NOAA Satellite and Information Service GOES NOAA Satellite and Information Service GOES OVERVIEW...
-
Upload
georgia-allen -
Category
Documents
-
view
214 -
download
1
Transcript of NOAA Satellite and Information Service GOES NOAA Satellite and Information Service GOES OVERVIEW...
- Slide 1
- NOAA Satellite and Information Service GOES NOAA Satellite and Information Service GOES OVERVIEW Cindy Hampton Office of Satellite and Product Operations Chief, Engineering Branch
- Slide 2
- Agenda GOES Mission Services Scan Operations Spacecraft Status GOES West Transition
- Slide 3
- Warnings to U.S. Public -- Detect, track and characterize Hurricanes Severe storms and winter cyclones Flash flood producing weather systems Imagery for weather forecasting Derived products for analysis and forecasting Surface temperatures (sea and land), Winds for aviation and NWS numerical models, Soundings and radiances for NWS models Atmospheric Stability, Lifted indices, precipital water, soundings, air quality, rainfall estimates Environmental data collection platforms including buoys, rain gauges, river levels, ecosystem monitoring Space weather monitoring and forecasting Search and Rescue For the protection and enhancement of the Nations economy, security, environment, and quality of life... GOES Mission
- Slide 4
- GOES On-Orbit Configuration 2 operational satellite configuration GOES-11 East - 75W longitude GOES-13 West 135W longitude Maintain at least 1 on-orbit spare Configured in sun-pointed storage mode with instruments off Can be activated ~ 48-72 hours time GOES-15 Support Space Weather GOES-14 in Storage Currently operating GOES-12 for South America GOES-East Full DiskGOES-West Full Disk 140E180140W100W60W20W20E Useful Camera Coverage 60 20 40 20 40 60 Communicatio n Range GOES (75 West) GOES (135 West) Sounder Raw Data 40 kbps, advanced data rate 720 kbps, 1,676 MHz Imager Raw Data 2.6208 Mbps, advanced data rate 2.934 Mbps, 1,676 MHz Processed Data 2.111 Mbps 2,027.7 MHz, uplink Processed Data 2.111 Mbps 1,685.7 MHz, downlink, advanced data rate 2.374 Mbps Processed Data Other Data and Service Users World Weather Building Seven Satellite Field Service Stations Satellite Operations Control Center Suitland, MD Command and Data Acquisition Station Wallops Island, VA
- Slide 5
- GOES Spacecraft Overview GOES I-M Series: Built by Space Systems / Loral in Palo Alto, CA Based on Loral 1300 bus series Design Life: 5yrs GOES N-P Series: Built by Boeing Satellite Systems in El Segundo, CA Based on Boeing 601 series Design Life: 10yrs (bus )
- Slide 6
- 6 GOES-13, 14 and 15 GOES-13/14/15 have similar instruments to GOES-8- 12, but on a different spacecraft bus. Spring and fall eclipse outages will be avoided by larger onboard batteries. Improved navigation Improved radiometrics GOES-11/12 GOES-13/14/15
- Slide 7
- GOES Services GOES Variable Format Data (GVAR) Transmits full resolution Imager and Sounder meteorological data to western hemisphere Includes telemetry, calibration data, text messages, spacecraft navigation data
- Slide 8
- 8 GOES Services Emergency Managers Weather Information Network (EMWIN): Specialized instruments on NOAA satellites relay critical information to users across the country. Emergency Managers can obtain weather information in near real time from a variety of sources, including the National Weather Service. Low Resolution Image Transmission (LRIT): NOAA satellites are used to relay satellite and weather products. These products are broadcast via a radio signal that can be received by users in remote locations, that do not have landlines or internet connections.
- Slide 9
- GOES Services Data Collection System Provides near real-time relay of information from over 19,000 data collection platforms located in remote areas Platforms consist of oceanographic buoys, balloons, and weather stations Used to collect data on seismic events, ocean currents, tsunami detection, forest fires, river flow rate, and floods.
