OptimizationProcessUMTS DT
-
Upload
abdul-majeed-khan -
Category
Documents
-
view
12 -
download
0
description
Transcript of OptimizationProcessUMTS DT

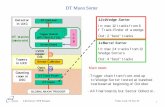
UMTS Drive Test Optimization Process Overview
Louis TanUMTS RF EngineeringEmail: [email protected]
September 25, 2002

2 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Presentation Objectives
Upon completion of this presentation, the participant will be able to:– Describe the roles and responsibilities of the deployment team
structure– Describe, in detail, the optimization process

3 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Objectives of RF Optimization
Purpose of RF Optimization:– Fine tune network elements– Ensure the performance and quality of the network in preparation for
live traffic Document system performance against exit criteria
Ensure acceptable uplink and downlink coverage Controlling soft handover regions Minimize dropped calls, and lower originations and terminations
failure Validating data throughput

4 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Process Overview
RF OptimizationPlanning Phase
Site Verification Phase
Cluster OptimizationPhase
System Verification Phase
Communication Flow

5 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Outline
Steps in an Optimization Process– RF Optimization Planning Phase
Staffing Planning Tools Equipment setup Spectrum Clearance Tests (As required) – refer to RF M&P documents
– Site Verification Phase Antenna Verification Integration Checklist Translation Verification Sector Verification

6 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Outline (cont.)
– Cluster Optimization Phase Unloaded Optimization Loaded Optimization
– System Verification Phase System Exit Test

OPTIMIZATION PROCEDURES
RF Optimization Planning Phase

8 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Staffing
Technical Manager (Lucent) Engineers
– Project Engineer (Lucent)– RF Lead Engineer– RF Optimization Engineers
RF Design Support Antenna Changes Support Highly Skilled Personnel
– Operations Management– Network Management

9 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Staffing (cont.) Skilled Temps
– Data Processor– Data Collector
Temps– Driver

10 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Organizational Model
DriversData Collectors
Project Engineer
Data Processors
RF LeadEngineer
RF Engineers
OperationsManagement
NetworkManagement
RF DesignSupport
AntennaChanges Support
Lucent
CoreIntegration
In-Field
Temps Temps
Maintenance Support
Technical Manager

11 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesTechnical Manager
Responsible for ensuring the deployment’s technical requirements are met
Responsible for ensuring that the deployment is completed on-time with zero penalties
Responsible for ensuring that deployment is completed within budget
Responsible for technical staffing and administration Responsible for ensuring that all optimization processes as
specified by the RF Optimization Methods and Procedures are in place and are being followed

12 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesProject Engineer
Identifies and makes recommendations for risk management Maintains the market’s technical staffing roster Formulates and maintains optimization schedules Ensures that a process is in place for cell site access, and reviews
system readiness processes (loaded testing, friendly user trials, ..) Tracks number of clusters under test simultaneously Monitors required test vehicles, test equipment, personnel, space... Updates project spreadsheets (integration complete, cell troubles,
RF punch-list antenna changes, sector test, cluster optimization,.. ) Deployment Technical Manager and RF Lead must share these
tasks if the position is vacant (smaller markets)

13 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesRF Lead Engineer
Interfaces with the RF Manager (Customer) for optimization requirements and ensures that necessary design data (coverage and morphology plots, site design information, topographical maps, etc.) are available
Key lead during the deployment’s planning stages (Spectrum clearance, RF design information, cluster definition, cluster control and system wide drive routes, optimization processes)– Recommended to have cell planning tool experience
ASSET, MSI-PLANET, AirPro, ...

