OPAMP-Bishawnath
-
Upload
sauravabidrahman -
Category
Documents
-
view
2 -
download
0
description
Transcript of OPAMP-Bishawnath
-
Types of OPAMPGeneral Purpose OPAMPNorton OPAMPInstrumentation OPAMPIsolation OPAMP
-
General Purpose OPAMPModerate values of the key parametersJFET based differential inputHigh input impedanceGood noise reduction
-
Norton OPAMPModerate values of the key parametersCurrent differencing OPAMP ( have different internal structure)Non-inverting input is derived from inverting inputCurrent mirror circuit is used
-
Instrumentation OPAMPVery high input impedanceVery large CMRRExtremely low values of offsetsSingle ended inputInternally combination of THREE OPAMPs.
-
Isolation OPAMPOutput is electrically isolated from inputDifferential input, single ended outputIsolation impedance in 1012 ohm, voltage 1kV
-
Interpreting OPAMP A709 : First IC OPAMP in 1965 by FairchildA741 : NextA741A, A741B, A741C and A741E MC1741 : Motorola CorporationLM741 : National SemiconductorSN72741 : Texas Instrument LM709 : National SemiconductorLM725 : National SemiconductorLM324 : National Semiconductor (Quad Comparator)
-
Desired Characteristics of an OPAMP Infinite input impedance, RIN = Zero output impedance, ROUT = 0Infinite gain, Av = Zero input offset voltageZero input offset currentInfinite bandwidthInfinite CMRRNot temperature dependentPerfect balance, when v1in = v2in , vout = 0.
-
Pin configuration of 741
-
Symbolic representation of 741
-
Symbolic representation of OPAMP
-
OPAMP characteristics Input offset voltage : The differential voltage that may exist internally although no input is connected externally. Therefore an output may exist even if no input is connected.This is the voltage to be supplied at the input to force the output to zero.Typical value is 2 mVolt.Input offset voltage drift : Rate of change of input offset voltage with temperature.Measured in Volt per degree celcius.
-
OPAMP characteristics Input bias current drift : Rate of change of input bias current with temperature.
-
OPAMP characteristics Input offset current : Difference of the two base currents, of an balanced amplifier.Input offset current drift
-
OPAMP characteristics (contd) Output offset voltage :Voltage available at output due to imbalance in differential amplifier.output offset voltage drift : Input common mode voltage range : The maximum safe voltage which can be connected at common mode input. Typical value is 13 V.Output voltage range : Maximum output voltage swing without significant distortion of the signal.Input differential mode voltage range : Maximum safe voltage in differential mode.
-
OPAMP characteristics (contd) Output voltage swing : Output saturation voltage. Typical value is 2 volts less than VCC.Power supply rejection ratio, PSRR : ratio of change of input offset voltage with the change of power supply voltage.Short circuit output current : Maximum current which will flow through a short circuit at the output.Large signal voltage gain : The gain is very large, the output signal is much larger than the input, known as large signal voltage gain.Offset voltage adjustment range : Range through which the input offset voltage can be adjusted. Typical value is 15 V
-
Typical parameters of 741 OPAMPOpen loop voltage gain 100,000Input offset voltage 2mvInput offset current 20 nAInput bias current 80 nAInput resistance 2MOffset voltage adjustment range 15 mVInput Voltage range 13 VCMMR 90 db
-
Typical parameters of 741 OPAMP(contd)Supply voltage rejection ratio 30 V/VLarge signal voltage gain 200,000Output voltage swing 13 VOutput Resistance 75 Output short circuit current 25 mASupply current 1.7 mAPower consumption 50 mWSlew rate 0.5 V / s
-
Frequency parameters roll off : Gain decreases as frequency increases
-
Slew rate
-
Slew rate
-
Slew rate
-
OPAMP applicationsLinear Application : Output changes in accordance with input.Example : inverting amplifier, Voltgae buffer, noninverting amplifier, current controlled voltage source etc.Non-linear Application : Output wave shape is different from that of input signal. Example : Differentiator, integrator, Comparator, Schimtt trigger, Zero crossing detector etc.
-
OPAMP applicationsVoltage Buffer : Isolating input from output, with unity gain.
-
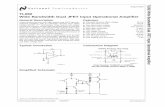
Current controlled voltage sourceI1-+Rf
-
Comparator
-
Zero crossing detectorVINOutput+-+VCC-VCCVREF