHCH22CHCH22CHCH22ClCl
CHCH33CHCH22CHCHCHCH22CHCH22CHCH33
BrBr
Methyl fluorideMethyl fluoride Pentyl chloridePentyl chloride
1-Ethylbutyl bromide1-Ethylbutyl bromide Cyclohexyl iodideCyclohexyl iodide
HH
II

Name as halo-substituted alkanes.Name as halo-substituted alkanes.
Number the longest chain containing theNumber the longest chain containing thehalogen in the direction that gives the lowesthalogen in the direction that gives the lowestnumber to the substituted carbon.number to the substituted carbon.
Substitutive Nomenclature of Alkyl HalidesSubstitutive Nomenclature of Alkyl Halides
CHCH33CHCH22CHCH22CHCH22CHCH22FF CHCH33CHCHCHCH22CHCH22CHCH33
BrBr
CHCH33CHCH22CHCHCHCH22CHCH33
II

Name as halo-substituted alkanes.Name as halo-substituted alkanes.
Number the longest chain containing theNumber the longest chain containing thehalogen in the direction that gives the lowesthalogen in the direction that gives the lowestnumber to the substituted carbon.number to the substituted carbon.
Substitutive Nomenclature of Alkyl HalidesSubstitutive Nomenclature of Alkyl Halides
CHCH33CHCH22CHCH22CHCH22CHCH22FF CHCH33CHCHCHCH22CHCH22CHCH33
BrBr1-Fluoropentane1-Fluoropentane
3-Iodopentane3-Iodopentane
2-Bromopentane2-BromopentaneCHCH33CHCH22CHCHCHCH22CHCH33
II

Substitutive Nomenclature of Alkyl HalidesSubstitutive Nomenclature of Alkyl Halides
Halogen and alkyl groupsHalogen and alkyl groupsare of equal rank when are of equal rank when it comes to numberingit comes to numberingthe chain.the chain.
Number the chain in theNumber the chain in thedirection that gives the direction that gives the lowest number to thelowest number to thegroup (halogen or alkyl)group (halogen or alkyl)that appears first.that appears first.
CHCH33
ClCl ClCl
CHCH33

Substitutive Nomenclature of Alkyl HalidesSubstitutive Nomenclature of Alkyl Halides
5-Chloro-2-methylheptane5-Chloro-2-methylheptane
2-Chloro-5-methylheptane2-Chloro-5-methylheptane
CHCH33
ClCl ClCl
CHCH33

Nomenclature of Alkyl Halides
CH3Cl CH3CH2FCH3CHI
CH3
CH3CH2CHBr
CH3chloromethane fluoroethane2-iodopropane 2-bromobutane
In the IUPAC system, alkyl halides are named as substituted alkanes
CH3CH2CHCH2CH2CH2CH3
CH3
Br
2-bromo-5-methylheptane
CH3CH2CHCH2CH2CH2Cl
CH3
CH31-chloro-5,5-dimethylhexane
CH2CH3
I
1-ethyl-2-iodocyclopentane
Br
Cl
CH3
4-bromo-2-chloro-1-methylcyclohexane

CHCH33CHCH22CHCH22CHCH22CHCH22FF
CHCH33CHCHCHCH22CHCH22CHCH33
BrBr
primary alkyl halideprimary alkyl halide
secondary alkyl halidesecondary alkyl halide
ClassificationClassification
CHCH33CCHCCH22CHCH22CHCH33
OHOH
CHCH33
tertiary alcoholtertiary alcohol
HH
OHOH
secondary alcoholsecondary alcohol

Different Kinds of Alkyl Halides

Aryl HalidesAryl Halides
Aryl halides are halides in which the halogen is Aryl halides are halides in which the halogen is attached directly to an aromatic ring.attached directly to an aromatic ring.
Carbon-halogen bonds in aryl halides are Carbon-halogen bonds in aryl halides are shorter and stronger than carbon-halogen shorter and stronger than carbon-halogen bonds in alkyl halides.bonds in alkyl halides.

Aryl HalidesAryl Halides
Aryl halides are halides in which the halogen is Aryl halides are halides in which the halogen is attached directly to an aromatic ring.attached directly to an aromatic ring.
Carbon-halogen bonds in aryl halides are Carbon-halogen bonds in aryl halides are shorter and stronger than carbon-halogen shorter and stronger than carbon-halogen bonds in alkyl halides.bonds in alkyl halides.
Because the carbon-halogen bond is stronger, Because the carbon-halogen bond is stronger, aryl halides react more slowly than alkyl halides aryl halides react more slowly than alkyl halides when carbon-halogen bond breaking is rate when carbon-halogen bond breaking is rate determining.determining.

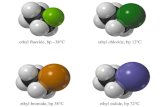
Boiling point increases with increasingBoiling point increases with increasingnumber of halogensnumber of halogens
CHCH33ClCl -24°C-24°C
CHCH22ClCl22 40°C40°C
CHCHClCl33 61°C61°C
CCClCl44 77°C77°C
CompoundCompound Boiling PointBoiling Point
Even though CClEven though CCl4 4 is the only compound in this list without a is the only compound in this list without a
dipole moment, it has the highest boiling point.dipole moment, it has the highest boiling point.
Induced dipole-induced dipole forces are greatest in Induced dipole-induced dipole forces are greatest in CClCCl44 because it has the greatest number of Cl atoms. because it has the greatest number of Cl atoms.
Cl is more polarizable than H. Cl is more polarizable than H.

Physical Properties of Aryl HalidesPhysical Properties of Aryl Halides
resemble alkyl halidesresemble alkyl halides
all are essentially insoluble in waterall are essentially insoluble in water
less polar than alkyl halidesless polar than alkyl halides ClCl
1.7 D1.7 D
ClCl
2.2 D2.2 D

RROOHH + + HHXX R RXX + + HHOOHH
Hydrogen halide reactivityHydrogen halide reactivity
HHFF HHClCl HHBrBr HHII
Reaction of Alcohols with Hydrogen HalidesReaction of Alcohols with Hydrogen Halides
least reactiveleast reactive most reactivemost reactive

An SN2 reaction proceeds in the direction that allowsthe strongest base to displace the weaker base

ExampleExample ClCl
OHOH
1.1. NaOH, HNaOH, H22OO
370°C370°C
2. H2. H++
(97%)(97%)

nitro-substituted aryl halides nitro-substituted aryl halides dodo undergo undergonucleophilic aromatic substitution readilynucleophilic aromatic substitution readily
But...But... ClCl
NONO22
++ NaNaOOCHCH33
CHCH33OHOH
85°C85°C
OOCHCH33
NONO22
++ NaNaClCl
(92%)(92%)

ReactionReaction FFNONO22
++ NaNaOOCHCH33
CHCH33OHOH
85°C85°C
OOCHCH33
NONO22
++ NaNaFF
(93%)(93%)

Aryl Halides Undergo Substitution WhenAryl Halides Undergo Substitution WhenTreated With Very Strong BasesTreated With Very Strong Bases ClCl
NHNH22
KNHKNH22, NH, NH33
––33°C33°C
(52%)(52%)

Hydrolysis of ChlorobenzeneHydrolysis of Chlorobenzene ClCl**
NaOH, HNaOH, H22OO 395°C395°C OOHH**++
OOHH
**
(54%)(54%)(43%)(43%)
1414C labeling C labeling indicates that indicates that the high-the high-temperature temperature reaction of reaction of chlorobenzene chlorobenzene with NaOH with NaOH goes via goes via benzyne.benzyne.