14 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesRF Lead Engineer (Cont.)
Determines, with the RF Manager (Customer), opt guidelines and approval processes
RF Contractual related points– Reviews contract for RF items– Understands specific implementation issues
Works with Project Engineer in the creation of market schedules and intervals
Interfaces with the Project Engineer for daily activities Ensures that the formal acceptance documentation is properly
prepared

15 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesRF Lead Engineer (Cont.)
Ensures that cluster information is documented and accurate (design and optimization)
Establishes default optimization translations, processes, databases, logs, checklists, etc.
Manages/ensures required internal Optimization tools (OCNS, RF Call Trace, translations scripts, etc.)
Ensure that latest documents are being used by all RF engineers during the deployment (RF M&P & Lucent Alert)
Ensure that RF Team is connected/utilizing MSS’ Knowledge Management System (KMS)

16 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesRF Lead Engineer (Cont.)
Ensures consistent RF Opt Methodologies amongst the RF Opt Engineers
Technically supervises the RF Engineers/ oversees cluster opt. Performs daily cluster opt reviews/approves all opt changes In conjunction with the deployment Technical Manager,
determines cluster Entrance and Exit gates

17 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Questions
The presenter will now ask for questions.
Webcast participants:Please email your questions via the email link on the webcast page. A moderator will relay your question to the presenter.
Conference room participants:The presenter will poll for questions from conference room participants.

18 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesRF Optimization Engineer
Creates/documents sector test, cluster control, and system wide drive routes (may use temps to assist documentation of routes)
Reviews Neighbor Lists provided by RF design team. If necessary, creates and implements Initial Neighbor Lists
Initiates drive test requests as necessary until opt is complete Analyzes drive test data/troubleshoots problem areas in real time
(if required)– Misc drive tests as requested by RF Lead (Driver’s License required)
Resolves problems via CW maps and topographic maps, RF Design Engineer embedded knowledge, and field surveys

19 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesRF Optimization Engineer (Cont.)
Makes opt recommendations (neighbors, translations, ant changes)
Maintains Database Integrity– Ensures default translations populated for cluster under test– Creates Change Record for database changes/deltas

20 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesRF Design Support
Provides RF Design data to the Optimization team Interfaces with RF Optimization Team to assist and make
recommendations on trouble areas Knows how to contact the Subject Matter Expert (SME) on the
cluster’s intended footprint, Customer critical coverage areas, terrain, antenna selections, and placements
Maintains RF Design information to reflect the “as built” network (i.e. plots, translations, antenna data, etc.)

21 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesAntenna Changes Support
Ensures that quality assurance processes are adequate and in-place– Reviews antenna alignment and downtilt processes– Reviews antenna sweep and acceptance procedures– Reviews optimization antenna crew selection and deployment process
Maintains master antenna database (type, azimuth, downtilt, BW, height, etc.)
Ensures that a comprehensive antenna replacement process is in place (antenna lead times, access to downtilt brackets and weatherproofing kits, etc.)
Interfaces with the Project Manager (PM) to set up selected antenna teams

22 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesAntenna Changes Support (Cont.)
Reviews Antenna change process with entire team Interfaces with the PM to review financial responsibilities,
charges and payment processes; provides feedback to Deployment manager
Manages and tracks all optimization antenna work If not staffed, the Technical Manager must ensure all these
tasks are covered

23 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Questions
The presenter will now ask for questions.
Webcast participants:Please email your questions via the email link on the webcast page. A moderator will relay your question to the presenter.
Conference room participants:The presenter will poll for questions from conference room participants.

24 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesOperations Management
High skill level individual (project management, technical experience; can be skilled temp)
Trains Data Collectors and Data Processors Monitors test equipment and vehicles performance; resolves
equipment difficulties Interfaces with RF Engineers to fulfill drive and data
processing requests Dispatches drive teams and coordinates/supports data
processing

25 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesOperations Management (Cont.)
Ascertains all log forms and books are completed and accurate
Maintains drive team status white boards (switch and optimization room)
Ensures that cells are alarm free and operational prior to test drives
Oversees/interfaces with Network Management personnel in execution of their function
Oversees archiving of drive test data, utilizing proper directory structure, ensures necessary disk drive space, etc.