- Slide 10
- GOES Services Search and Rescue: NOAA satellites are used to relay distress alerts from aviators, mariners and land-based users Approximately 250 persons are rescued in the United States annually Partnership between NASA, NOAA, USAF and USCG 38 countries participate in program internationally
- Slide 11
- V1 Sep 2010 11 GOES Services Status SpacecraftLRITEMWINSARSATDCSGVAR GOES-11Operational GOES-13Operational GOES-14Standby GOES-15Standby GOES-12StandbyOperationalStandby Central & South Americas
- Slide 12
- GOES Services Space Environment Monitoring X-Ray Sensor (XRS): provides primary measure of solar x-ray flux and flare magnitude Extreme Ultra-Violet Sensor (EUV) measures solar extreme ultra-violet flux, which is primary energy input to the upper atmosphere and ionosphere Energetic Particle Sensor (EPS) and High Energy Proton and Alpha Particle Detector (HEPAD) detect energetic electron and protons Magnetometer measures Earths magnetic field components Solar X-Ray Imager (SXI) Monitors solar disk activity, including solar flares, coronal holes, and coronal mass ejections. Data is used to issue space weather forecasts and alerts
- Slide 13
- GOES Scan Strategy GOES East GOES West RoutineRapidSuper Rapid 15 min CONUS coverage 5 min CONUS coverage 1 min SRSO coverage Sounder
- Slide 14
- Slide 14 Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES) Operations Status Payload Instrument GOES-11 (West) Launch: May 00 Activation: Jun 06 GOES-12 (S. American) Launch: Jul 01 Activation: Apr 03 GOES-13 (East) Launch: May 06 Activation: Apr 10 GOES-14 (Storage) Launch: Jun 09 GOES-15 (Standby) Launch: Mar 10 Imager GGGGG Sounder GYGGY Energetic Particle Sensor (EPS) GYGGY Magnetometers GGGGG High Energy Proton and Alpha Detector (HEPAD) GGGGG X-Ray Sensor (XRS) RRRGG Solar X-Ray Imager (SXI) N/ARYGS/C Spacecraft Subsystems Telemetry, Command & Control S/CGGGG Attitude and Orbit Control GGGGG Inclination Control GRGGG Propulsion GYS/CGG Mechanisms GGGGG Electrical Power YGGGG Thermal Control GGGGG Communications Payloads S/CGGG Key Operational Spacecraft issues but no user impacts Operational with limitations Non-operational Not Applicable G R S/C Y N/A
- Slide 15
- GOES-11(L) Status Launch Date: May 3, 2000 Orbital Location: 135W longitude Designation: Operational West Power: Reduced battery 1 capacity. Services may be turned off during eclipse periods XRS: X-ray Positioner electronics failed. XRS cannot track Sun 10 Feb 2008 COMM: Primary Sensor Data transmitter failed. Switched to redundant transmitter - 16 May 2006
- Slide 16
- GOES-13 (N) Status Launch Date: May 24, 2006 Orbital Location: 75W longitude Designation: Operation East SXI: Solar X-Ray Imager CCD detector partial damage during X9 solar flare 5 Dec 2006 New on-board software loaded for protection against large flares. Propulsion: N2 thruster anomalous thrust level. Thruster use restricted. XRS: A capacitor short. Does not detect flares
- Slide 17
- GOES-14 (O) Status Launch Date: June 27, 2009 Orbital Location: 105W longitude Designation: Storage Mode No Spacecraft or Instrument Issues
- Slide 18
- EMWIN: S-Band Receiver 1 failed SXI: Power on failure at initial turn on. Now that it is working, there are no plans to turn off. Sounder: Patch Temperature Control problems due to blanket issue Yaw Flip at Equinox to control temperature. User impact - data outage during recovery from maneuver SEM: MAGED Telescope 7 channel is noisy GOES-15 (P) Status Launch Date: March 4, 2010 Orbital Location: 89.5W longitude Designation: Standby Space Environment Operational
- Slide 19
- GOES-12(M) Status Launch Date: July 23, 2001 Orbital Location: 60W longitude Designation: South America EPS: Energetic Particle Sensor channels noisy XRS: X-ray positioner electronics failed and cannot track Sun. SXI: Solar X-Ray Imager high voltage power supply failed Propulsion: Thruster 2B oxidizer valve leak. B side thrusters isolated. Imager: Periodic Cycle Slips Sounder: Filter Wheel Motor Problems Dec 2009
- Slide 20
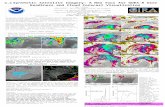
- GOES STRAY LIGHT CORRECTION GOES-13/14/15 imagers and sounders are capable of scanning the sun without health and safety issues. Intolerable Sun intrusion causes NOAA to cancel images within 6 o of sun, equivalent to 6 days of imaging. NOAA and ITT Industries have characterized the effect of the Sun intrusion and developed a ground correction algorithm to claim >95% of lost images and improve images up to 20 o of the Sun. The ground system algorithm consists of two parts: Subtracting the known amount of stray light from the signal outside 6. Using the longer wavelength signal in combination with 3.9-um signal to estimate a truer 3.9-um signal in areas where the sun is within 6 of the pixel and the stray light effect is overwhelming. Corrected 3.9um Image Please visit poster GOES Imager Stray Light Correction for more information
- Slide 21
- GOES-West Transition GOES-West Transition to occur December 2011 PLAN: GOES-14 will replace GOES-11 GOES-14 taken out of storage before fall eclipse season for yearly inclination maneuver and imager testing Start drift to 135 Deg W - October 2011
- Slide 22
- 22 4km water vapor Imager Scott Bachmeier
- Slide 23
- Improved spatial resolution of GOES-15 Imager band 6 The 13.3 um band 6 of the GOES-13 (top panel) has an 8 km IGFOV (Instantaneous Geometric Field of View); while the same band on the GOES-15 (lower panel) has a 4 km IGFOV. Note the finer resolution of the cloud edges and the cleaner image. 23
- Slide 24
- More Information http://www.oso.noaa.gov/goesstatus/ For GOES-14/15 Science Test Information: http://cimss.ssec.wisc.edu/goes/blog/archives/3054 http://rammb.cira.colostate.edu/projects/goes-o/ Don Hillger and Tim Schmit co-lead the GOES-14/15 NOAA science testing. Hyre Bysal OSPO and Tim Schmit STAR on Stray Light Testing