26 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesNetwork Management
High skill level temp (computer skills) Monitor the GUI screens continuously to ensure that cells
and network elements in clusters under test are alarm free Real time support for drive teams Obtain support to resolve cell difficulties Initiate and monitor downlink loading (OCNS) Initiate and monitor RF Call Trace (RFCT)

27 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesData Processor
Skilled temp (solid PC skills: DOS, Windows, and MS-Word/Excel)
Receives directions and guidance from Operations Management
Operates the Data Analysis Computer running LDAT, SPAT, etc. software tools per instructions on the Data Request form
Performs miscellaneous administrative (word processing) tasks such as documenting drive routes

28 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesData Collector
Skilled temp (basic PC, DOS/Windows skills) Receives directions and guidance from Operations
Management Collects drive data with the RF Test Kit Maintains the drive logs during testing Provides navigation assistance to the test vehicle’s driver Ensures integrity of data collected during testing and
delivers to the Data Processor Data Collector and Driver may be interchangeable with
appropriate skills

29 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Roles and ResponsibilitiesDriver
Temp (driver’s license and navigational skills) Performs daily vehicle maintenance review (fuel, oil, clean
vehicle, etc.) Drives test vehicle during test runs Driver and Data Collector may be interchangeable with
appropriate skills

30 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Questions
The presenter will now ask for questions.
Webcast participants:Please email your questions via the email link on the webcast page. A moderator will relay your question to the presenter.
Conference room participants:The presenter will poll for questions from conference room participants.

31 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Planning Monitor hardware status- installation and integration
– The TM or the project manager should maintain a list of all sites in the system. This list should have all the information needed, site installation, site integration, and site readiness
Cluster Planning– Groups of approximately 19 geographically contiguous cells for ubiquitous
coverage. This changes with different data rates – Groups are influenced by geography (bodies of water, mountains, etc.) and
customer preference– Sites can be in more than one cluster. The system is first divided into
clusters with each cell appearing in only one cluster – Goal is to create clusters so that handoff conditions are tested– Maps should be made showing the boundaries for each cluster and lists of
the cells in each cluster recorded– Cluster definitions should be shared with the Project Manager (PM) for
coordination with Installation and Integration teams

32 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Planning (cont.)
Sample of 1 UMTS cluster coverage with mixed services
x
x
x
x
x
x
x x
x
x
x
xx
x
x
x
x
x
x
Legend X – UMTS Sites64 Kbps
384 Kbps
384 Kbps

33 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Planning (cont.)
Define/Review RF Optimization Entrance Criteria– RF optimization will begin after certain number of sites/clusters are
installed and integrated; buy-in from RF Lead, PM, TM, and customer required
Define Drive Test Routes.– Optimization drive routes should be determined with customer
approval. All drive test routes should be defined by using information such as coverage prediction plots, morphology and clusters
– Major highways and major streets should be included first, then if time allows include some secondary streets
– Total optimization time to drive all routes in a typical cluster should be anywhere from 6 to 8 hours, depending on the number of cell sites in the cluster

34 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Planning (cont.)
Verify Database Parameters– Check neighbor list, Gold codes, power attenuation and all handover
threshold parameters Review Customer Contract, and its exit criteria Training is conducted for data collectors and data
processors Quality record forms are in place

35 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Tools
CDMA Air Interface Tool (CAIT) or HP Air Interface Measurement System – Real-time monitoring of data– Data logging
Lucent Data Analysis Tool for 3rd Generation(LDAT3G)– Processes CAIT files and RF Call Trace data– Generates plots, graphs and histograms – LDAT 3G required for data opt
Lucent Cells Application Tool (LCAT) (optional)– generates cell information for LDAT3G

36 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Tools (cont.)
MapInfo– Used in parallel with LDAT to plot Agilent data
RF Call Trace (feature)– Uplink measurements
OCNS Script - Orthogonal Channel Noise Simulator (feature)– Simulate traffic for running loaded tests
Friendly Viewer (FV)– Parses all logged UE messages, including over the air RRC
messages

37 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Equipment Setup
The number of Data Analysis Computers required The RF Test Vehicles must be fully configured
– UMTS terminal programming– RF kit installation– Dead Reckoning calibration (if equipped)– In-Vehicle Penetration Loss and uplink loading calculations should
be computed for each test van/UE combination and attenuator box

38 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Questions
The presenter will now ask for questions.
Webcast participants:Please email your questions via the email link on the webcast page. A moderator will relay your question to the presenter.
Conference room participants:The presenter will poll for questions from conference room participants.

Optimization Procedures
Site Verification Phase

40 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Sector Verification
Purpose– Determine antenna azimuth/orientation. Sector verification is
the first phase of RF Optimization. It ensures that the hardware is operating in a reasonable manner before aggressive data collection and parameter adjustment begins
Note: Sector Verification is an optional item within the Site Verification. It is done at Lucent’s discretion
Procedure– This test can be done on individual sites as soon as they have
passed integration, completed installation of the antenna systems and the spectrum has been cleared so that it is safe to radiate
– Setup a call or session (not both) when doing this test. Plot the data by Gold codes for each sector

41 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Sector Verification
Procedure (cont.)– Each site should be driven in an approximate circle. Avoid
driving very close to the site as all faces appear equally strong in this area, and avoid sections of road which may be extreme coverage holes
– Prior to driving, verify the neighbor list for all sites. The NDP process and Navis RCM will be able to support this effort
– After this test is completed, verify that each sector of every site in the cluster, meets the following criteria
The signal is radiating at a common sense power level Antennas are transmitting in the correct direction and with the
correct Gold code Sector-to-sector handovers of each site is working properly

42 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Questions
The presenter will now ask for questions.
Webcast participants:Please email your questions via the email link on the webcast page. A moderator will relay your question to the presenter.
Conference room participants:The presenter will poll for questions from conference room participants.

Optimization Procedures
Cluster Optimization Phase

44 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Unloaded Optimization
Purpose– Unloaded coverage test results may identify coverage holes,
handover regions, neighbor list problems and multiple pilot coverage areas in a UMTS network
– Unloaded coverage testing will measure the Common Pilot Channel (CPICH) and Block Error Rate (BLER) on the uplink and downlink. This phase performs calls/sessions quality testing by monitoring a call/session over a drive route
Procedure– Drive all optimization routes for a long call test– Use RF Call Trace to log uplink BLER (if required)– Log CAIT files. Make sure correct logging mask is used for
appropriate data collection tool and service

45 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Unloaded Optimization
Procedure (cont.)– Process CAIT files on LDAT– Plot and analyze the following:
CPICH Ec/Io Max Finger Ec/Io of Dominant Pilot UE Transmit Power UE Receive Power BLER
Note: These are the plots typically used; however, additional plots may be generated and analyzed
– Run Friendly Viewer to troubleshoot problems

46 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Unloaded Optimization
Procedure (cont.)– Repeat the optimization process as required until problems
are fixed– Number of measurements to be collected will depend on the
software releases– When all the issues have been resolved satisfactorily,
proceed to loaded optimization

47 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Loaded Optimization
Purpose– During this optimization phase, traffic is simulated on both
uplink and the downlink. Downlink loading is simulated using Orthogonal Channel Noise Simulator (OCNS). Uplink loading is simulated using an attenuator in the UE’s RF transmit path
Procedure– Load OCNS on every site in the cluster and it’s surrounding– Suspect interference from “friendly users”. During this phase
of testing the system is artificially loaded to an agreed upon capacity. Any additional calls will cause a dramatic drop in performance. Phones turned on in the area can cause unwanted problems

48 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Loaded Optimization Procedure (cont.)
– Place a required data rate type of call using single UE– Ensure that the number of measurements being performed is
consistent with committed KPIs– Use RF Call Trace to log uplink BLER– Log CAIT files on all optimization routes– Process CAIT files on LDAT– Plot and analyze the following:
CPICH Ec/Io Max Finger Ec/Io of Dominant Pilot UE Transmit and Receive Power BLER
Note: These are the plots typically used; however, additional plots may be generated and analyzed

49 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Loaded Optimization
Procedure (cont.)– Perform all changes necessary to the database parameters
and continue drive testing– Verify all performance numbers against customer exit criteria.
If all routes in the cluster meet the exit criteria, then loaded optimization is complete and this cluster is ready for origination and termination data collection. Exceptions can be deferred to system testing but should be entered on a punch-list and agreed by the customer

50 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Loaded Optimization
Note: A punch-list is any coverage problems which cannot be solved with a basic parameter change that are deferred, with customer’s approval. These exceptions must be recorded and included in the cluster exit documentation presented to the customer. The punch-list should include the following: cause of the problem, tentative solution, person responsible for specific problem (customer or Lucent) and when problem will be resolved

51 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
UE Origination Tests (Loaded)
Purpose: – For UE origination tests, it is desired to originate successive UE
calls of about 20 seconds duration (or as specified by customer contract) over the entire control drive route. A delay of at least 10 seconds should be set between calls. An origination script file will automate origination testing on the CAIT, eliminating dialing errors and controlling the timing of originations. CAIT software can be configured to run origination tests automatically
Procedures:– UE Origination Tests are performed under loaded conditions.
OCNS is used for downlink loading, and attenuation in the UE transmit path is used for the uplink loading. It is important to resolve any loaded condition issues before proceeding with these tests

52 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
UE Origination Tests (Loaded)
Procedures (cont.)– 1 measurement shall be performed in U01.01 for 64Kbps– During UE origination tests, CAIT is used to log data files as in
normal cluster tests. All the origination failures can be identified and parsed from the Friendly Viewer log files
– Log CAIT files (use the appropriate log mask)– Process all CAIT files using LDAT – Run the ORIG program– Overlay plots of origination failures or ALERT. Output may also be
generated and analyzed– Determine the total percentage of origination failure and check
numbers against customer exit criteria

53 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
UE Termination Tests (Loaded)
Purpose – During UE termination tests, successive landline calls are attempted to a
designated UE that is connected to an CAIT data collection kit in the drive test van. Call duration is about 20 seconds and at least a 10 second delay is used between calls
Procedures– If required, UE Termination Tests are performed under loaded conditions.
OCNS is used for downlink loading, and attenuation in the UE transmit path is used for the uplink loading. It is important to resolve any loaded condition issues before proceeding with these tests
– 2 measurements shall be performed in U01.01 for 64Kbps and 384 Kbps– The CAIT is used to log CAIT files as in normal cluster tests. All the
termination failures can be identified and parsed from the Friendly Viewer

54 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
UE Termination Tests (Loaded)
Procedures (cont.)– Do not take UE out of sleep mode during termination tests as this is
not representative of realistic operation– Log CAIT files; stop logging after termination script is stopped– Process all CAIT files using LDAT– Run the TERM program – Overlay plots of termination failures or ALERT output may also be
generated and analyzed– Determine the total percentage of termination failure and check
numbers against customer exit criteria

55 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Questions
The presenter will now ask for questions.
Webcast participants:Please email your questions via the email link on the webcast page. A moderator will relay your question to the presenter.
Conference room participants:The presenter will poll for questions from conference room participants.

Optimization Procedures
System Verification

57 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
System Verification
Purpose – System Exit Testing focuses specifically on collecting overall
performance statistics with the entire UMTS network activated and loaded
Procedure– All optimization should be completed before beginning system route
testing– All of the known problems upon exiting Loaded Testing should be
fully understood and documented on a punch-list– RF Call Trace, OCNS, the test van and all RF test equipment must
be functioning properly.

58 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
System Verification
Procedure (cont.)– All cell sites in the system should be checked from the OMC to verify
that each site is continuing to operate properly– The System Control Route should be chosen to give an overview of
the entire system. This route should include main highways and primary roads which carry the most airtime traffic. System control routes should cover highway interchanges, entrance/exit ramps to arterial roads, over water bridges, raised highways, and other areas where reliable UMTS coverage is mandatory
– System Control Route testing is used to exit a complete market. The data must meet the minimum requirements set by the customer and contract
– Measurements to be performed in are as follows: Long call drive test for various data rate committed in the KPI Origination / Termination for the various data rate committed in the KPI

59 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
System Verification
Procedure (cont.)– Log CAIT files on all system control routes– Process CAIT and RF call trace files on LDAT– Use LDAT to make the typical plots listed below. Additional plots
may also be used or some plots may be omitted depending on customer requirements
Ec/Io Aggregate UE Receive Power UE Transmit Power Number of Pilots Dominant Pilot BLER Transmit Gain Adjust

60 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
System Verification
Procedure (cont.)– Run Friendly Viewer and ALERT and analyze the data– Create Overlay Plots for Dropped Calls, Originations, and
Terminations– Binning the Data - The binning parameters (binning size, percent of
bins kept, and BLER threshold), specified by contract, should be the same ones used in Cluster Exit Testing
– Approval to exit the system is based on the terms of the contract which are customer and market specific
– System test exit criteria consist of the following items. Items may be different depending on customer contract. These are the same parameters used for cluster exit

61 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
System Verification
Procedure (cont.)– Block Error Rate
Both the downlink and uplink block error rates are examined, if required. The error rates are determined by binning the data. The size of the bins and the percent of bins which are kept are determined by the contract
– Dropped Call Rate The dropped call rate is usually calculated as the total number of drops
in bins which were kept divided by the number of calls made (length of call divided by 90s). However, some contracts require all dropped calls to be counted. The dropped calls which are left out of the calculation are determined by plotting the location of the dropped call on the binned BLER plot and then throwing away the dropped calls in discarded bins

62 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
System Verification
Procedure (cont.)– Origination Success Rate
The origination success rate is calculated as the total number of origination success divided by the total number of origination attempts. Depending on the contract, the originations failures which can be removed are determined by plotting the location of the origination on the binned BLER plot and then throwing away the origination failures in discarded bins
– Termination Success Rate (if required) The termination success rate is calculated as the total number of
termination success divided by the total number of termination attempts. Depending on the contract, the termination failures which can be removed can be determined in the same manner as the originations
– Throughput

63 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
System Verification (cont.)
Procedures (cont.)
Once the System exit criteria has been met, and the Customer has signed off on the results, the UMTS network is considered ready for commercial service.

64 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Questions
The presenter will now ask for questions.
Webcast participants:Please email your questions via the email link on the webcast page. A moderator will relay your question to the presenter.
Conference room participants:The presenter will poll for questions from conference room participants.

65 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Quiz!
1. How big is a cluster size (sites)?a. 19b. 7c. 15d. All the above
2. How many type of measurements are performed for a loaded optimization in U01.01?a. 3b. 4c. 5d. 6

66 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
Quiz!
3. What are the common KPIs that are used as part of a warranty?a. Dropped Call Rateb. BERc. Handover Delaysd. All the above
4. Which is not the responsibility of a Lead RF Engineer?a. Interfaces with the customer for optimization requirementsb. Technically supervises the RF Engineersc. System administrator to the OMCd. Ensure that latest documents are being used by all RF Engineers

67 Lucent Technologies - Proprietary
References
Farouk Zeineddine / Markus Shute – CDMA RF Optimization Procedures
Dave Maag – UMTS Deployment Guidelines: RF Optimization Staffing Models
RF M&P documents